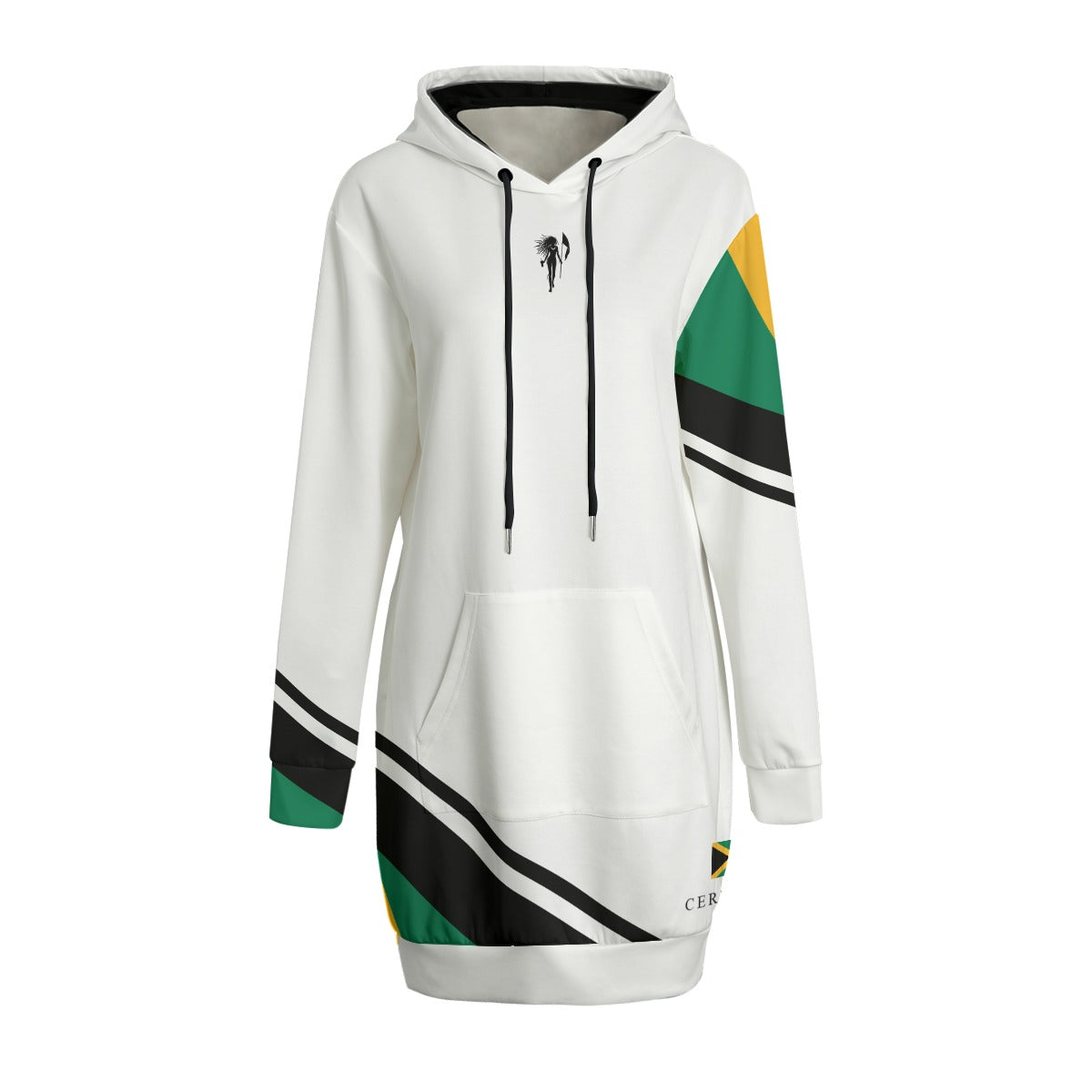
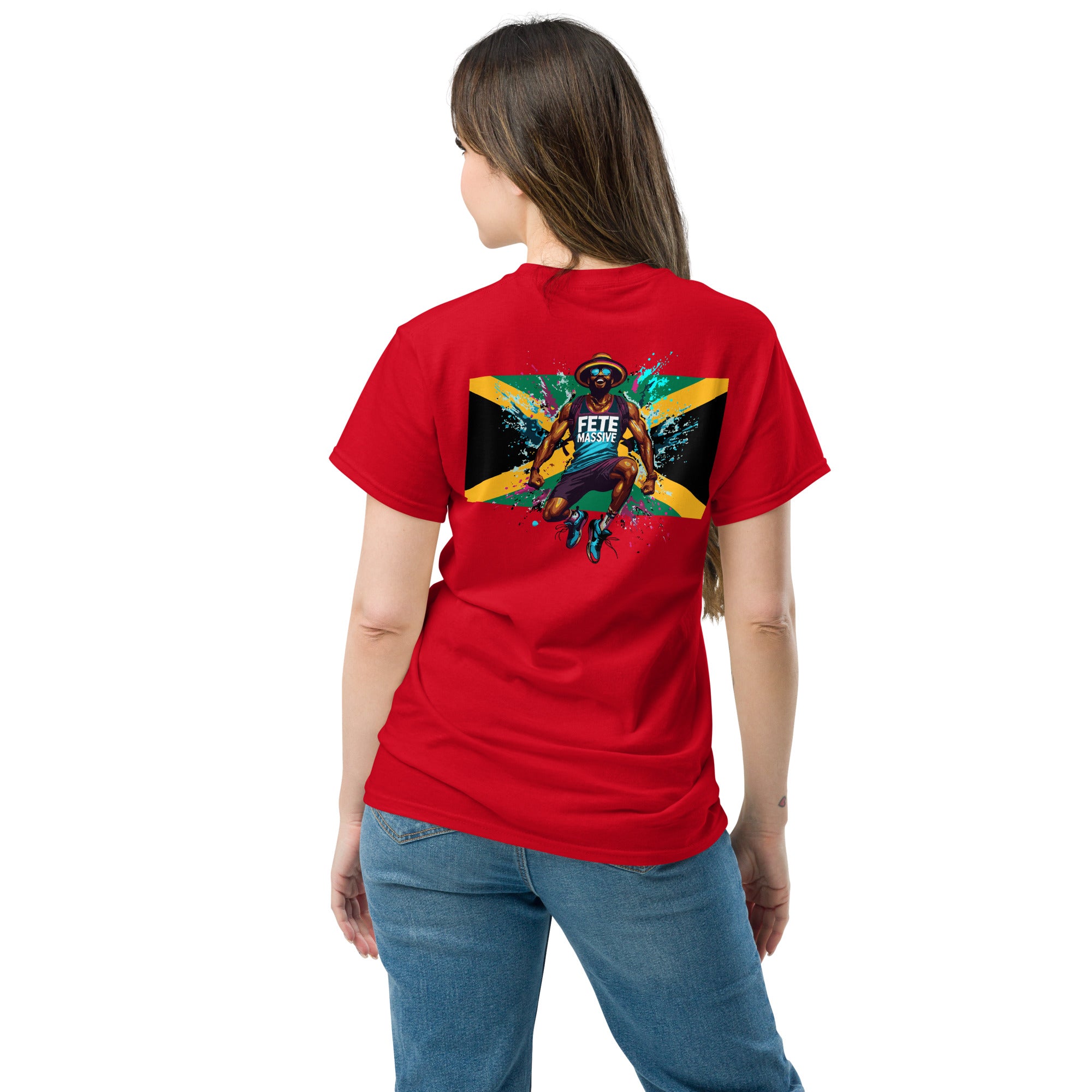
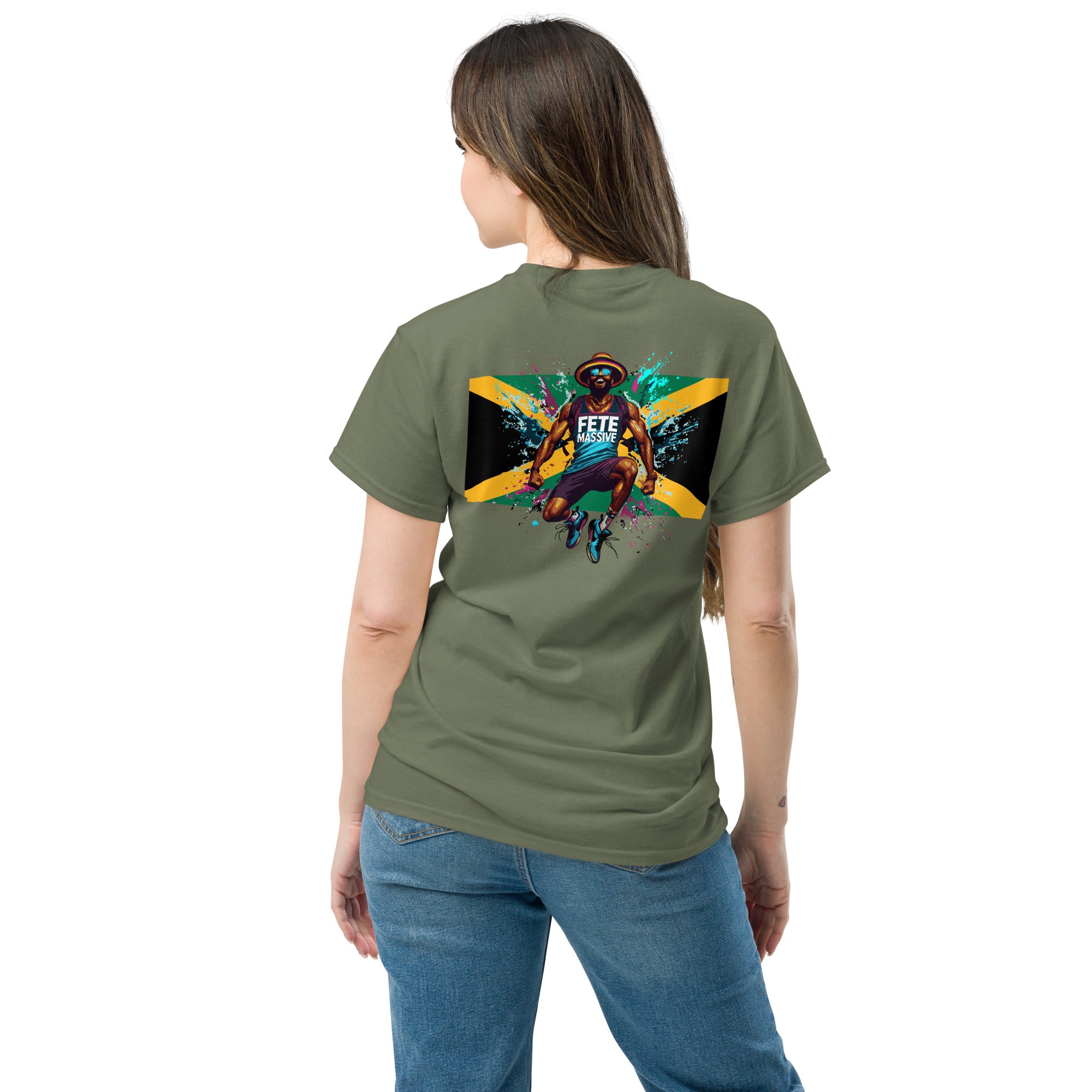
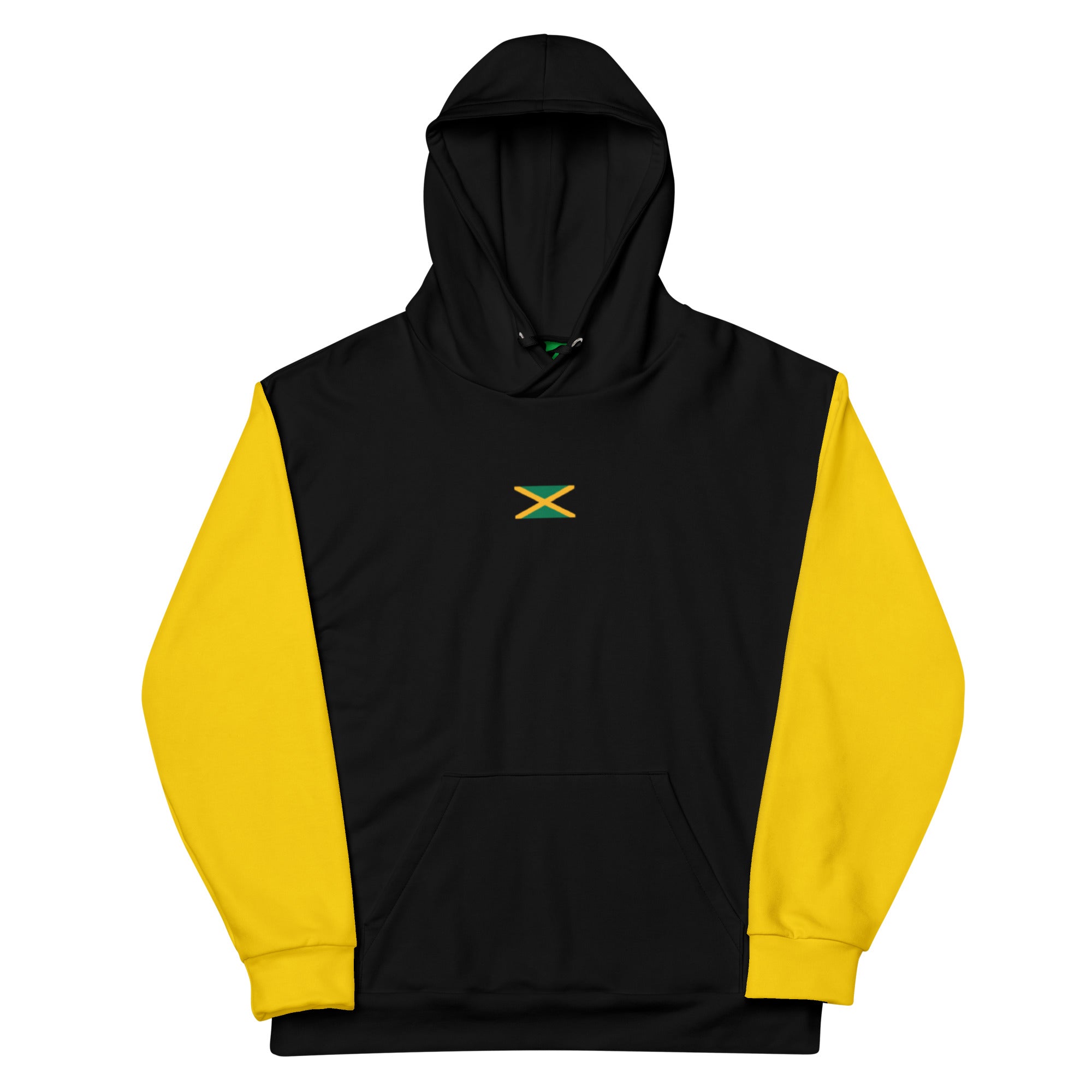
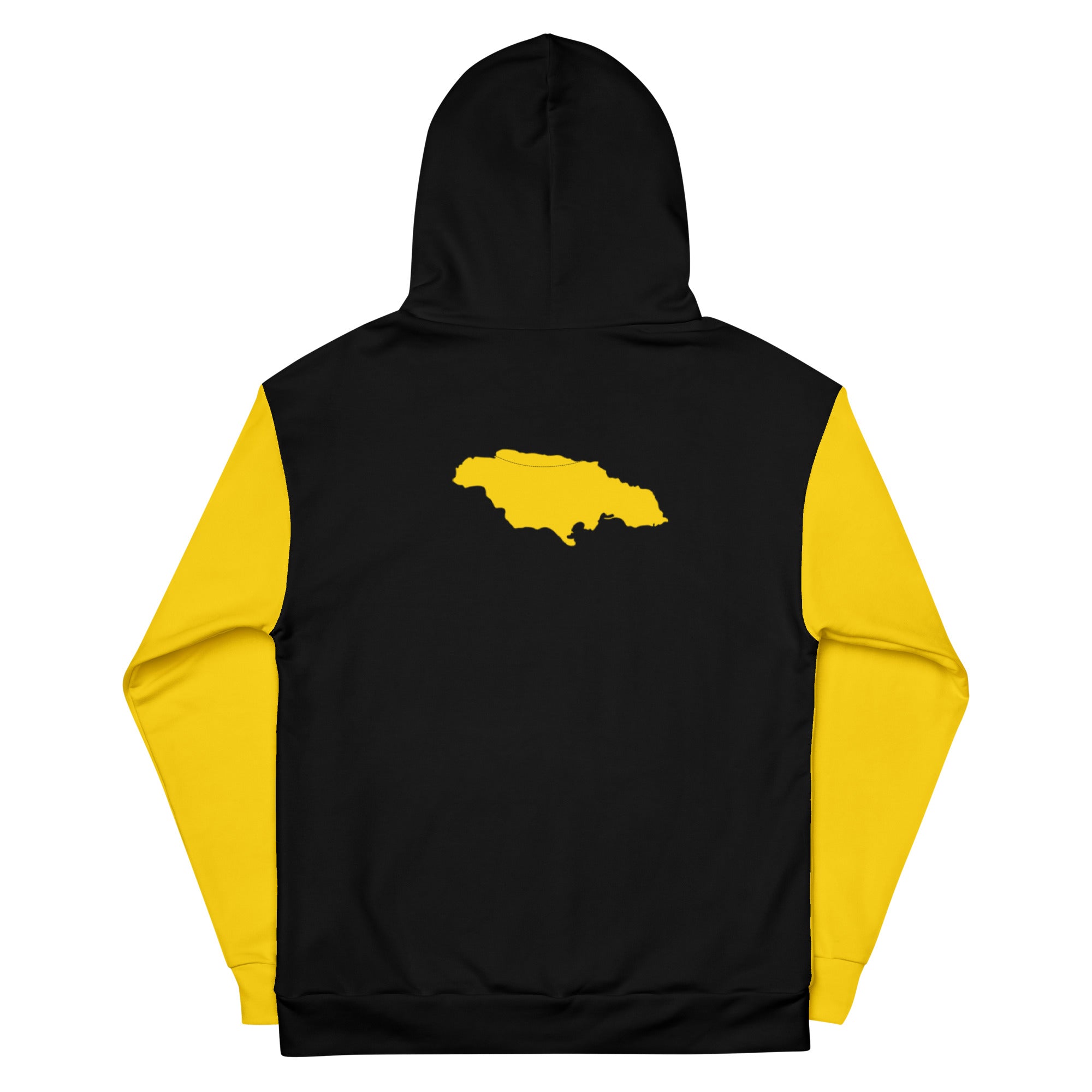
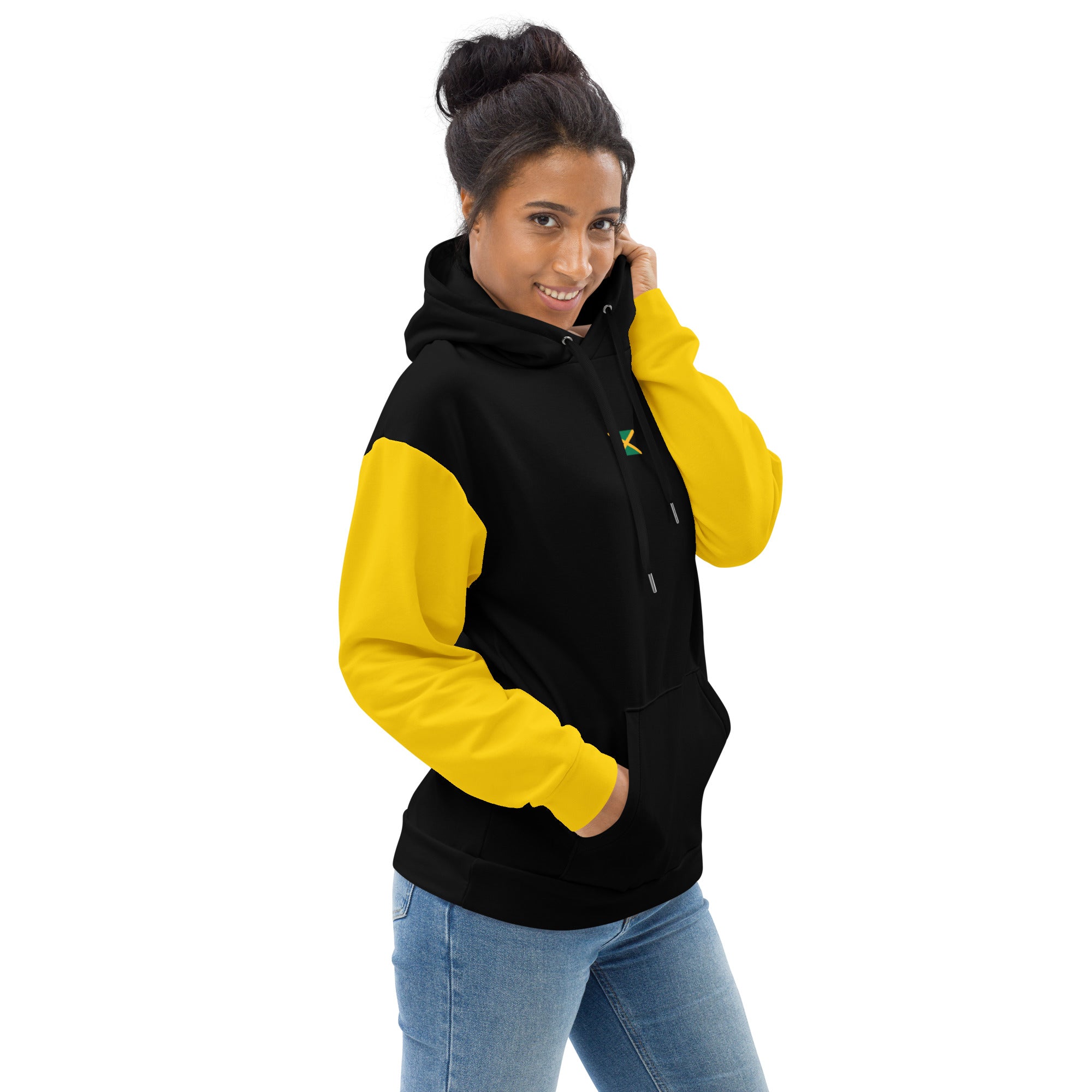
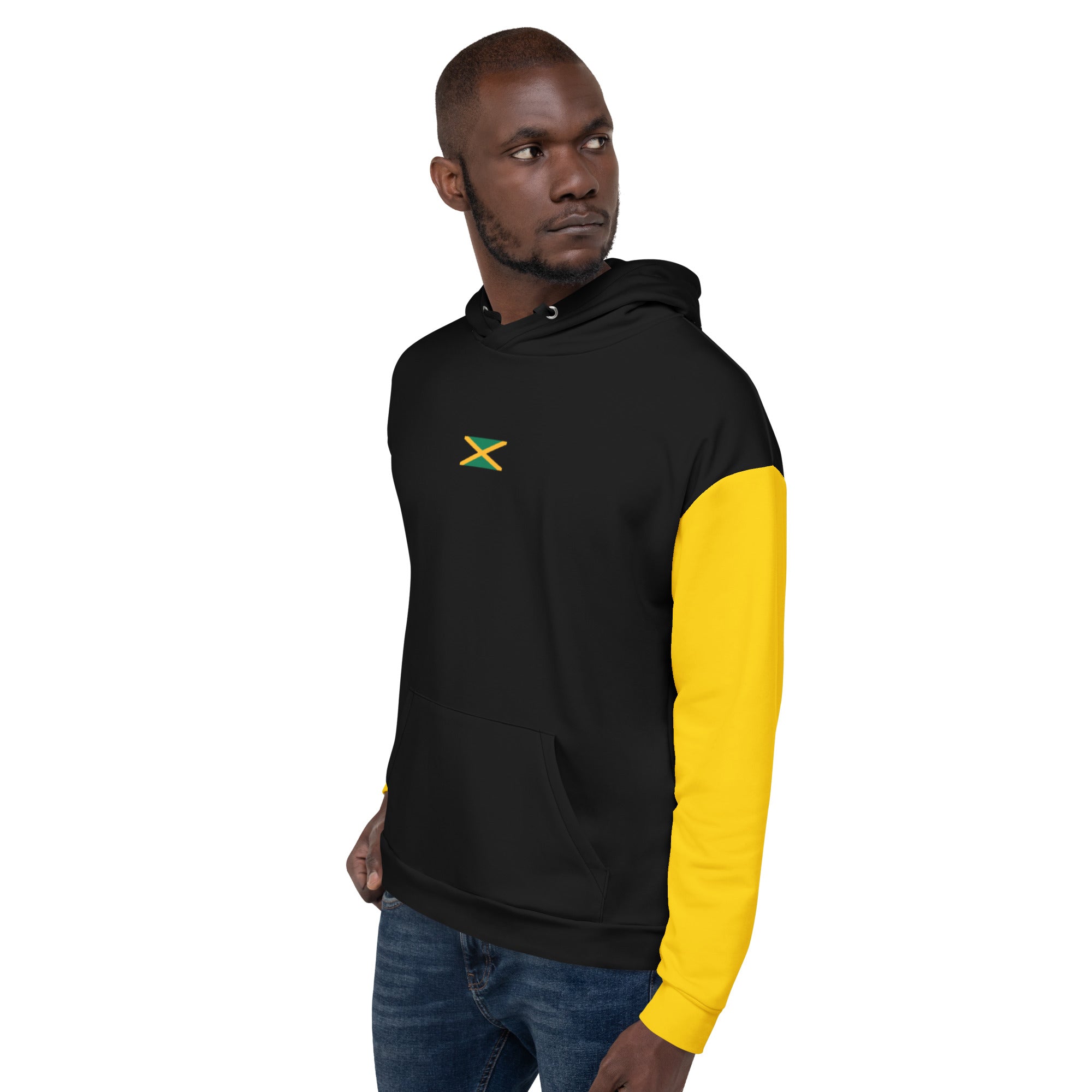
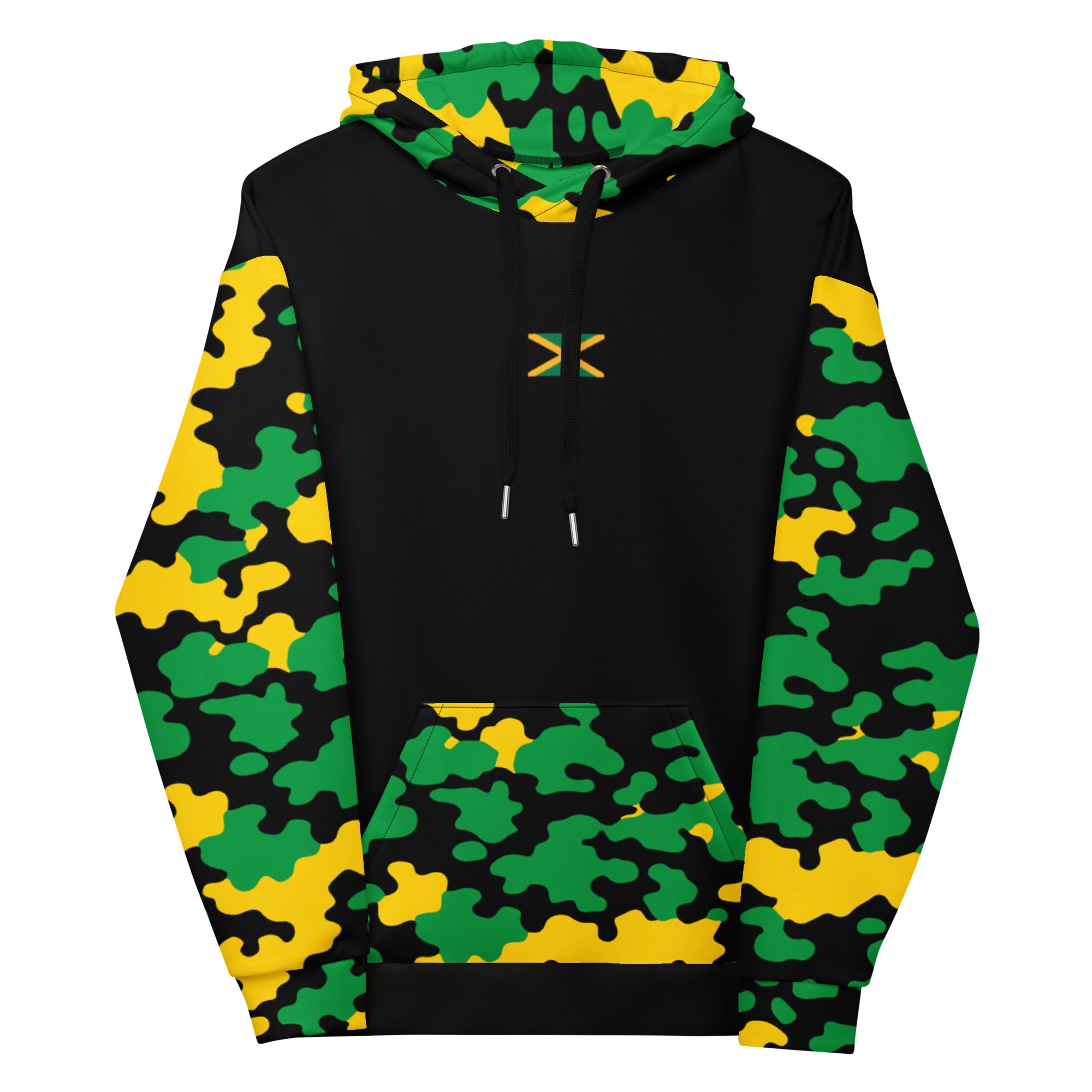
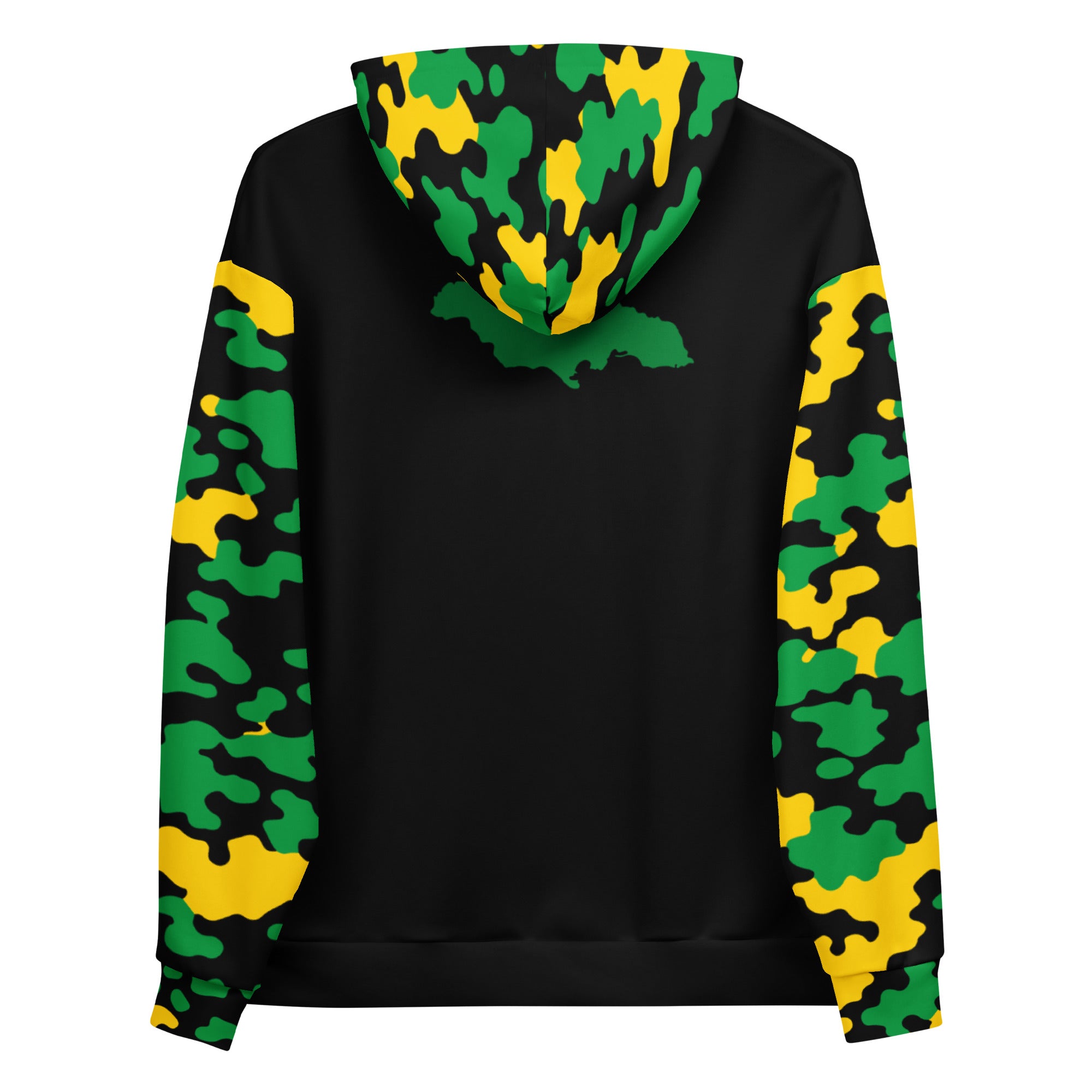
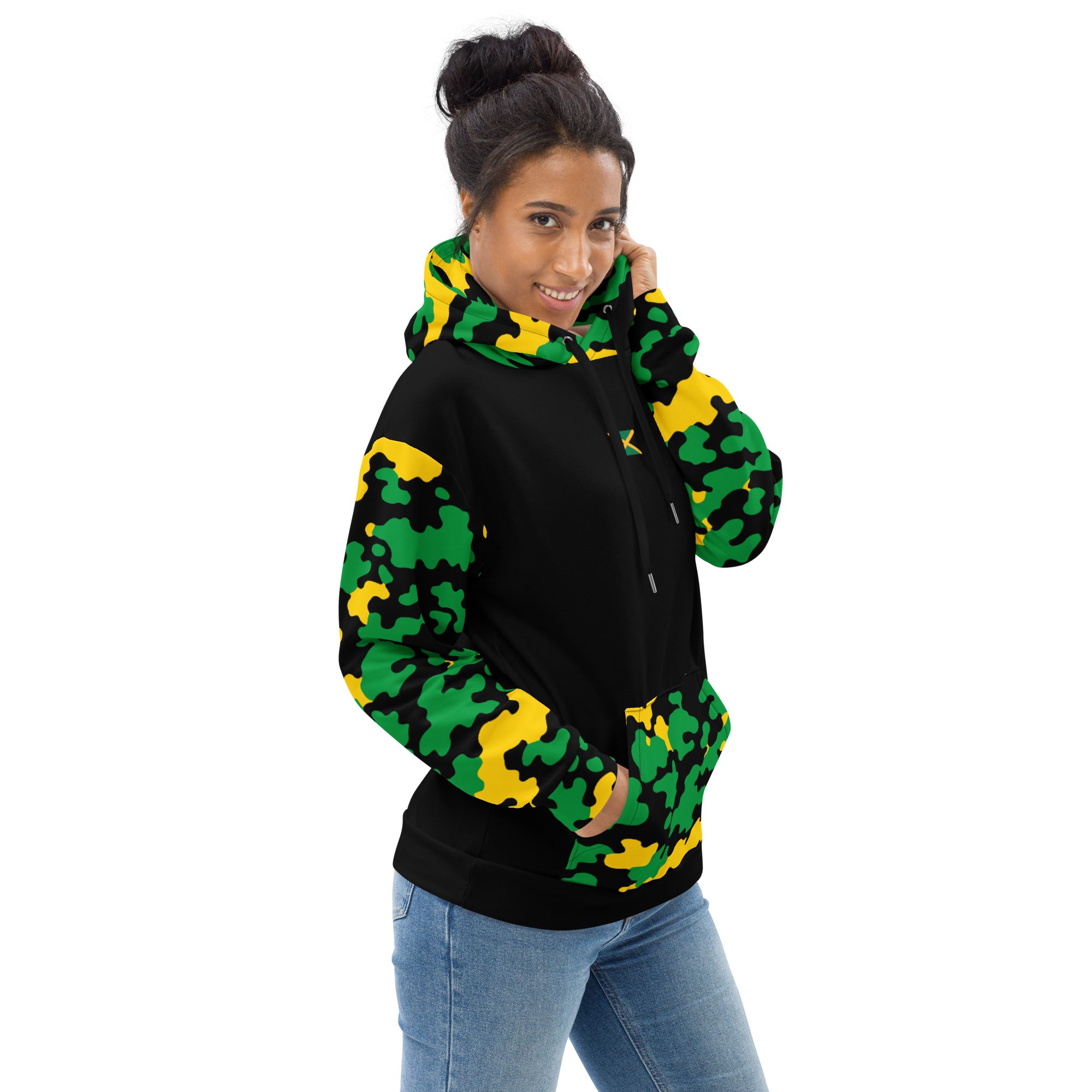
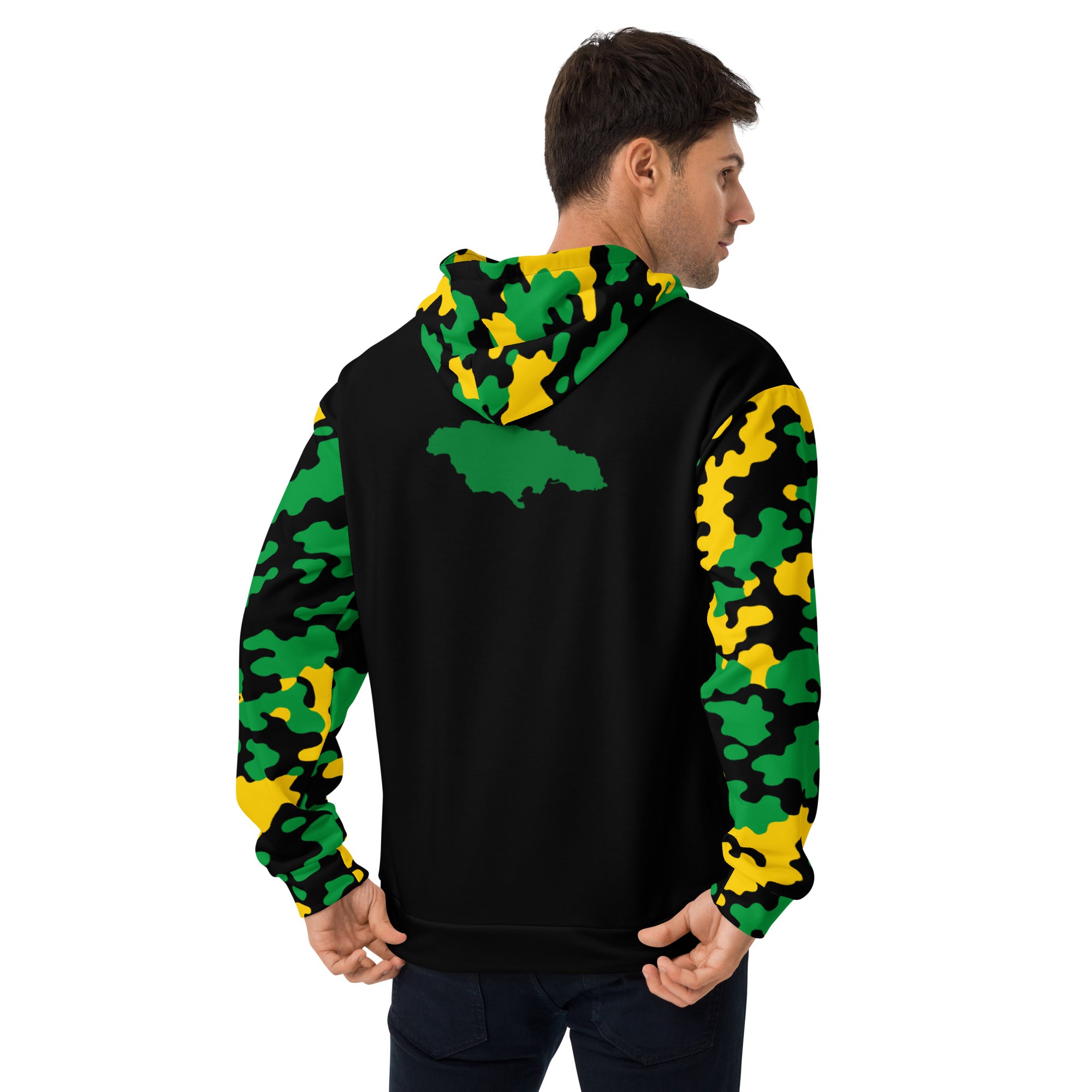
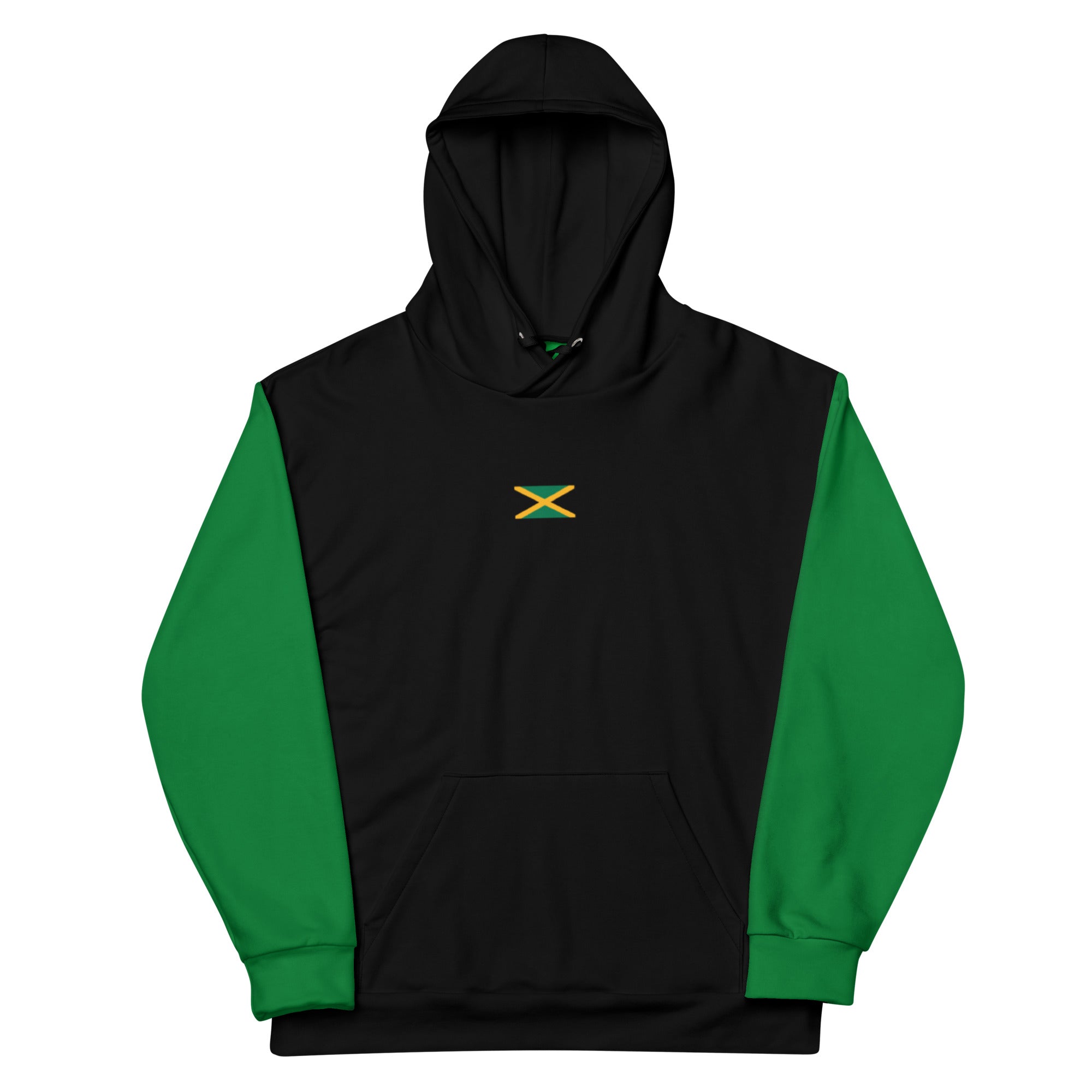
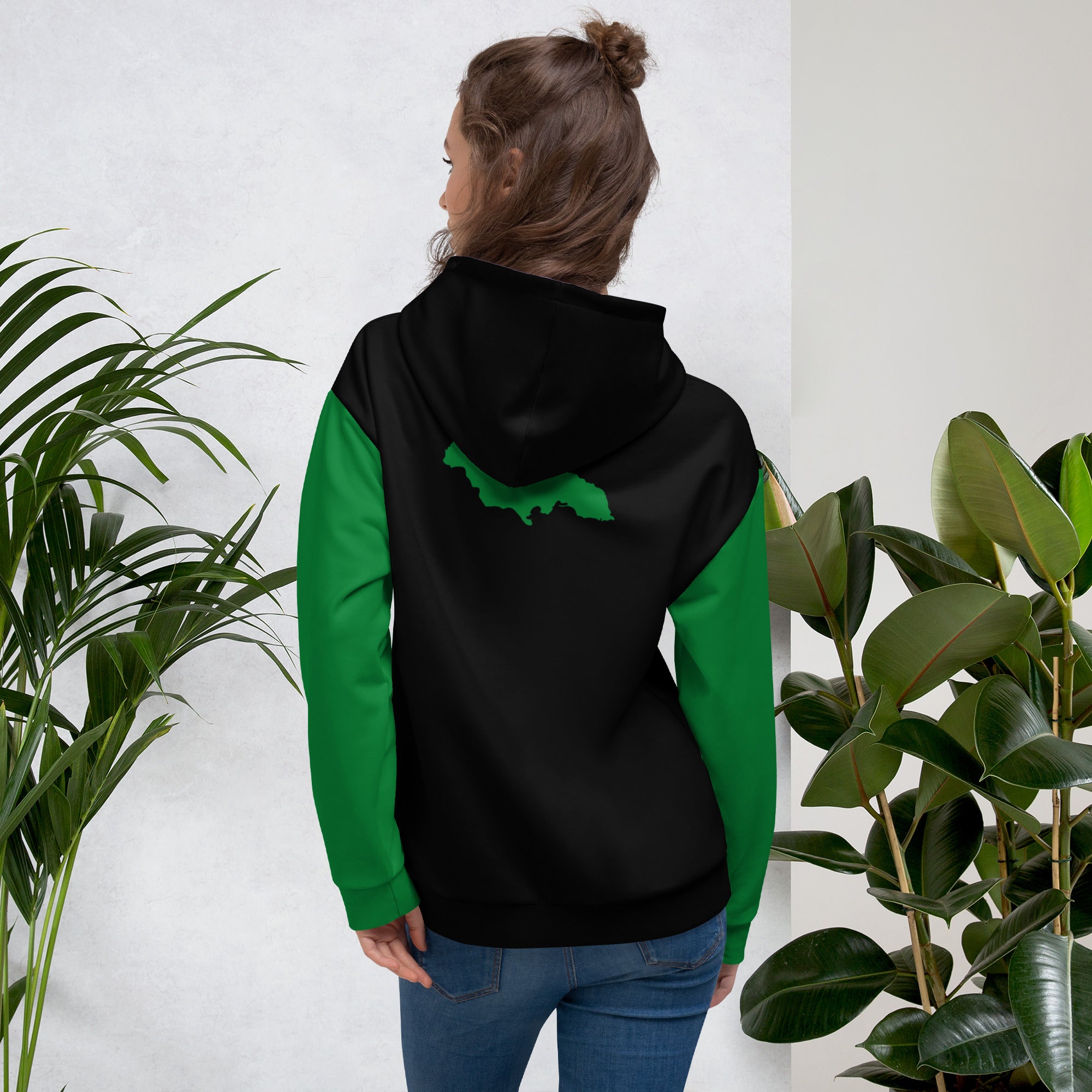
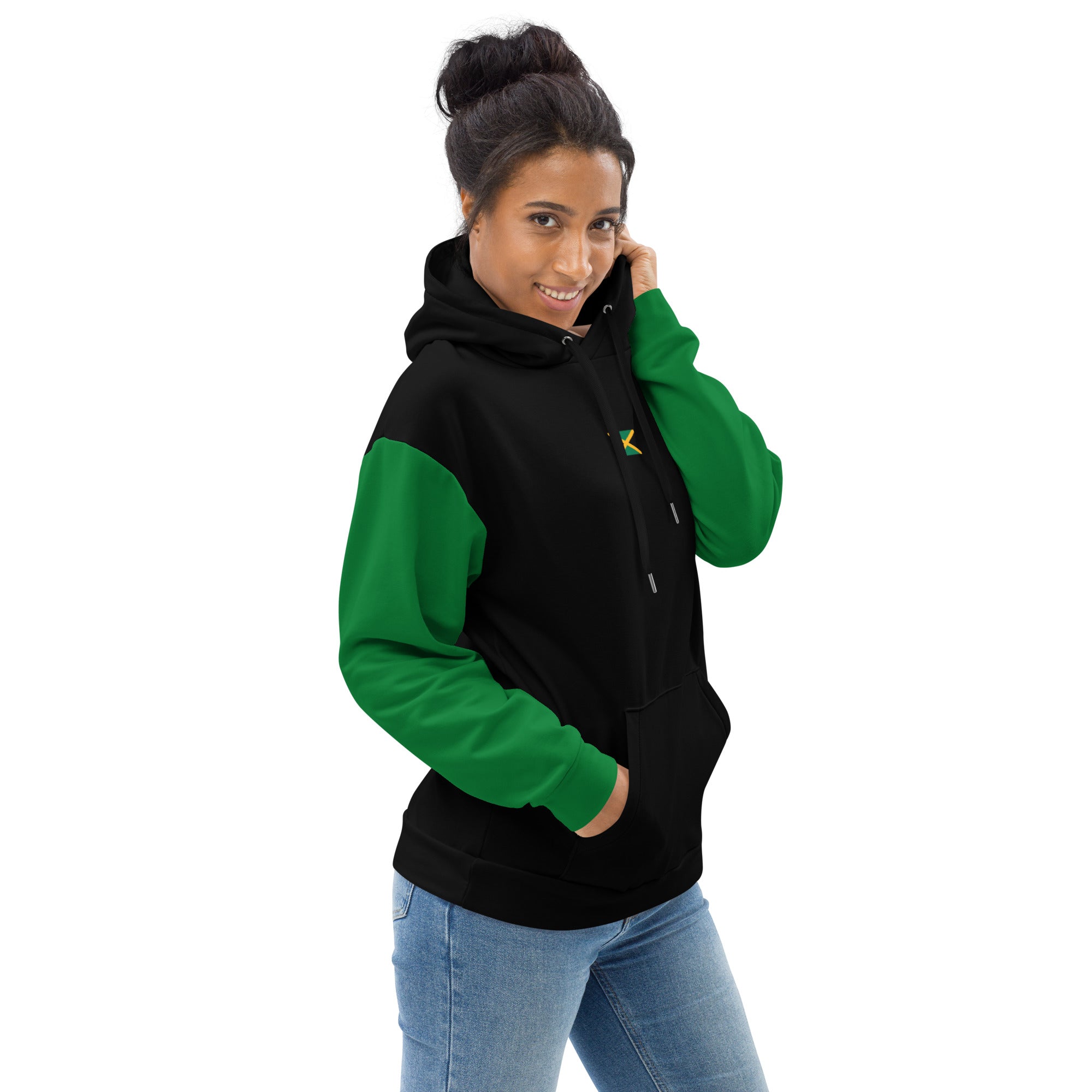
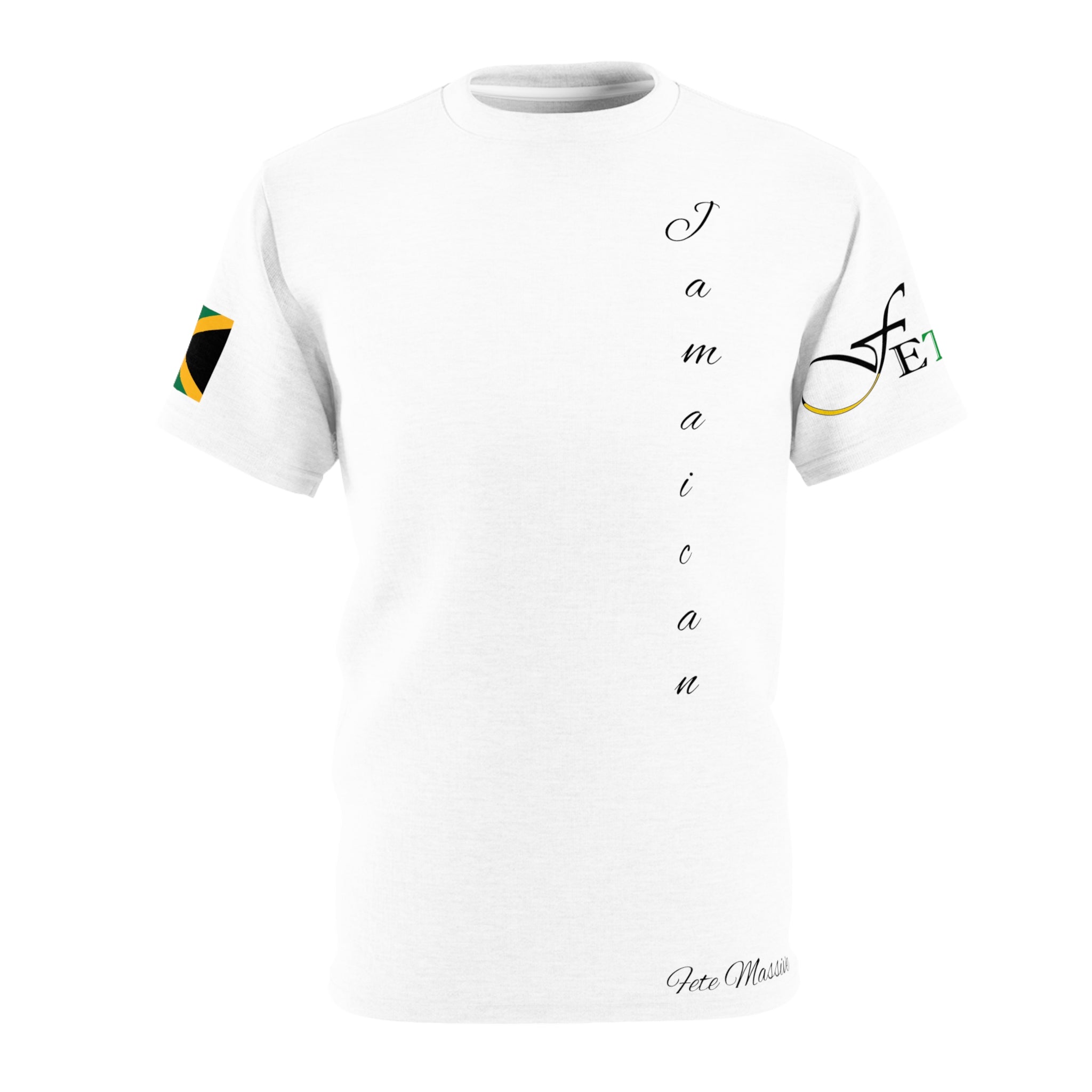
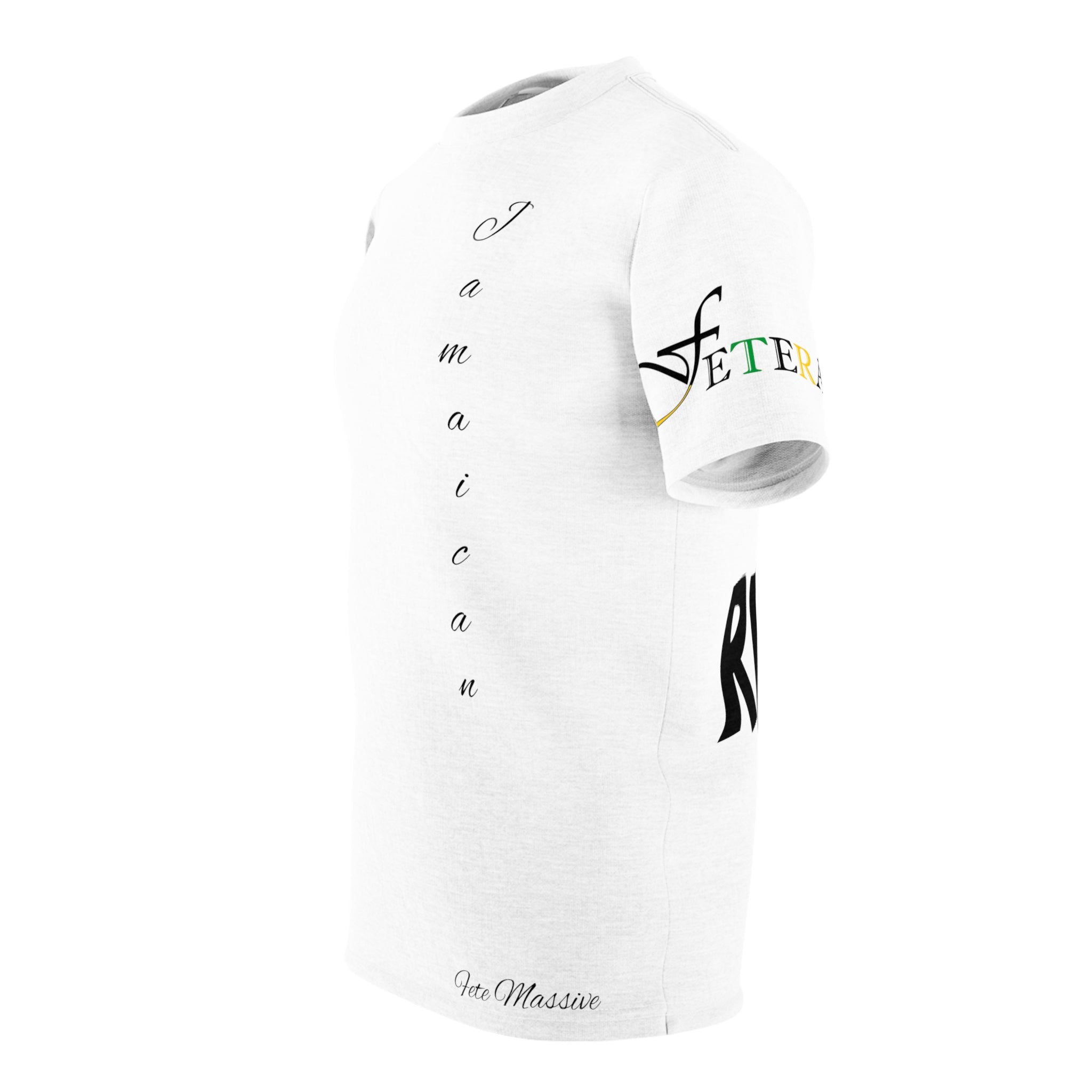
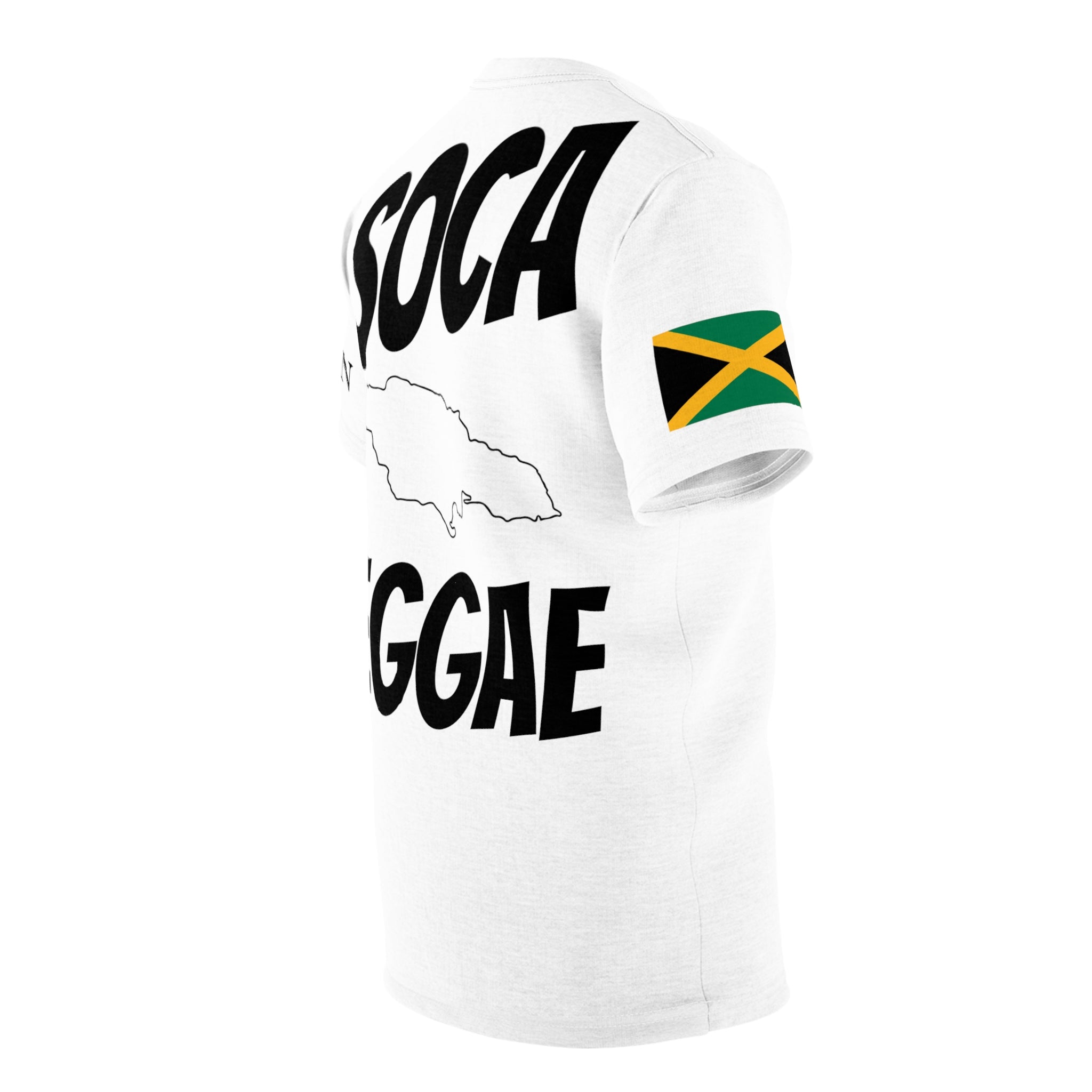
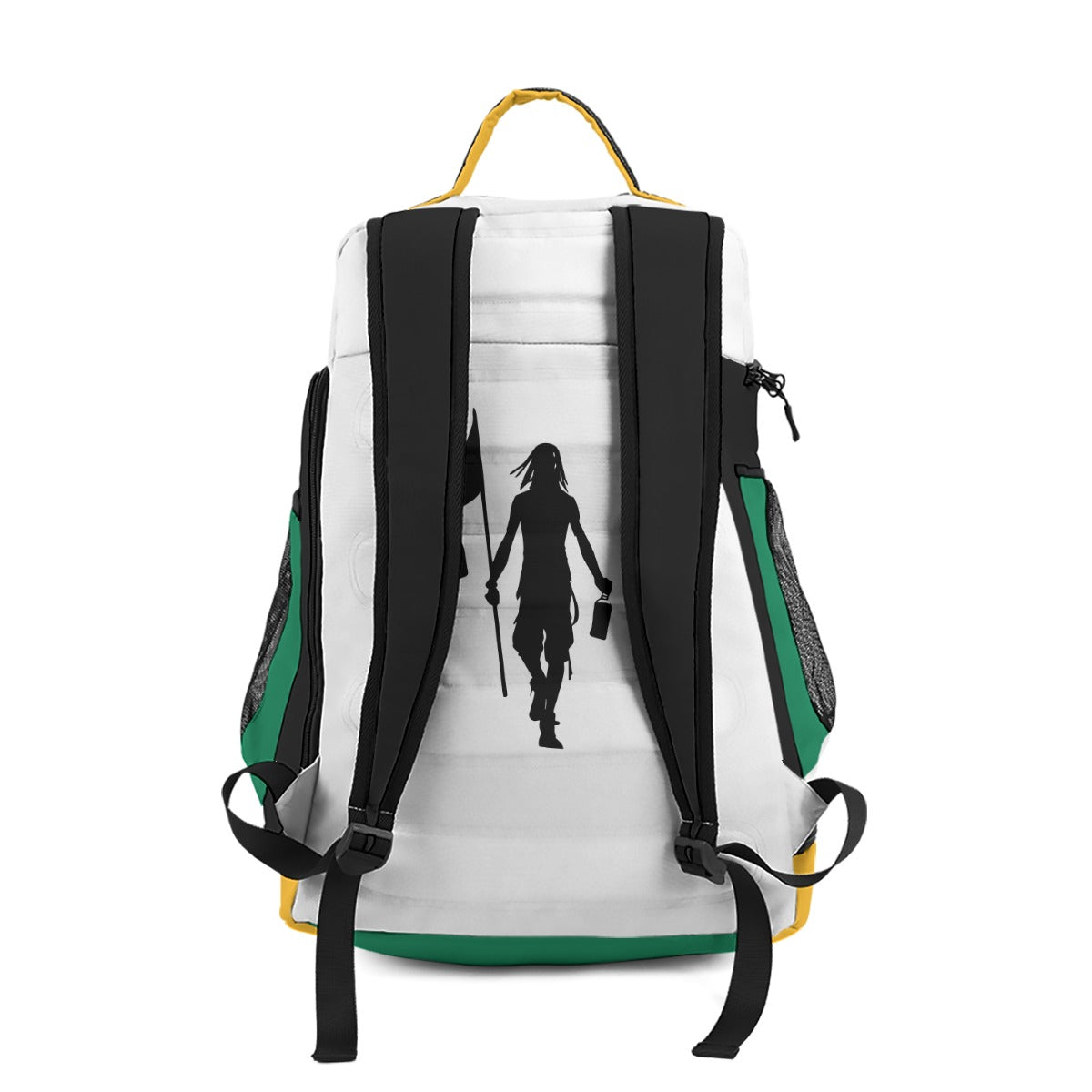
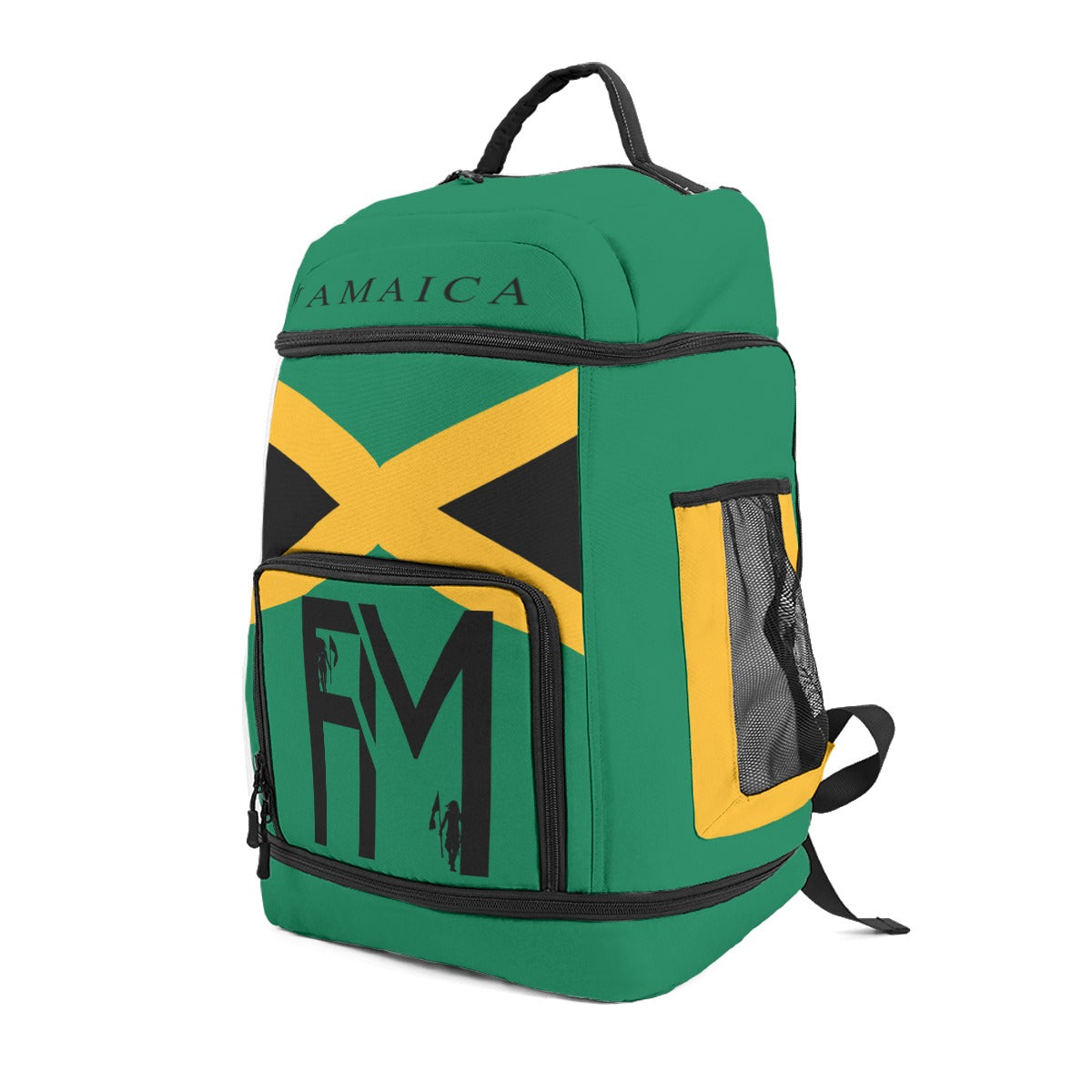
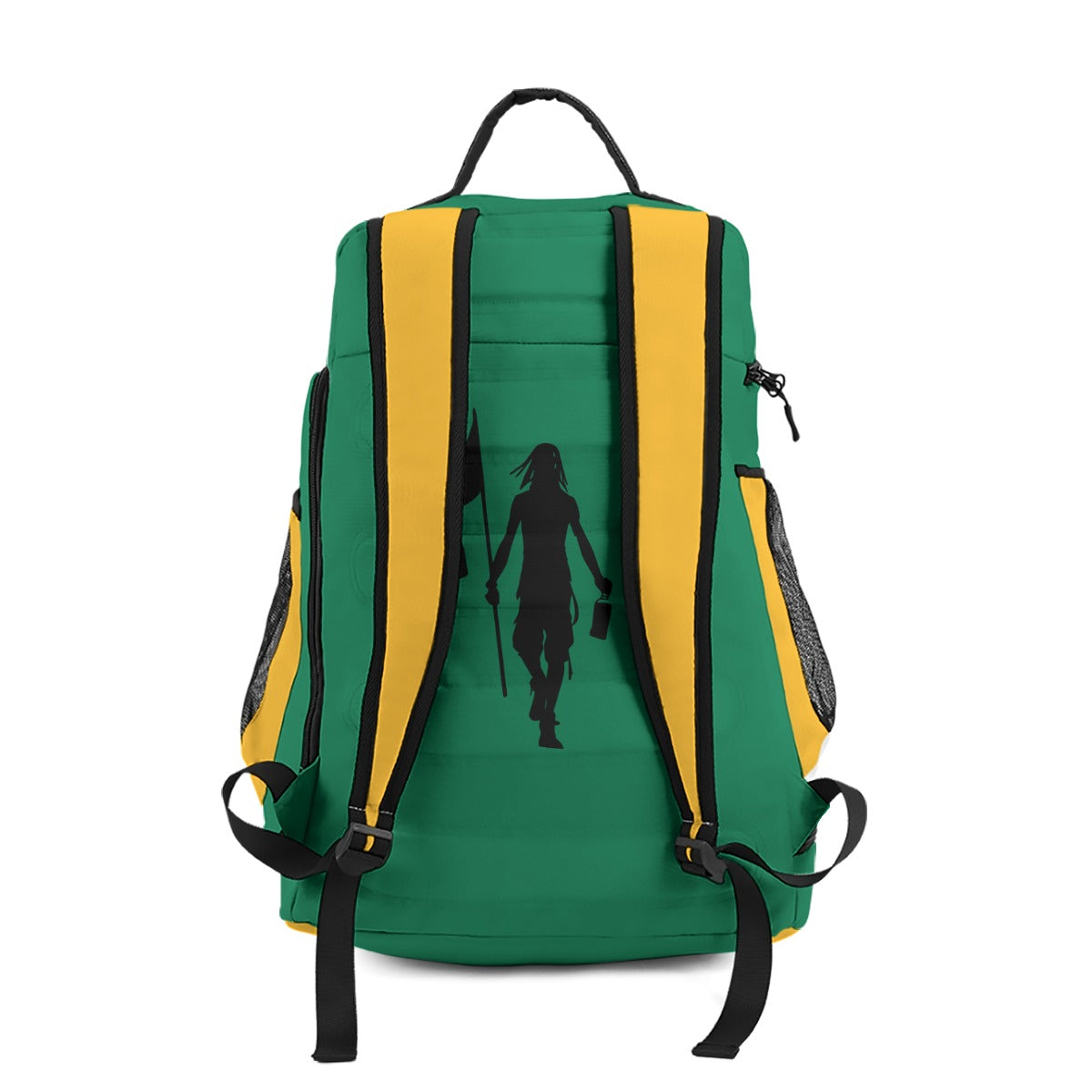
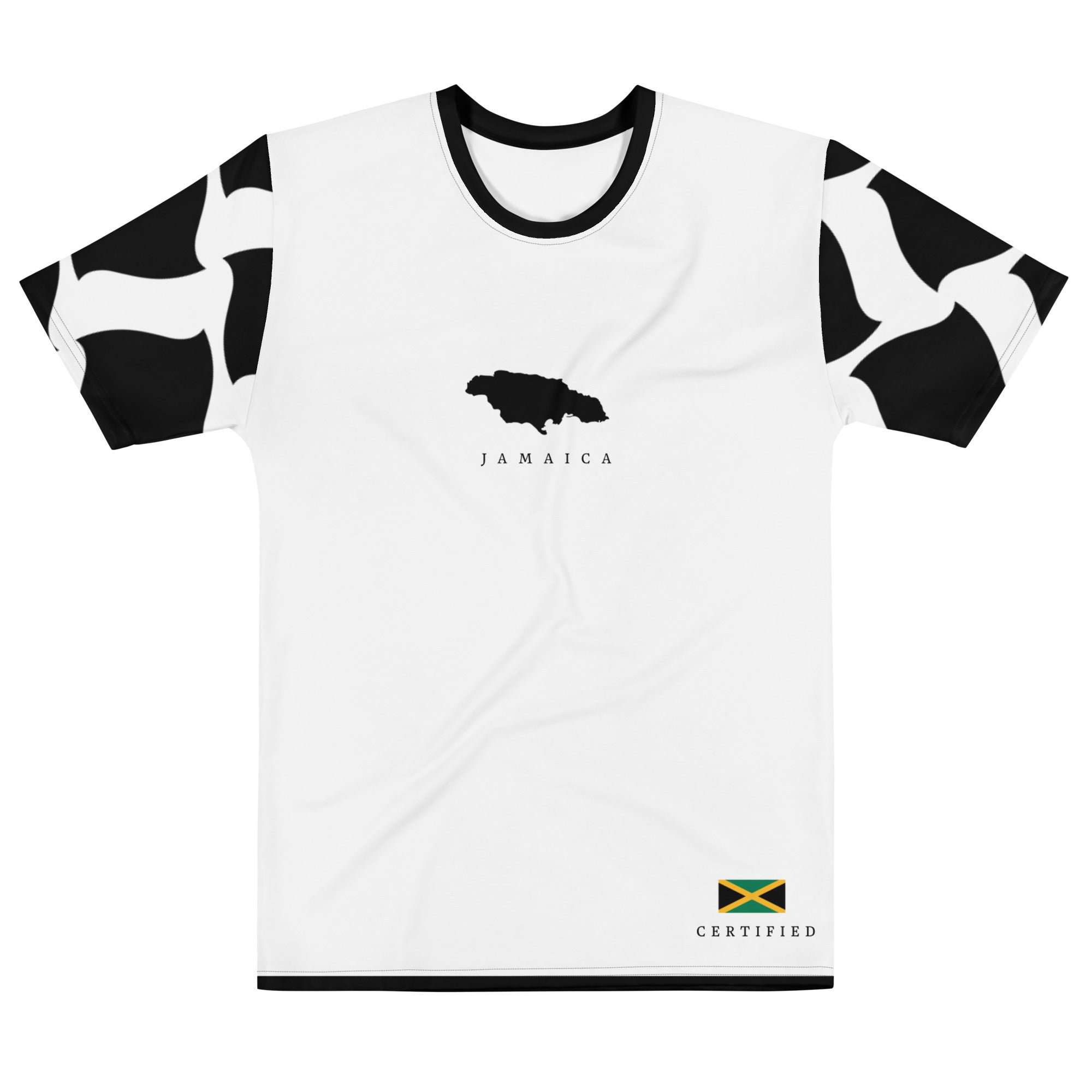
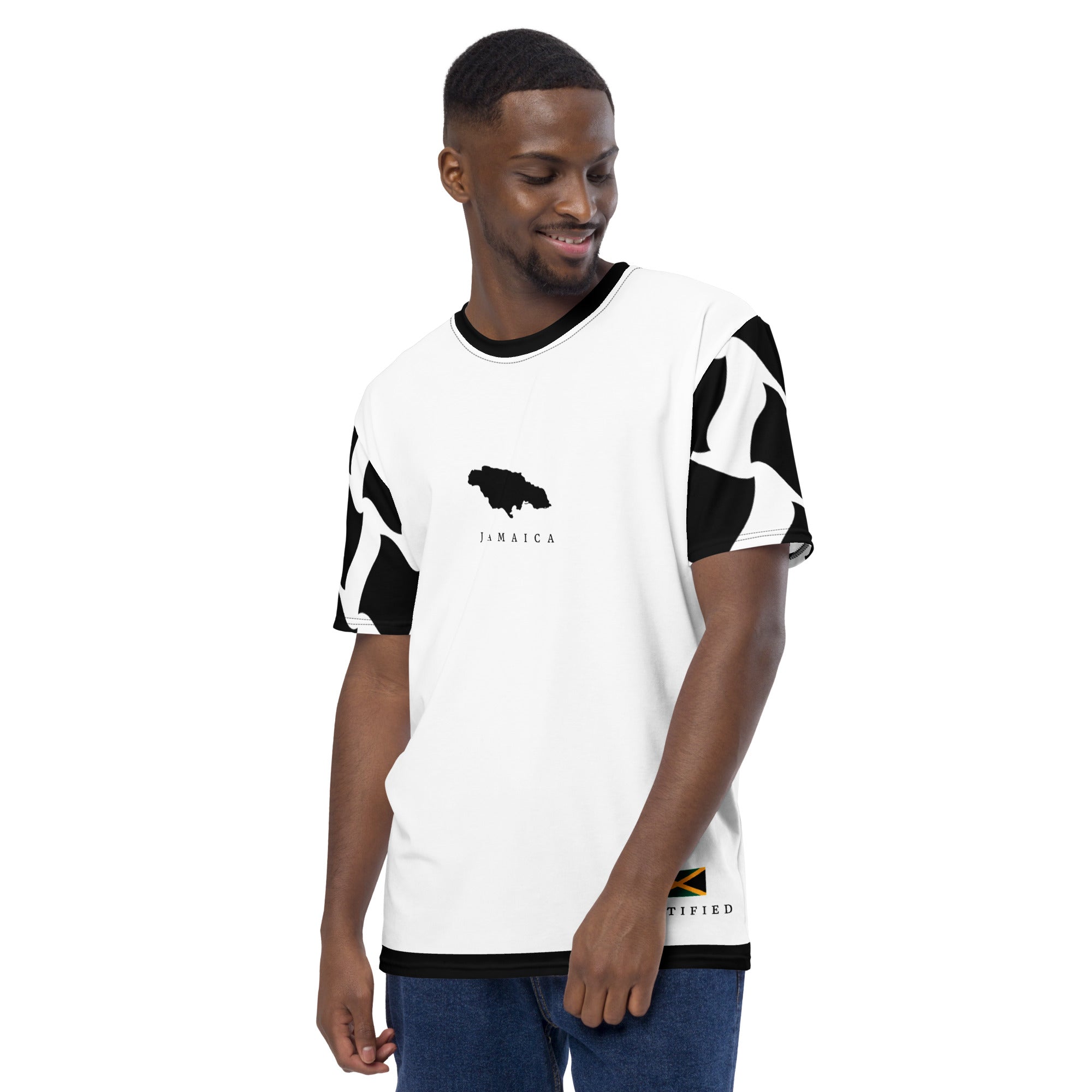
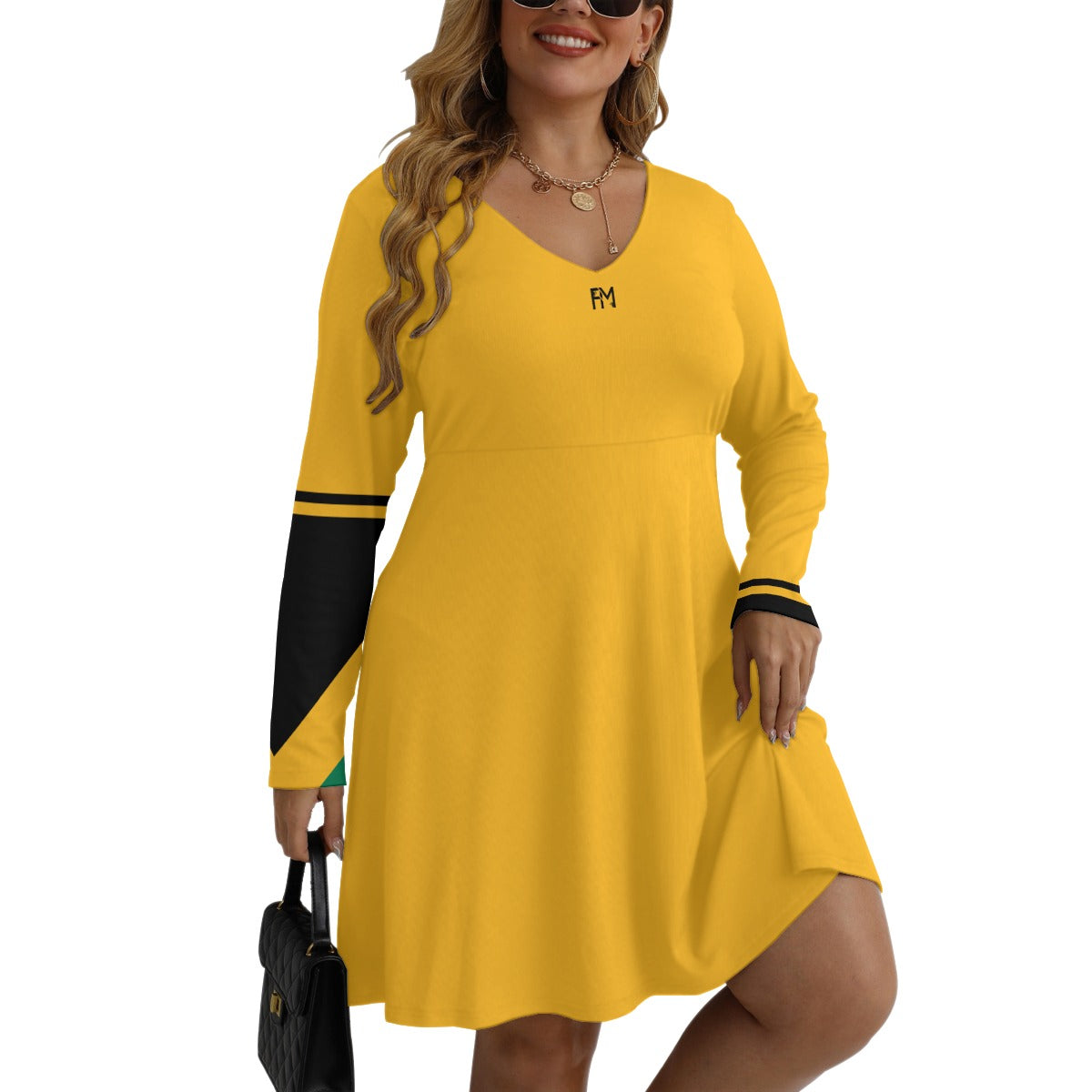
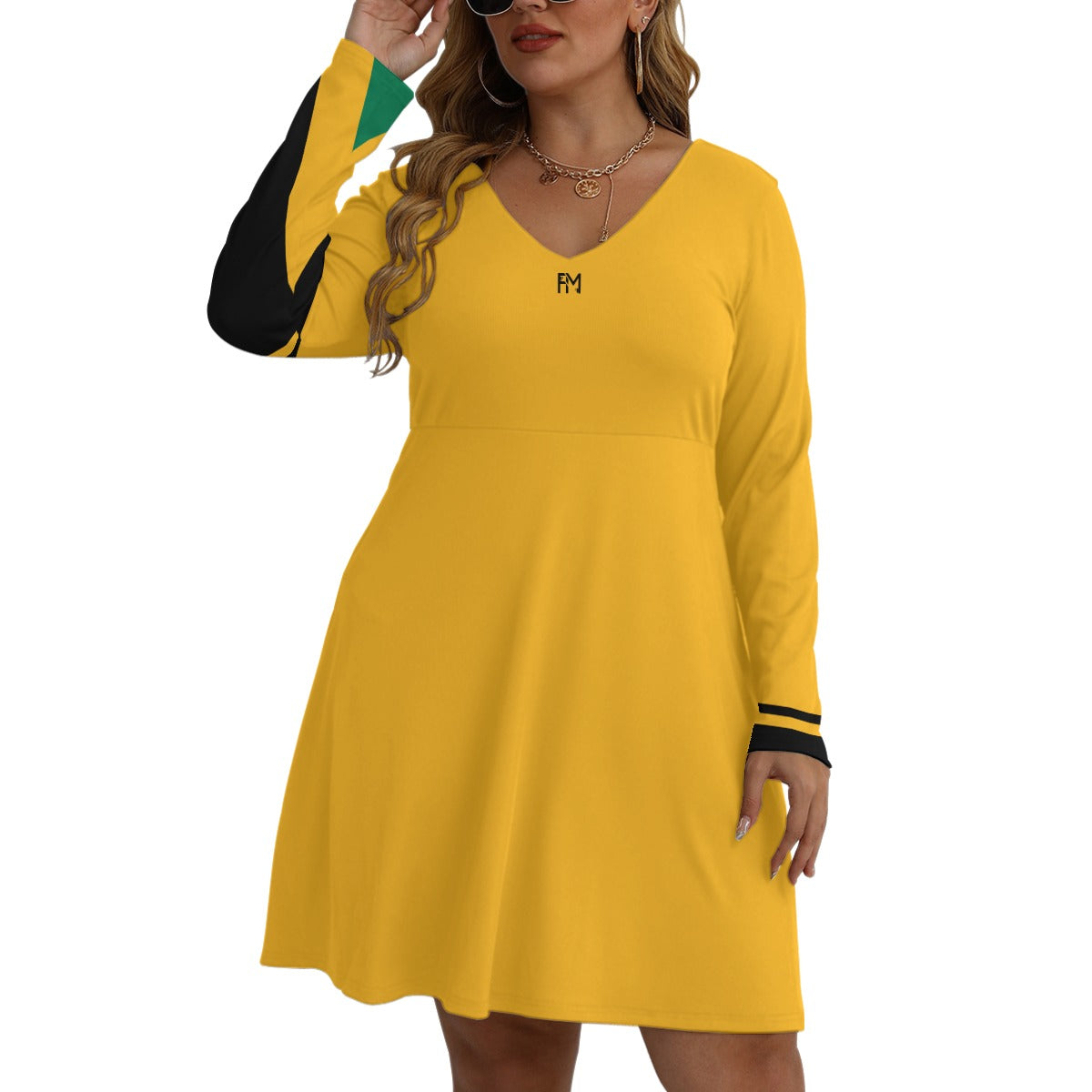
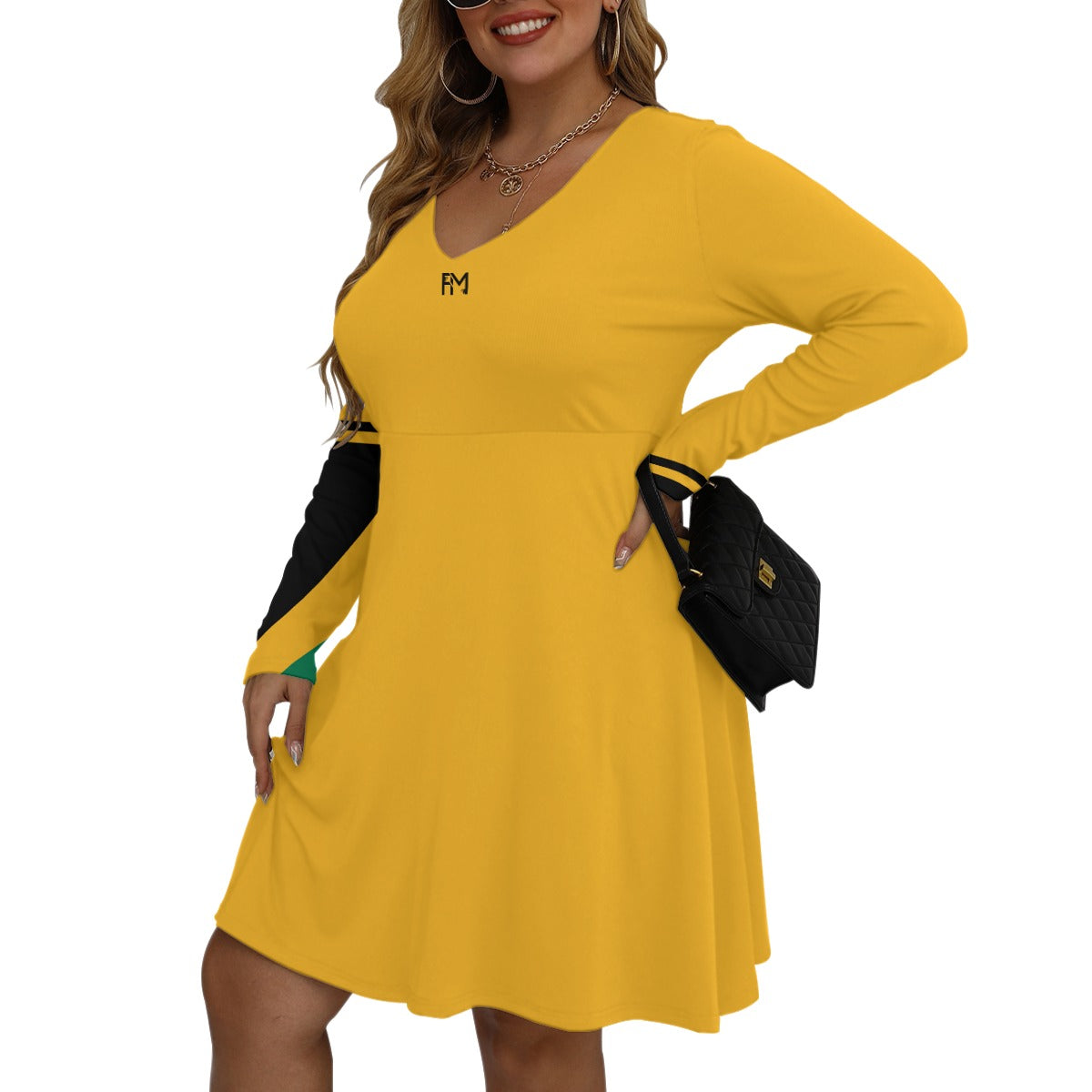
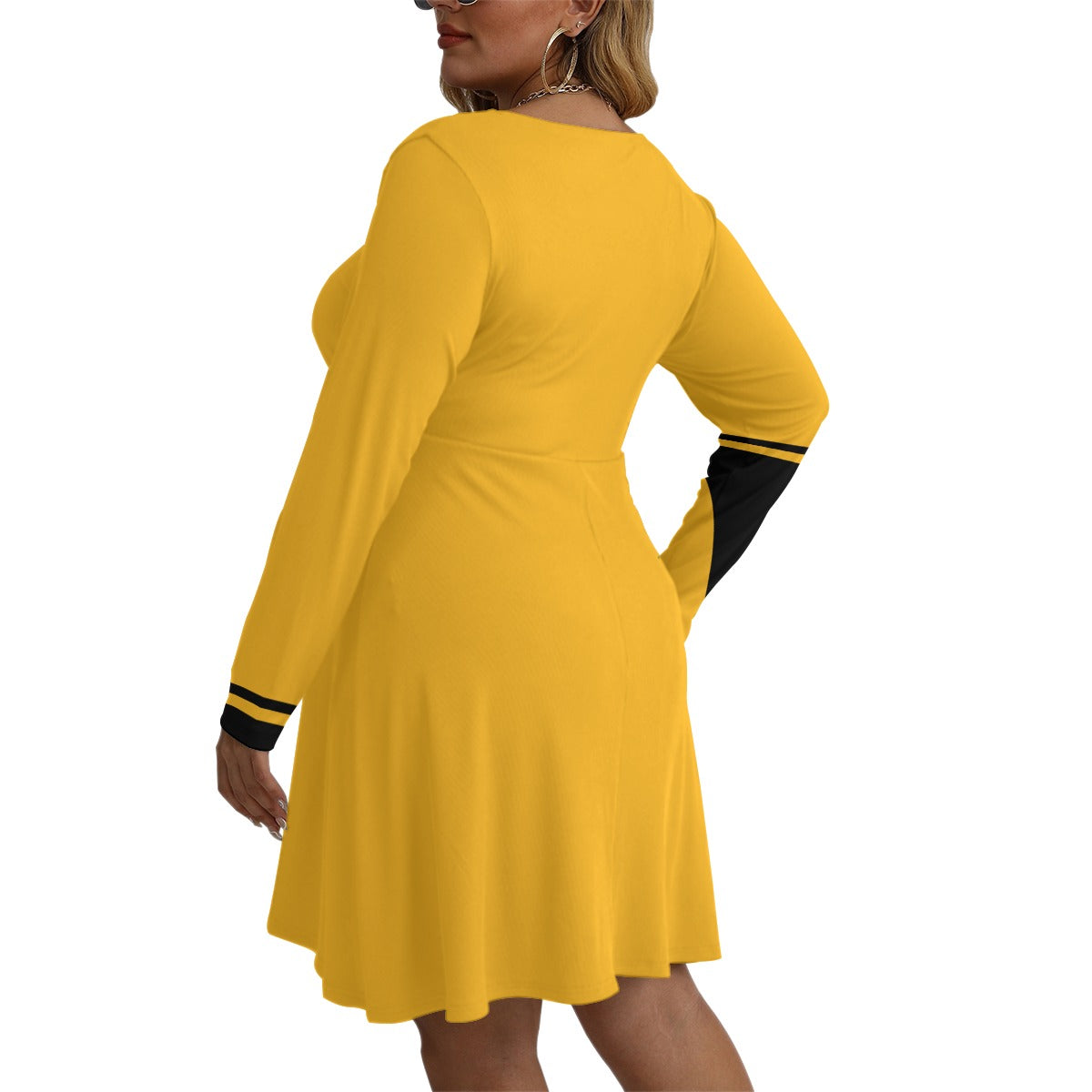
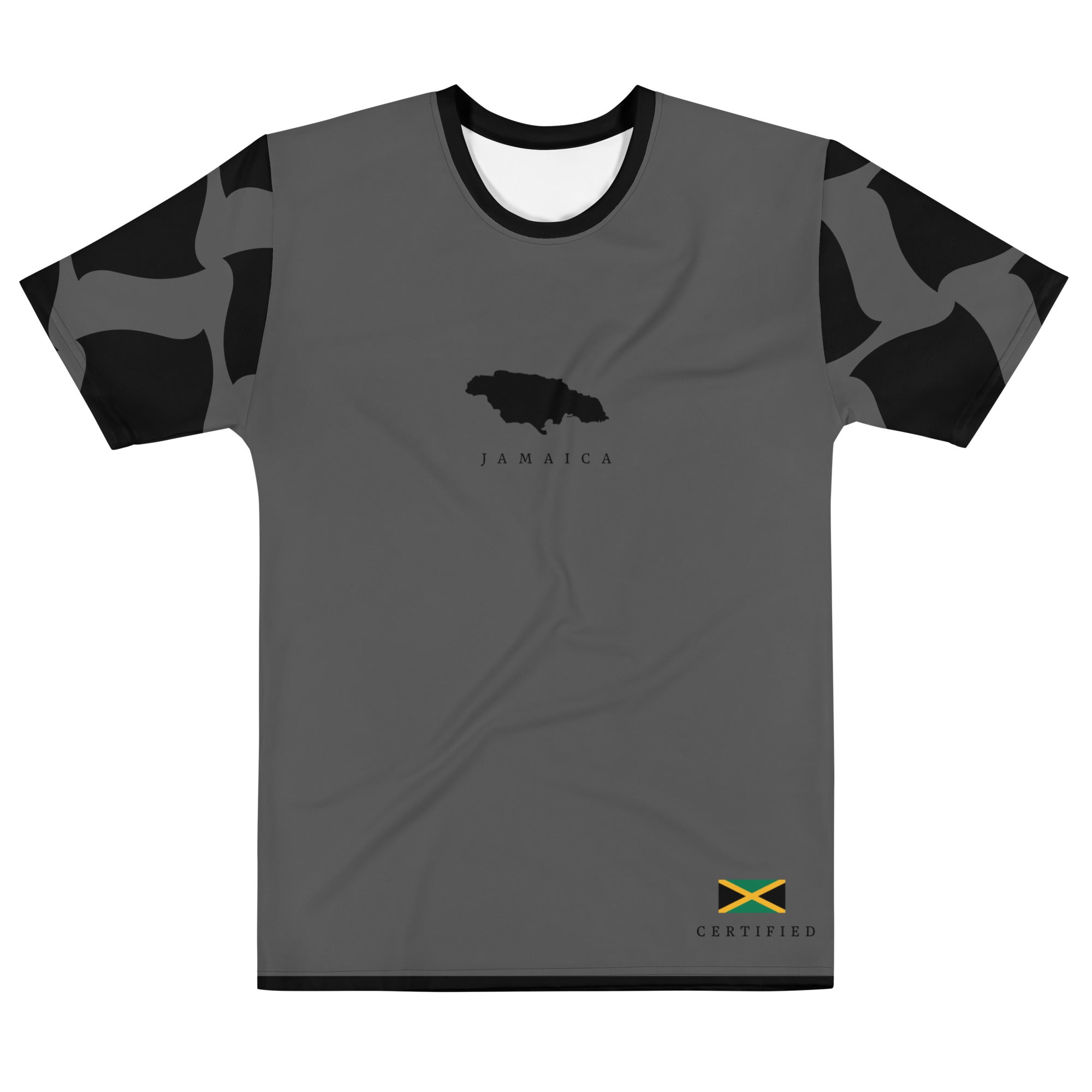
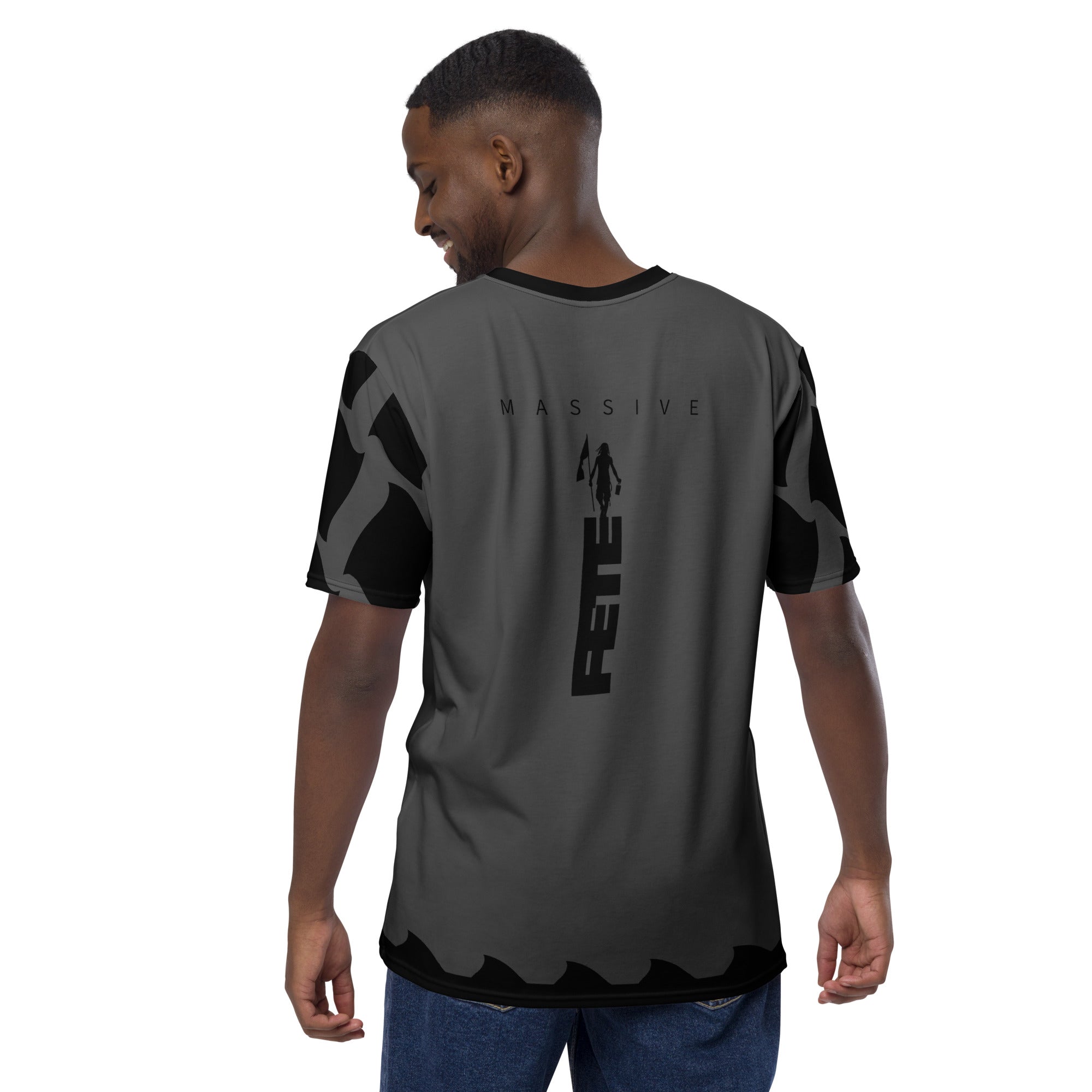
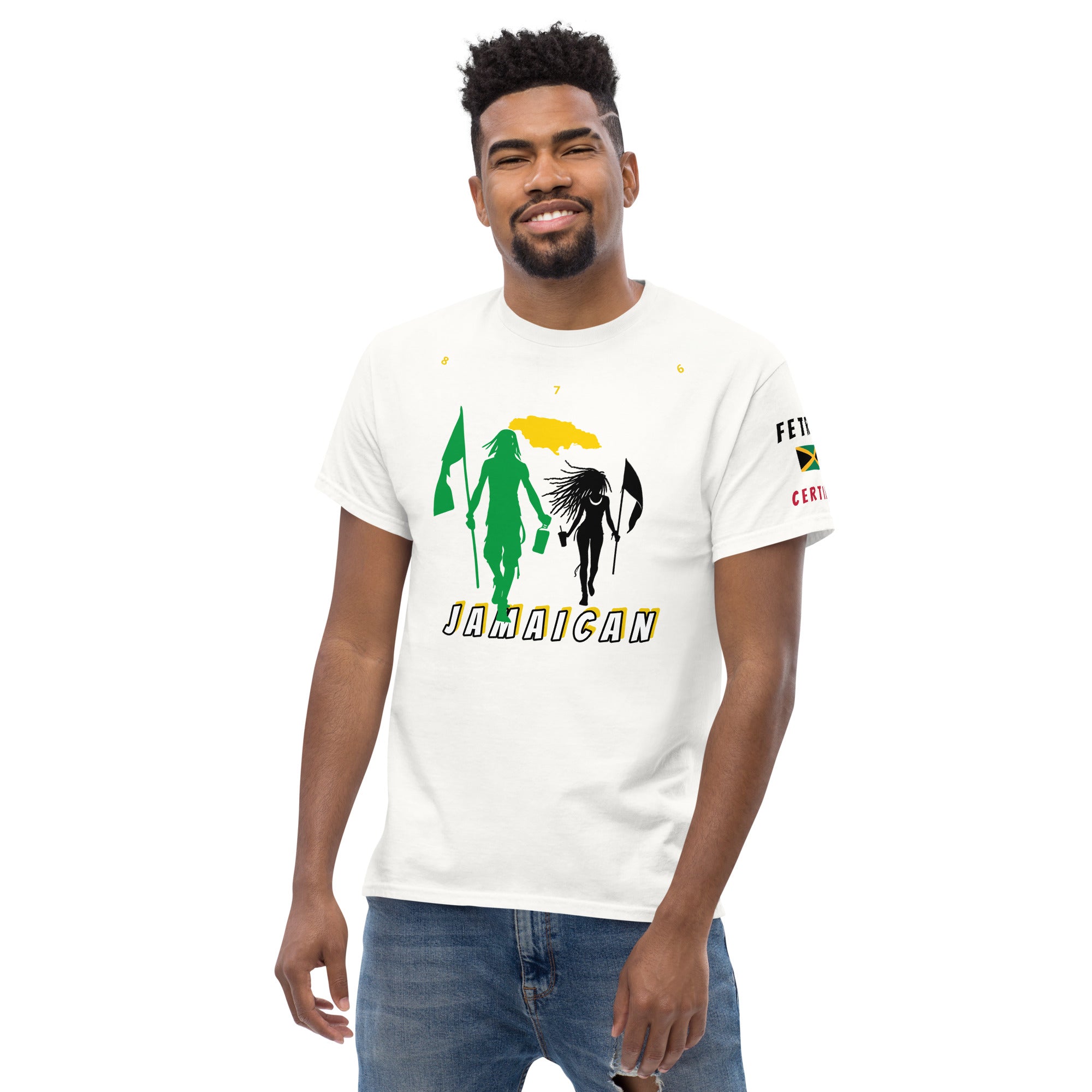
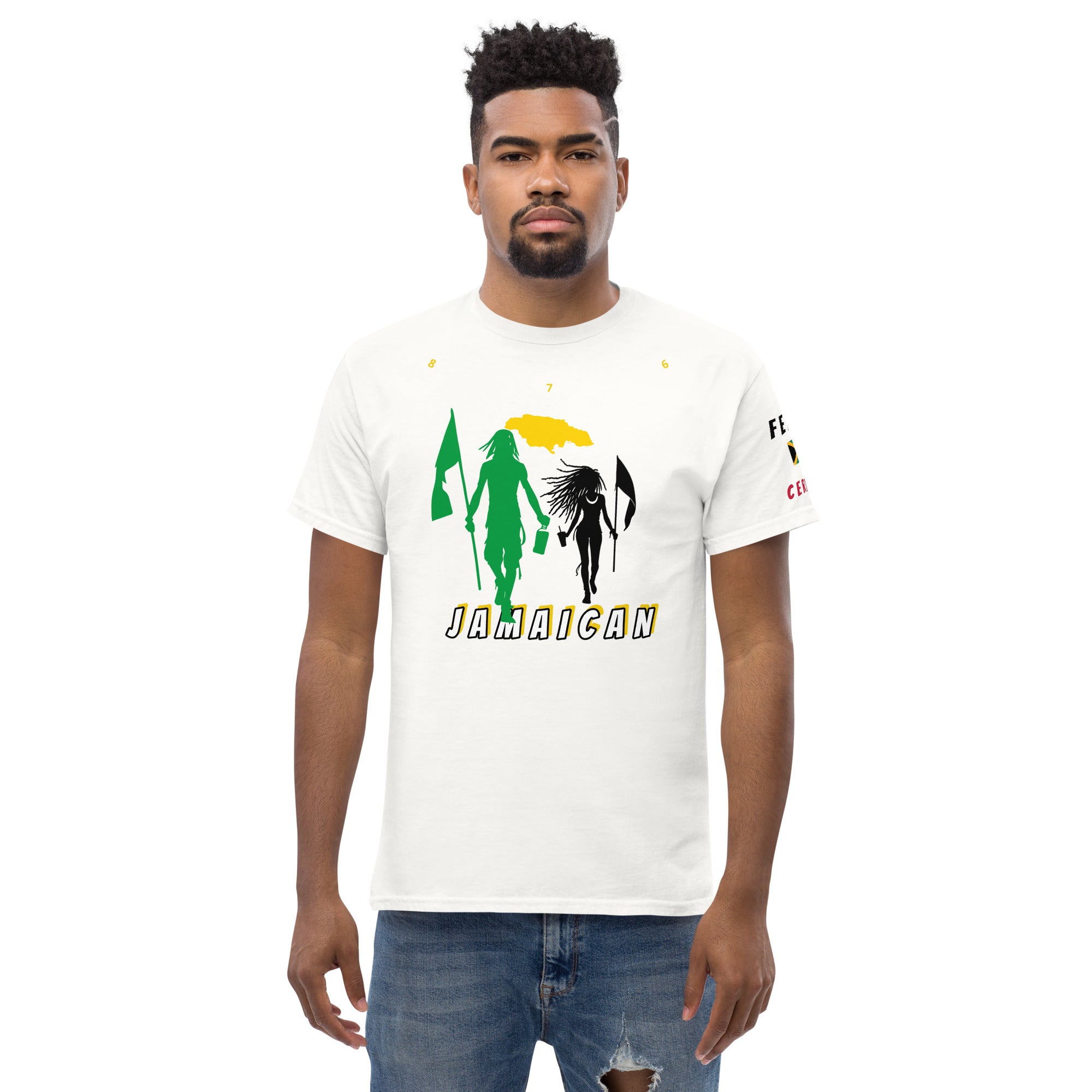
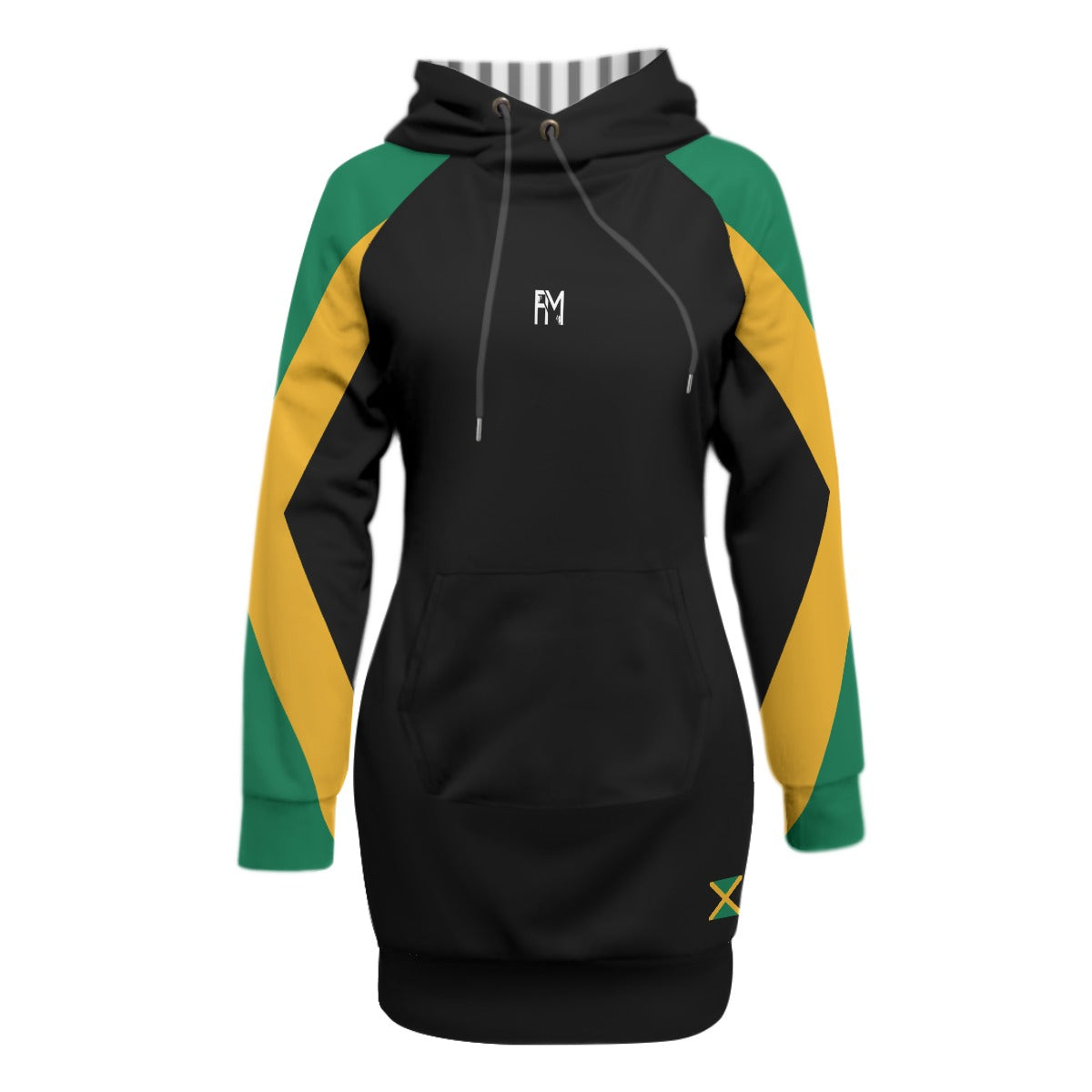
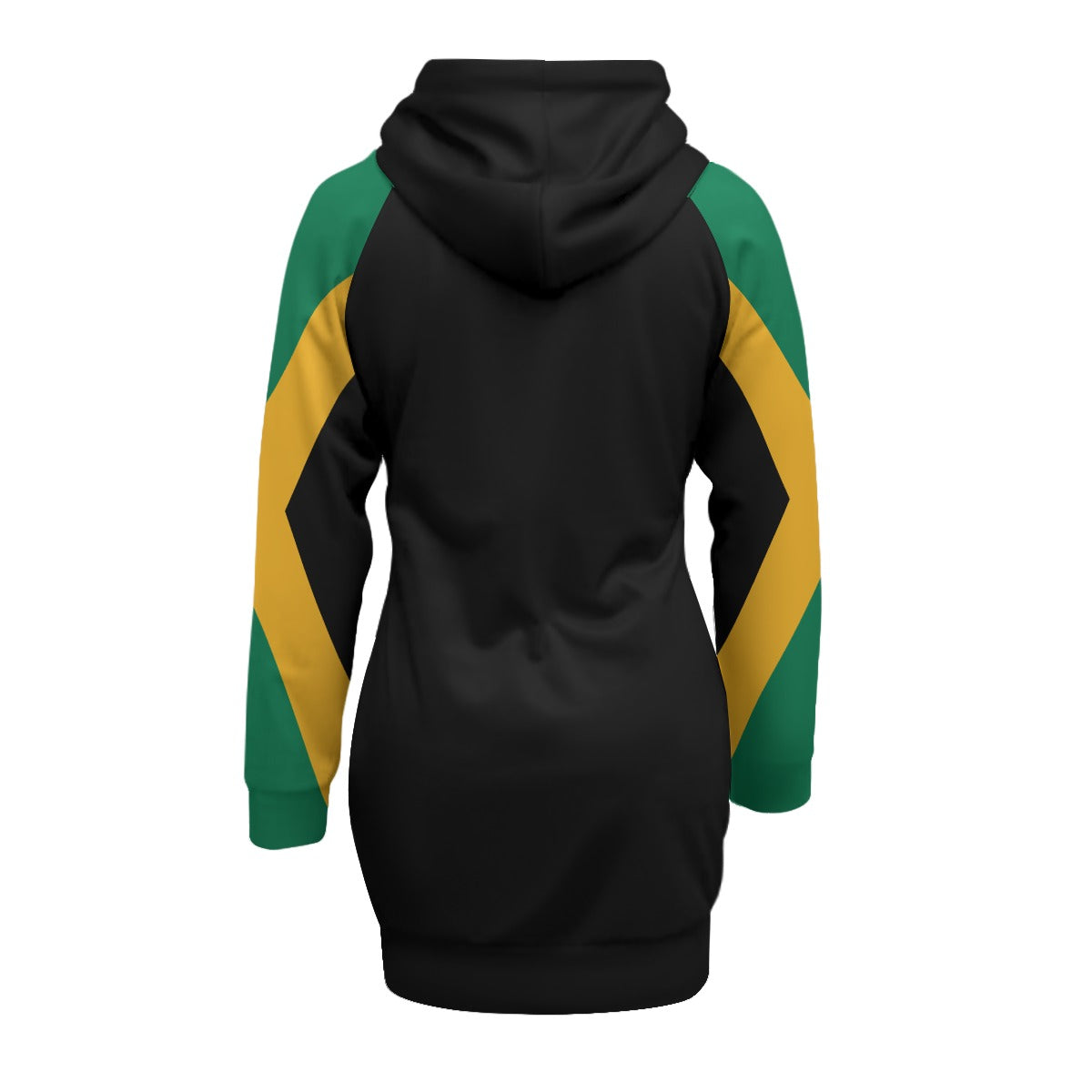
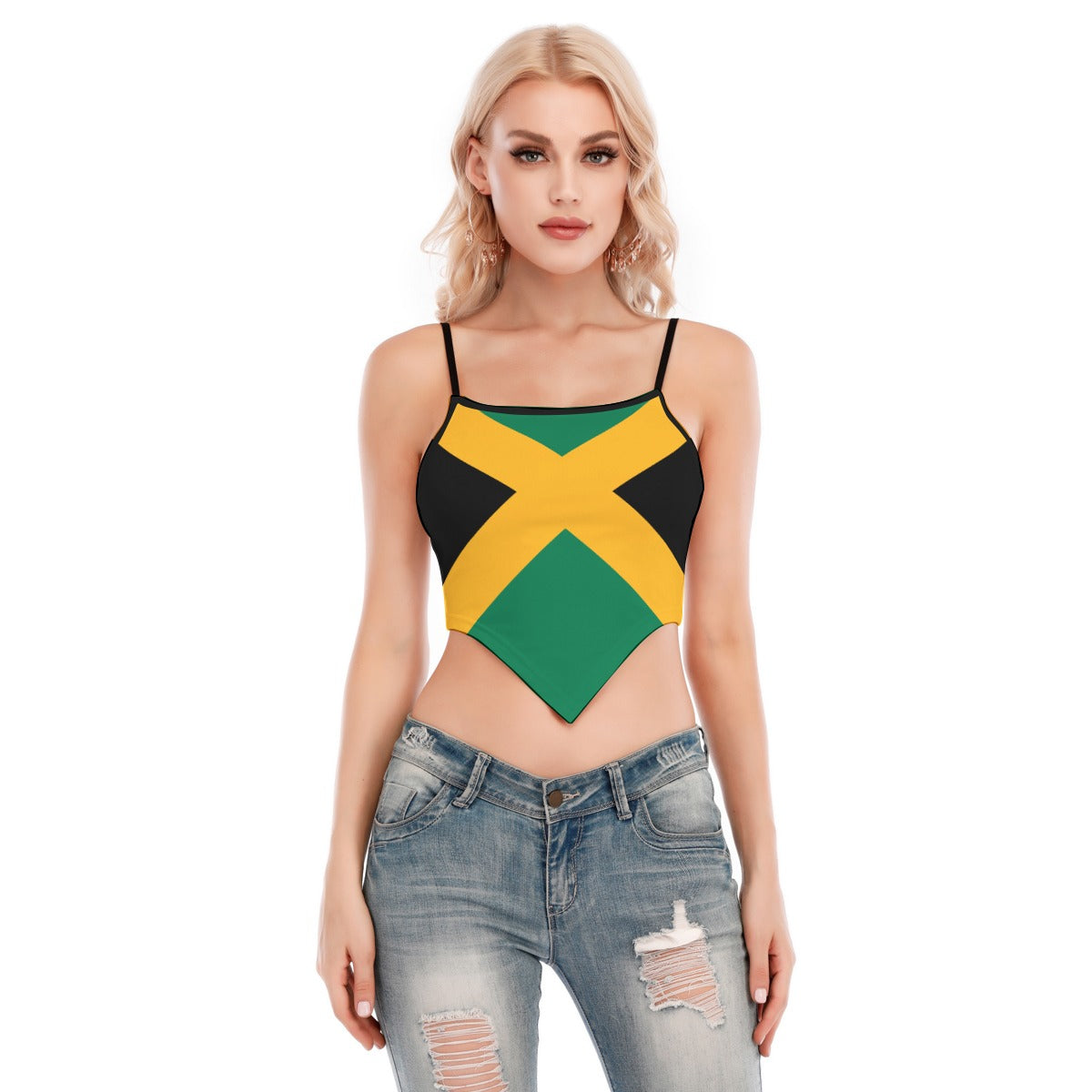
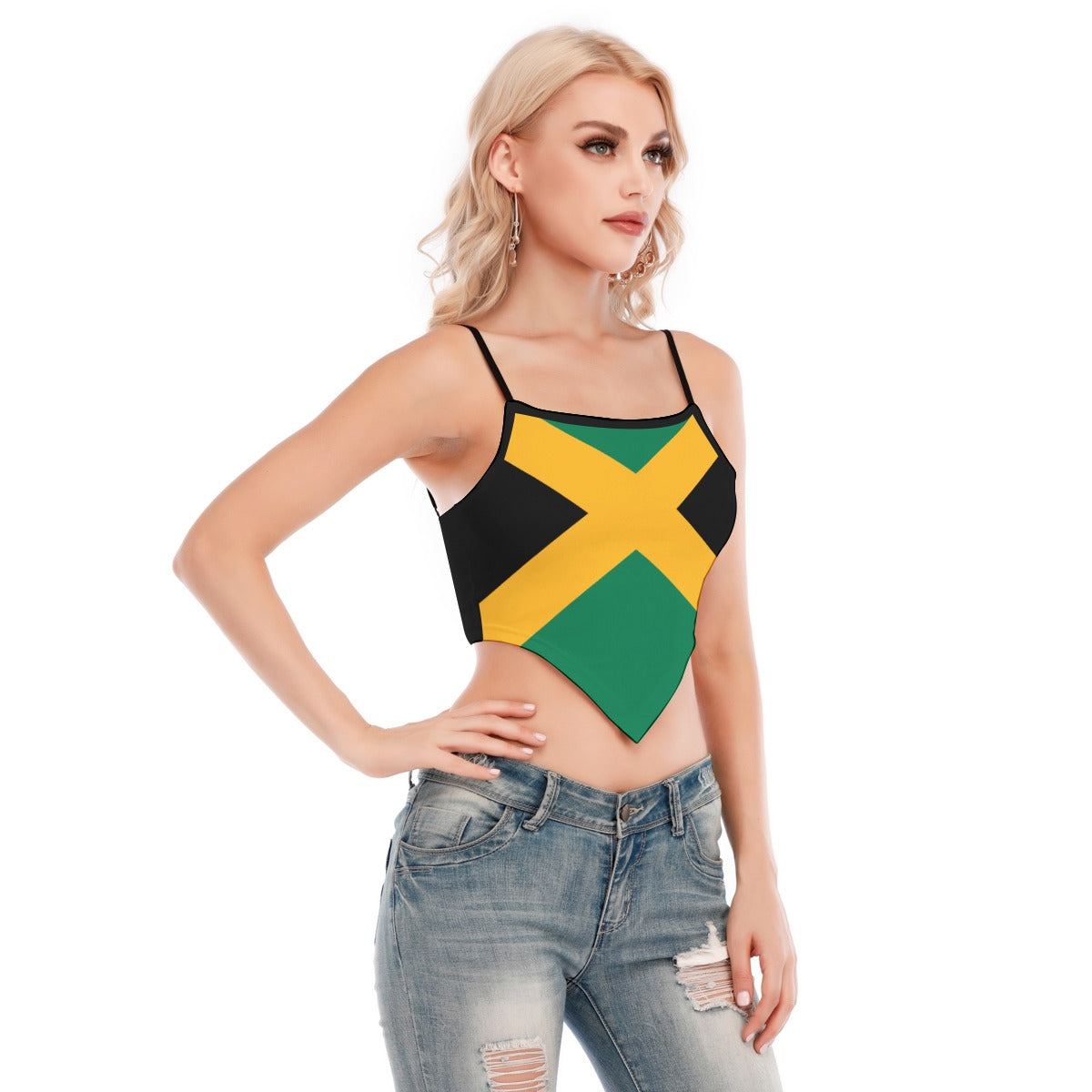
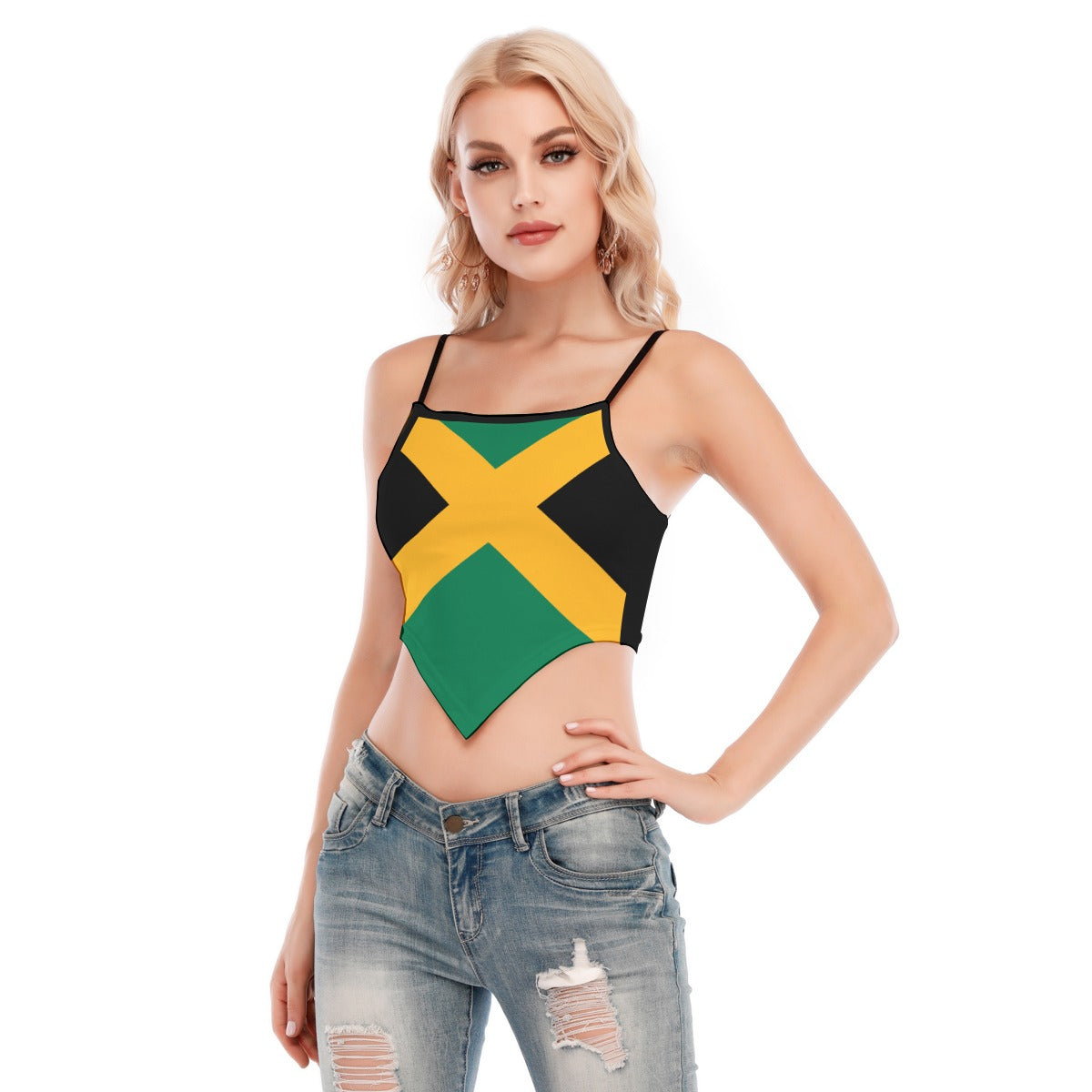
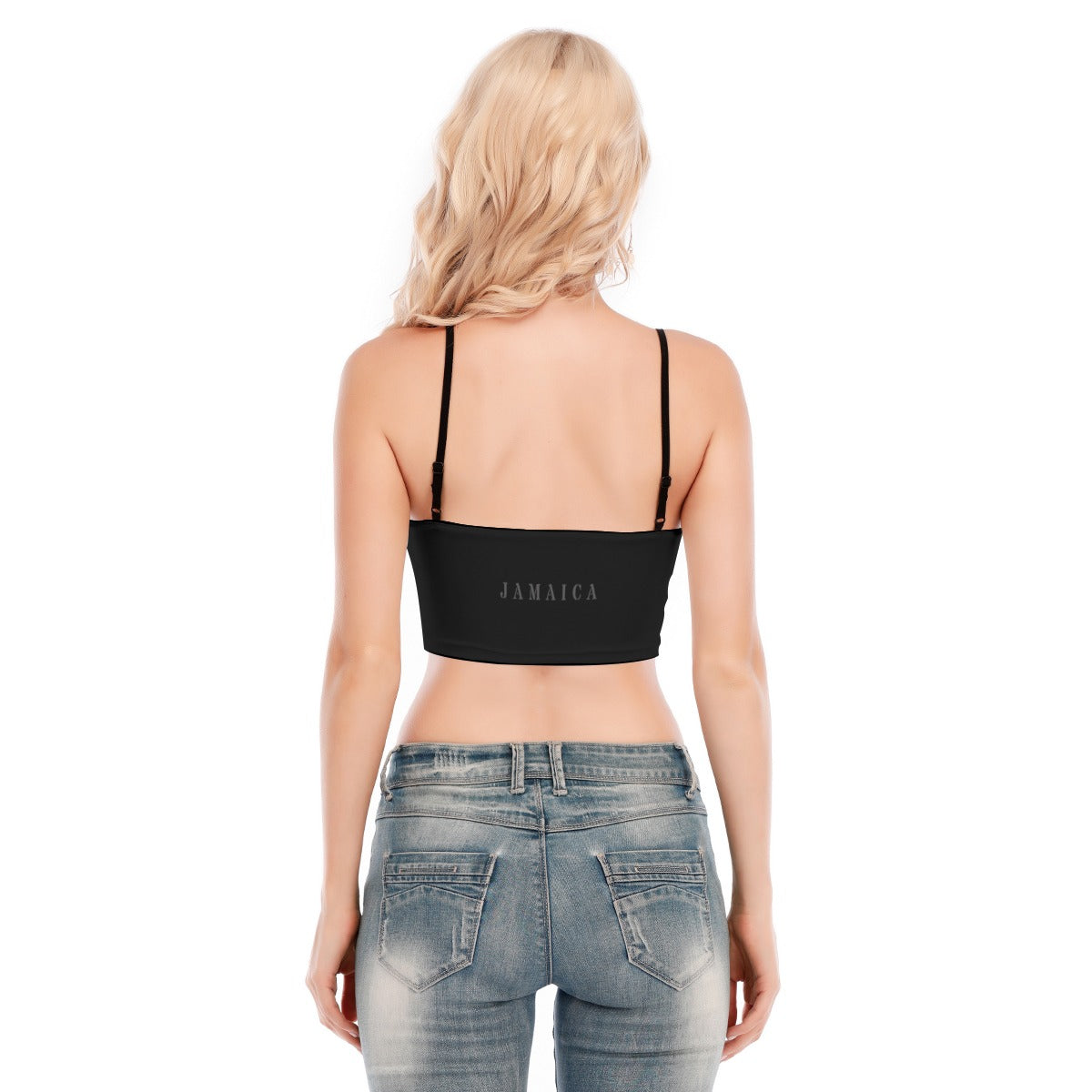
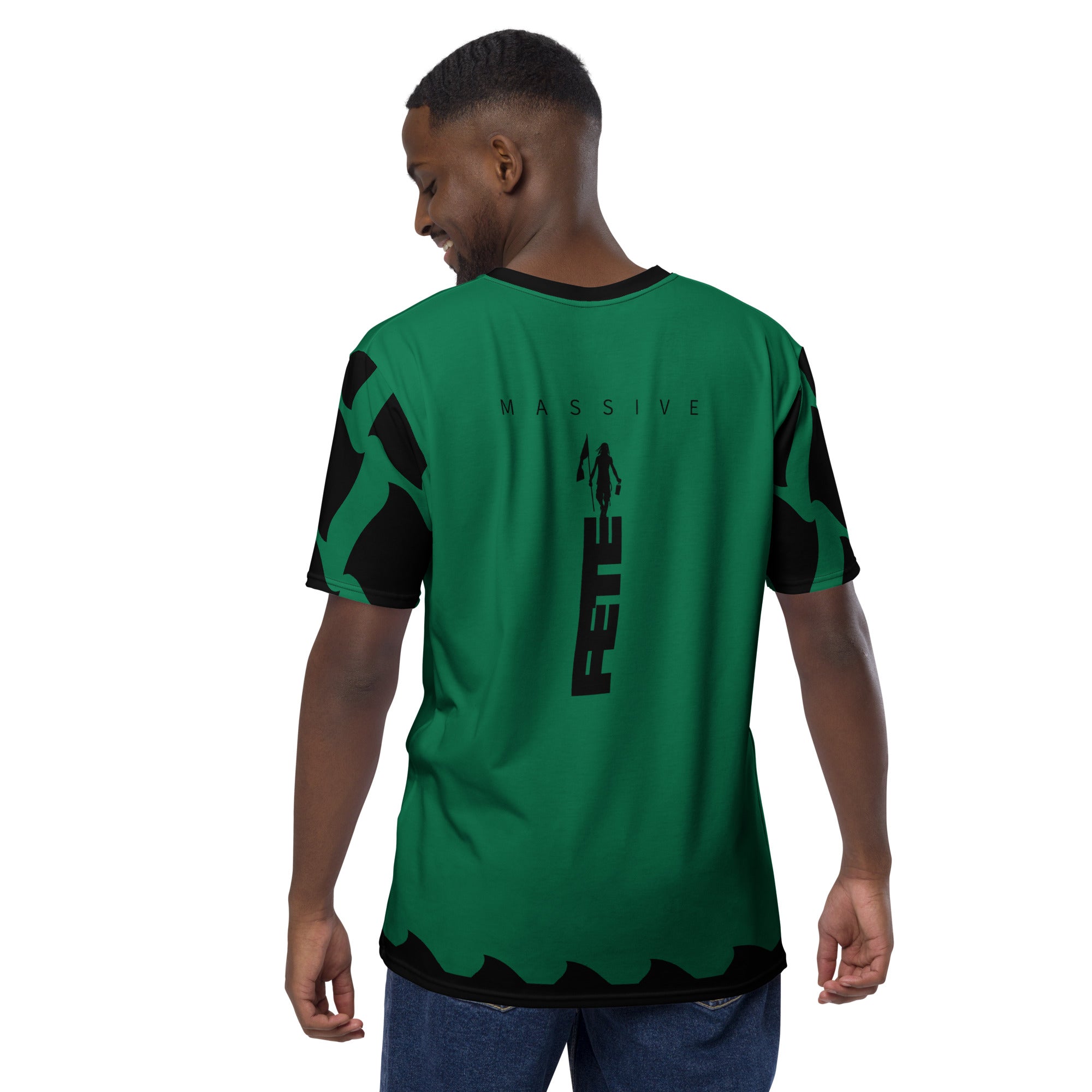
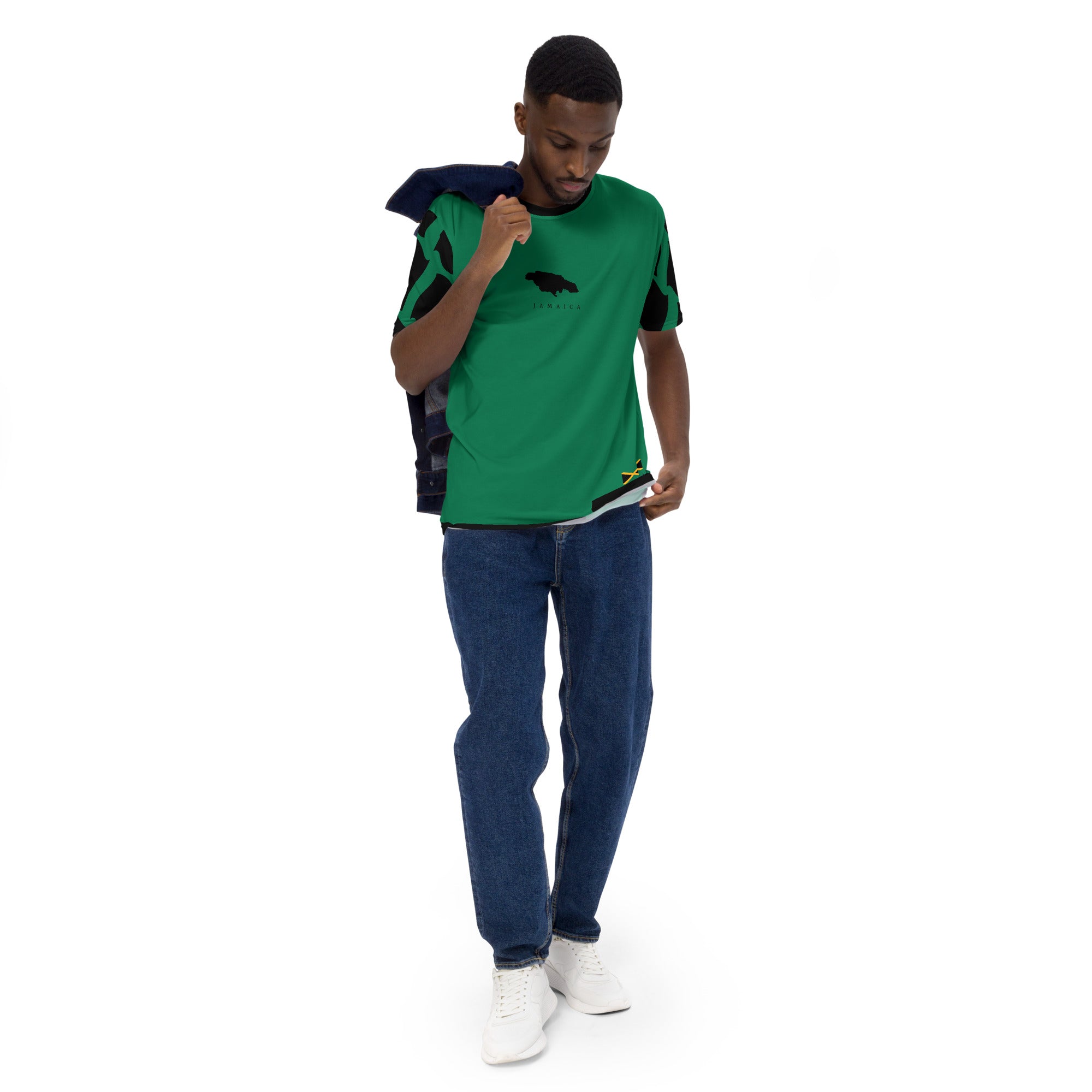
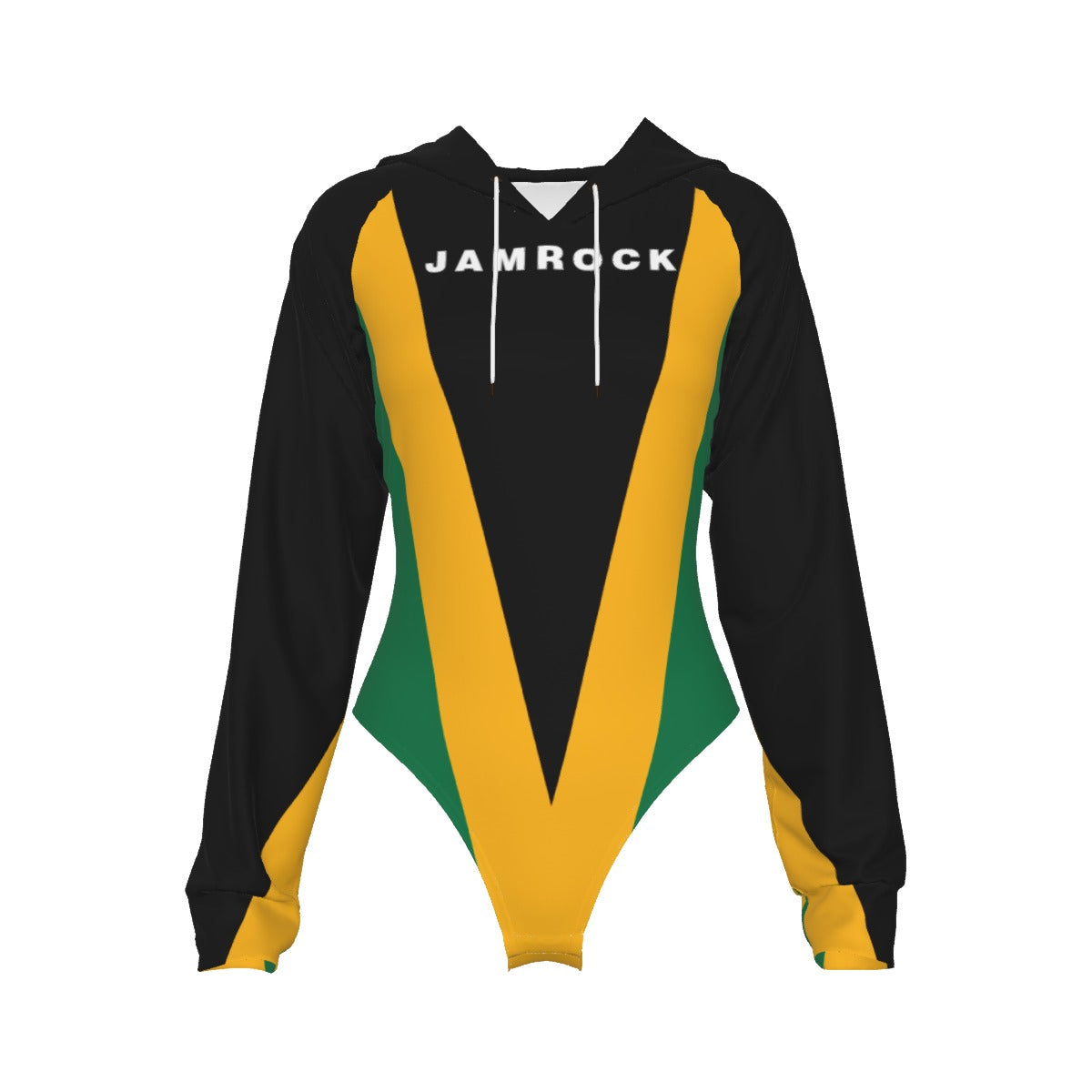
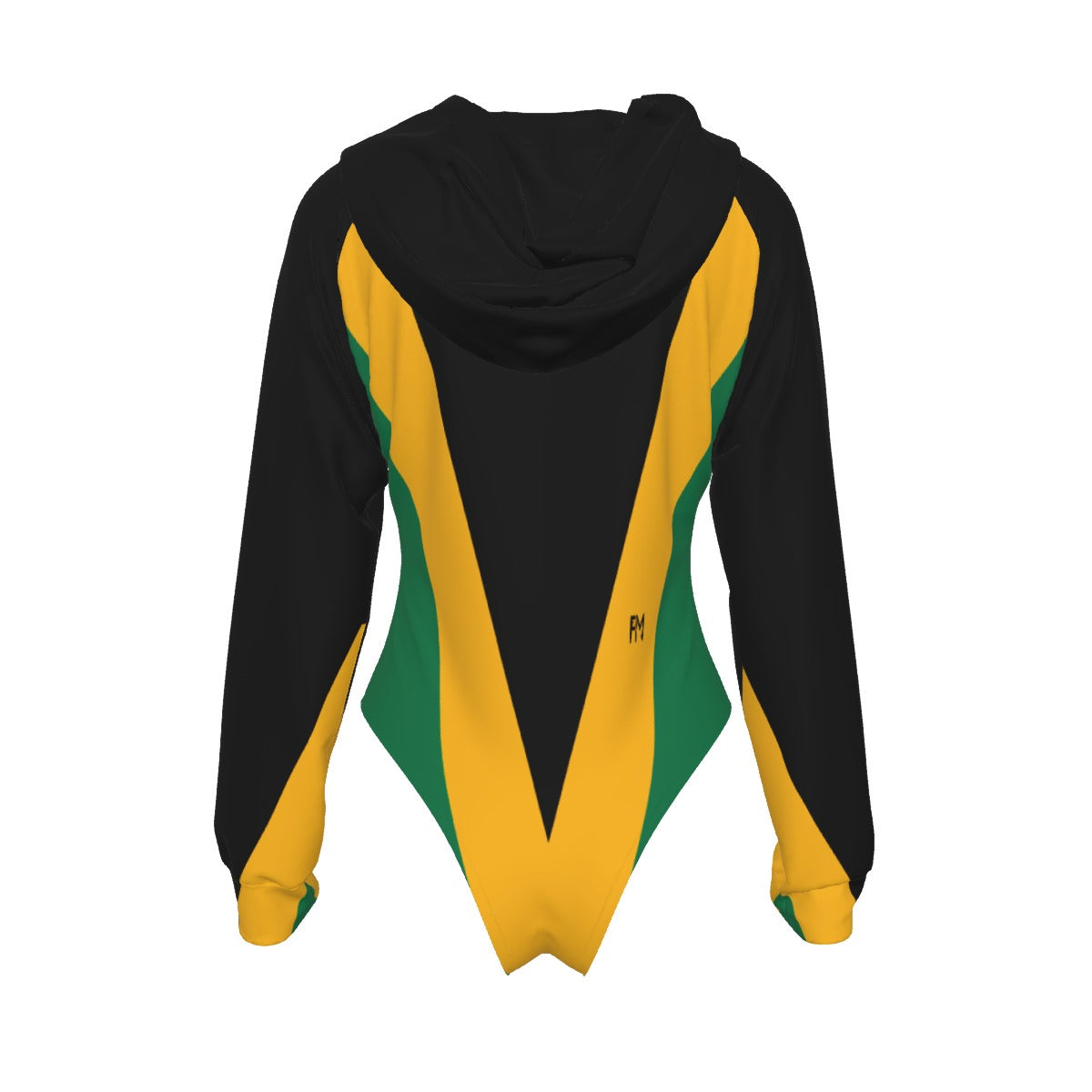
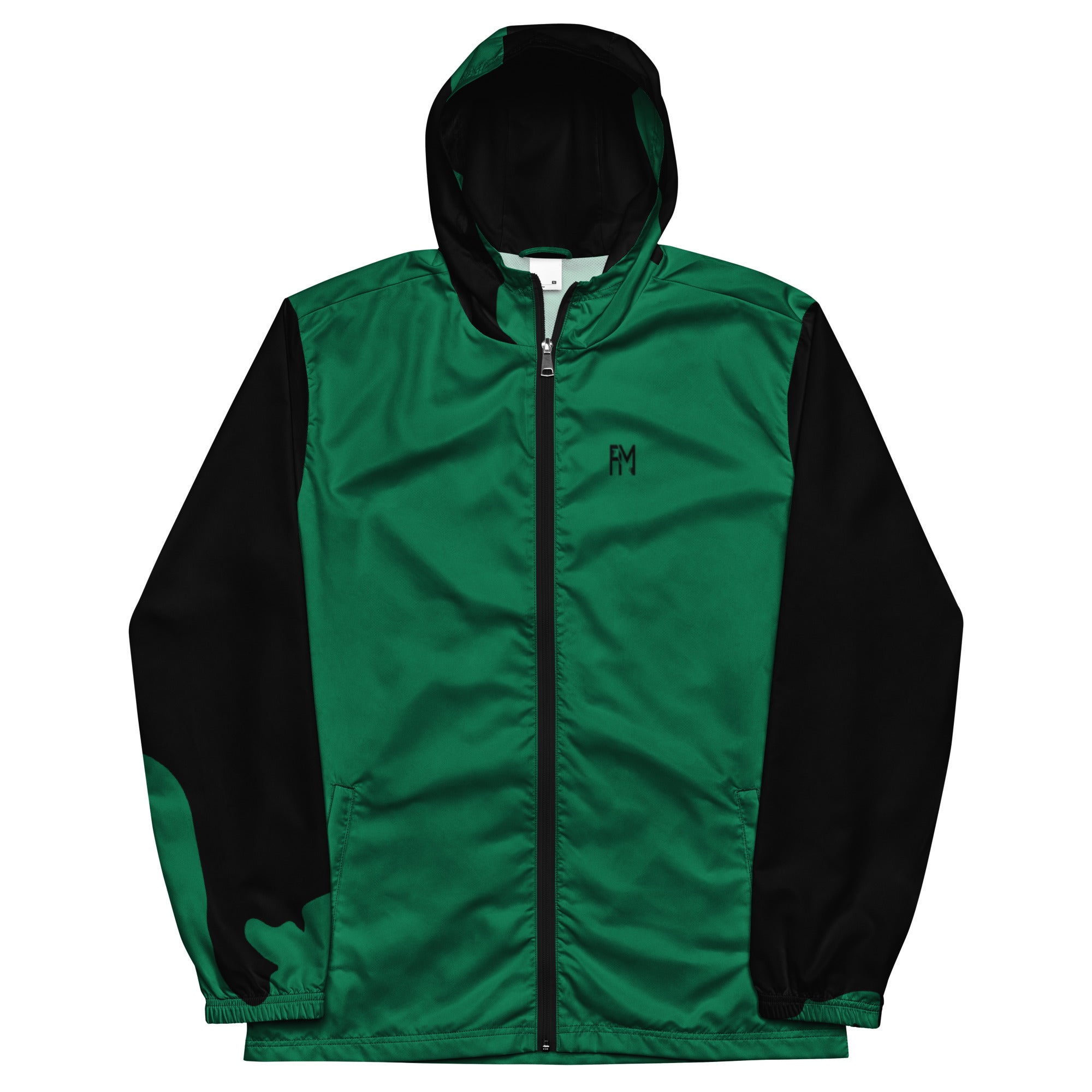
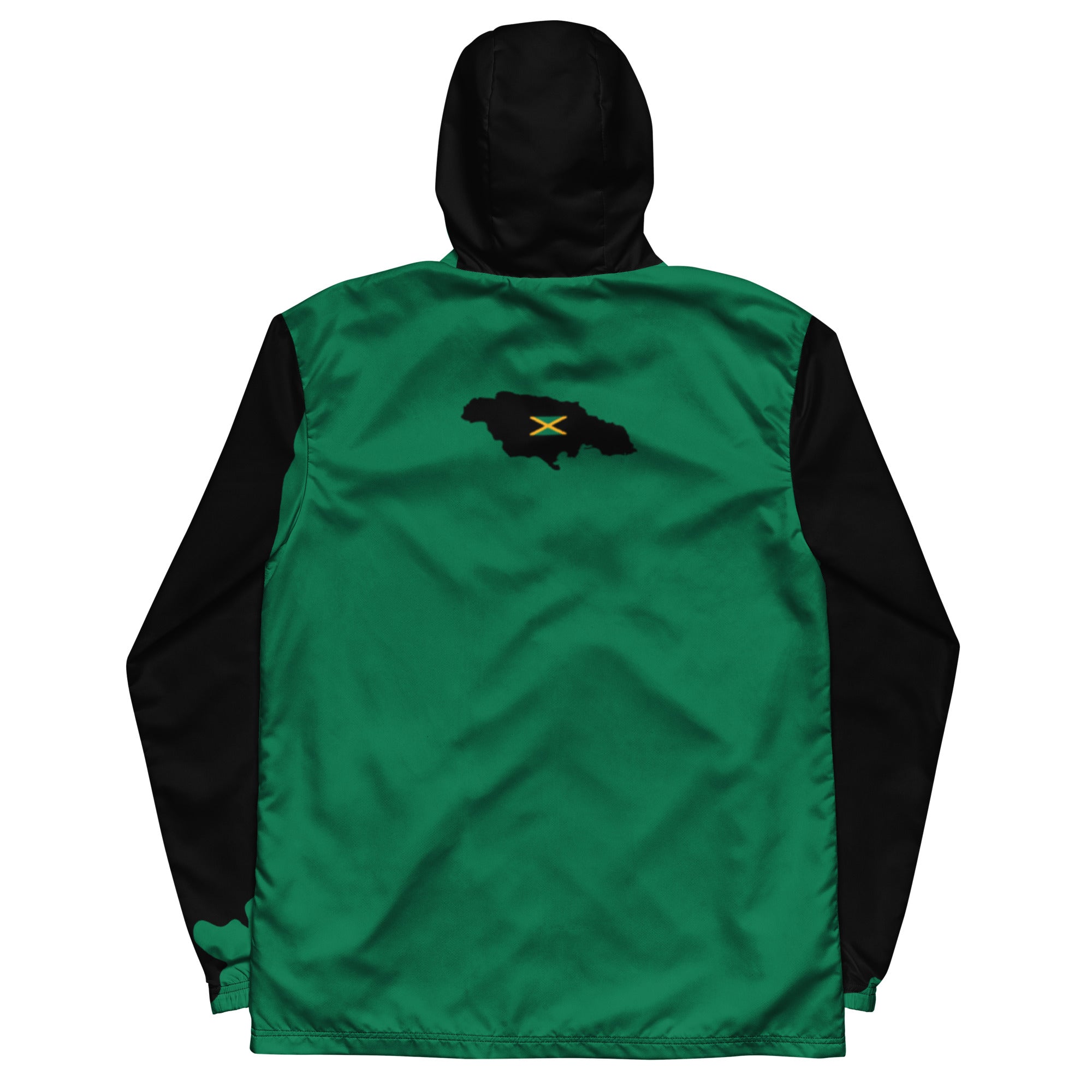
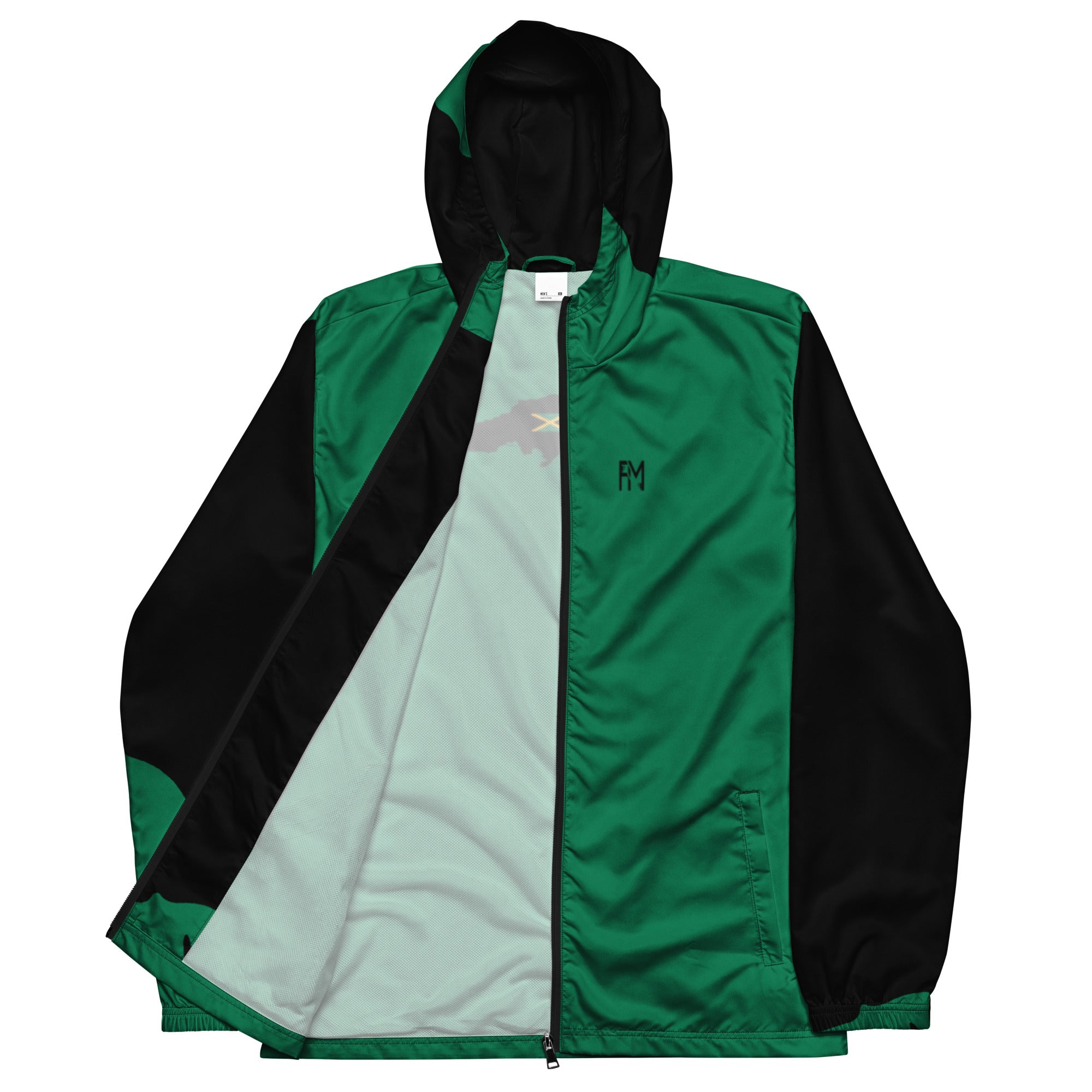
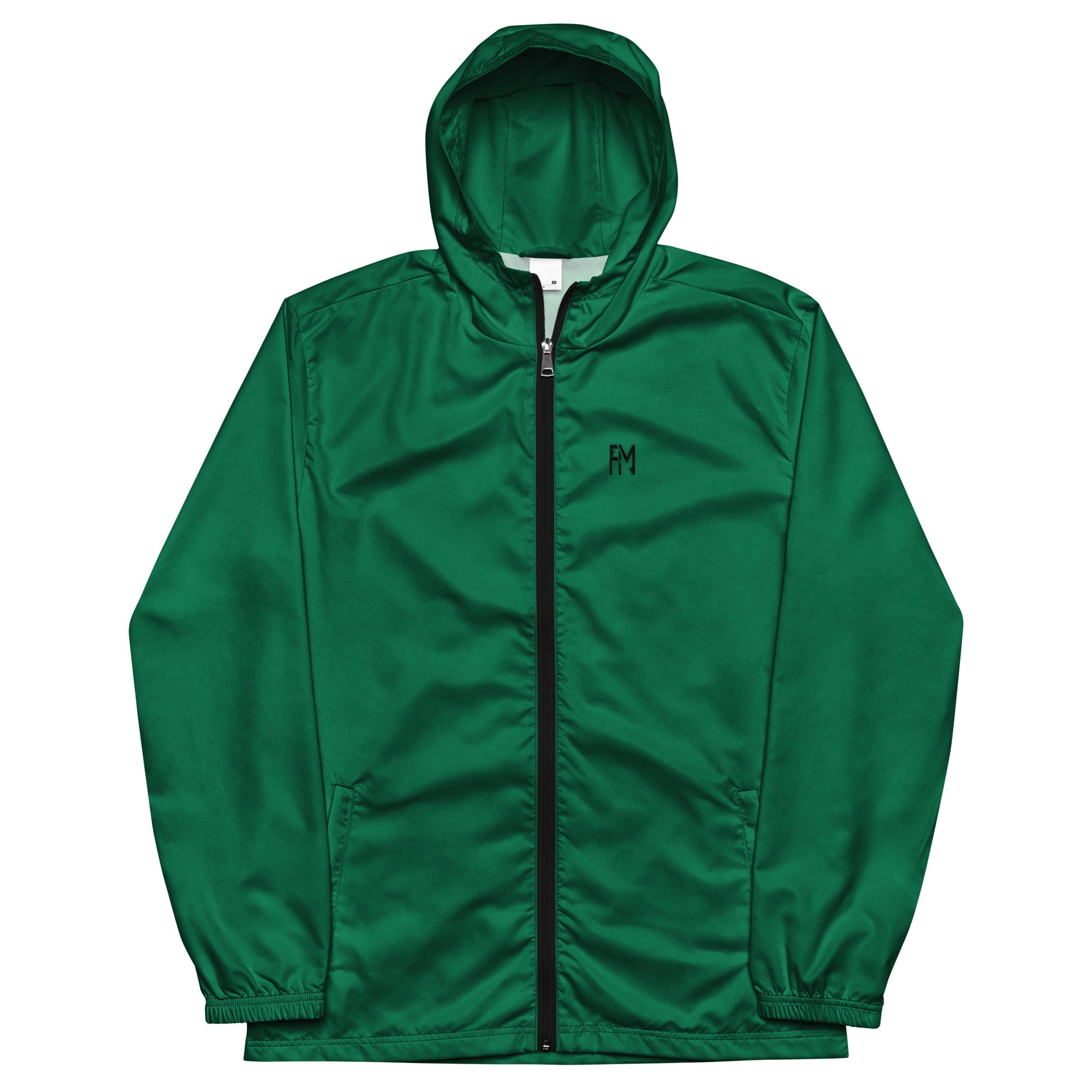
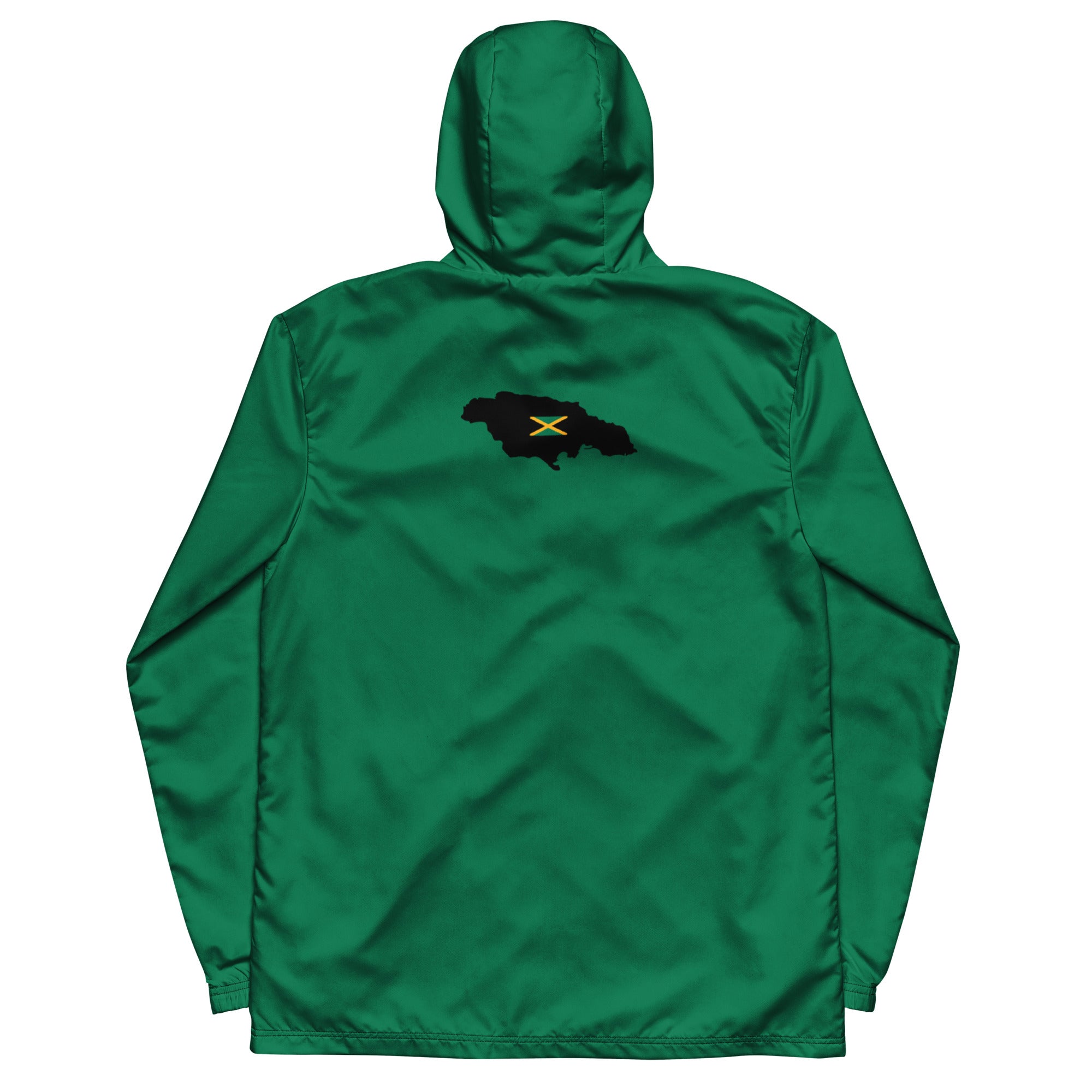
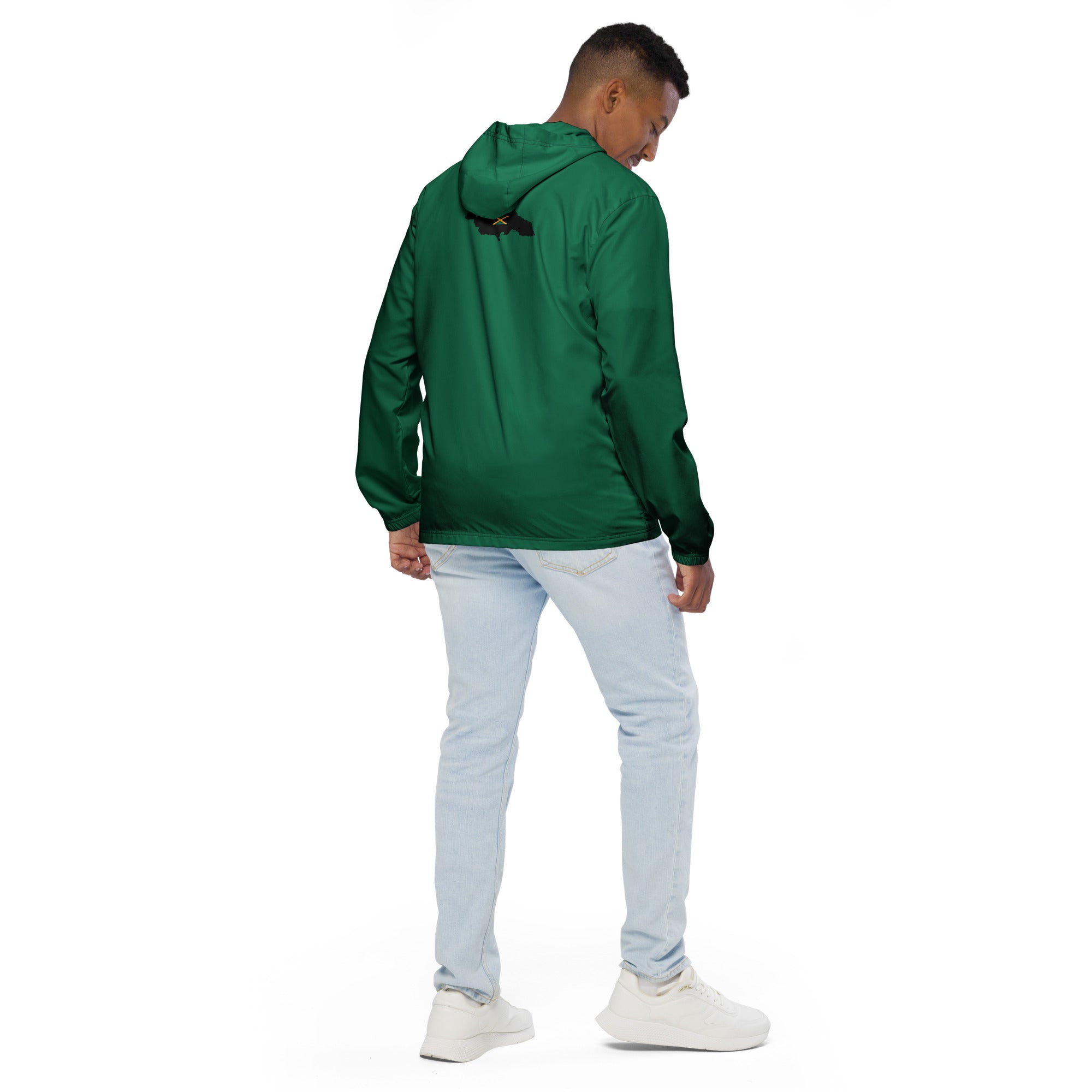
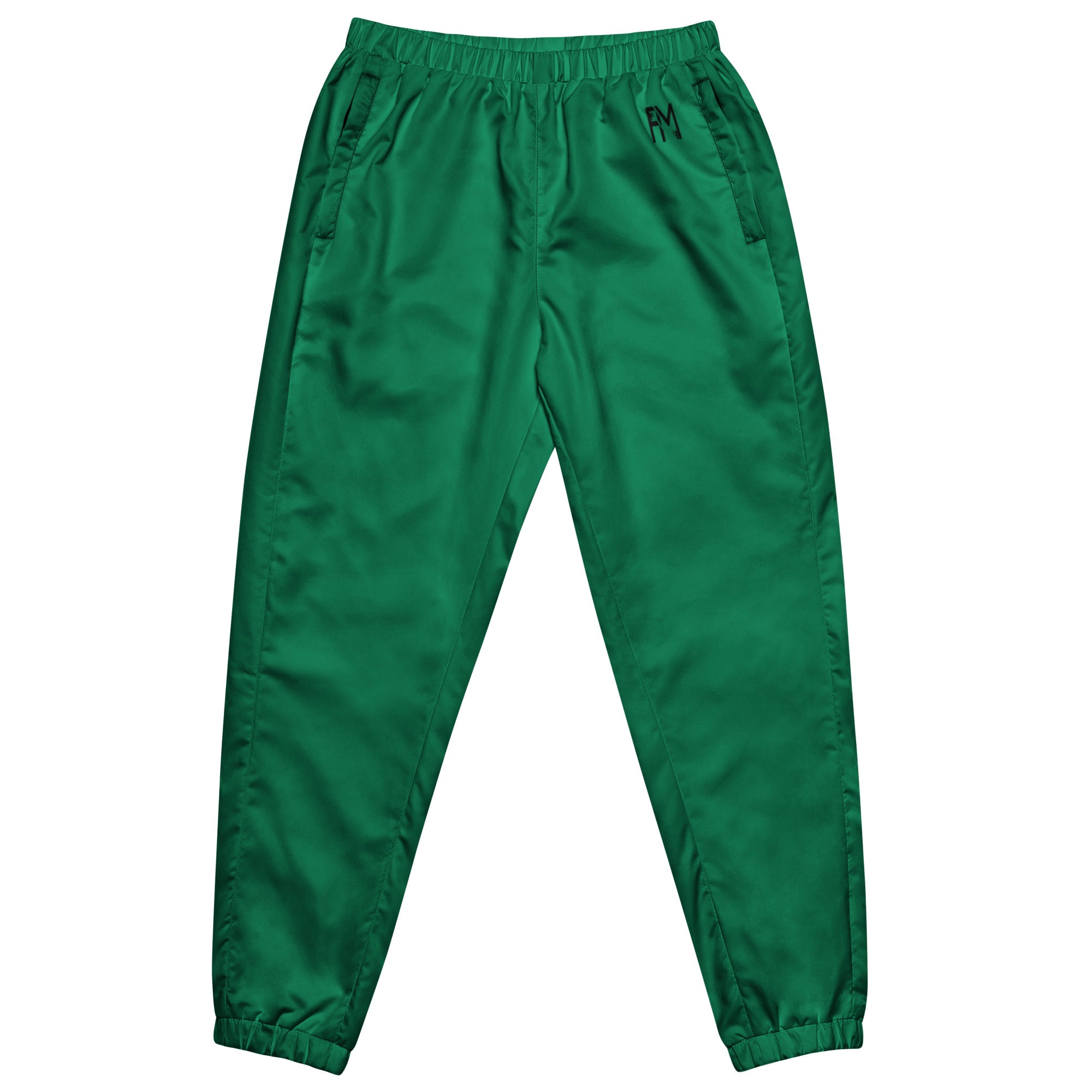
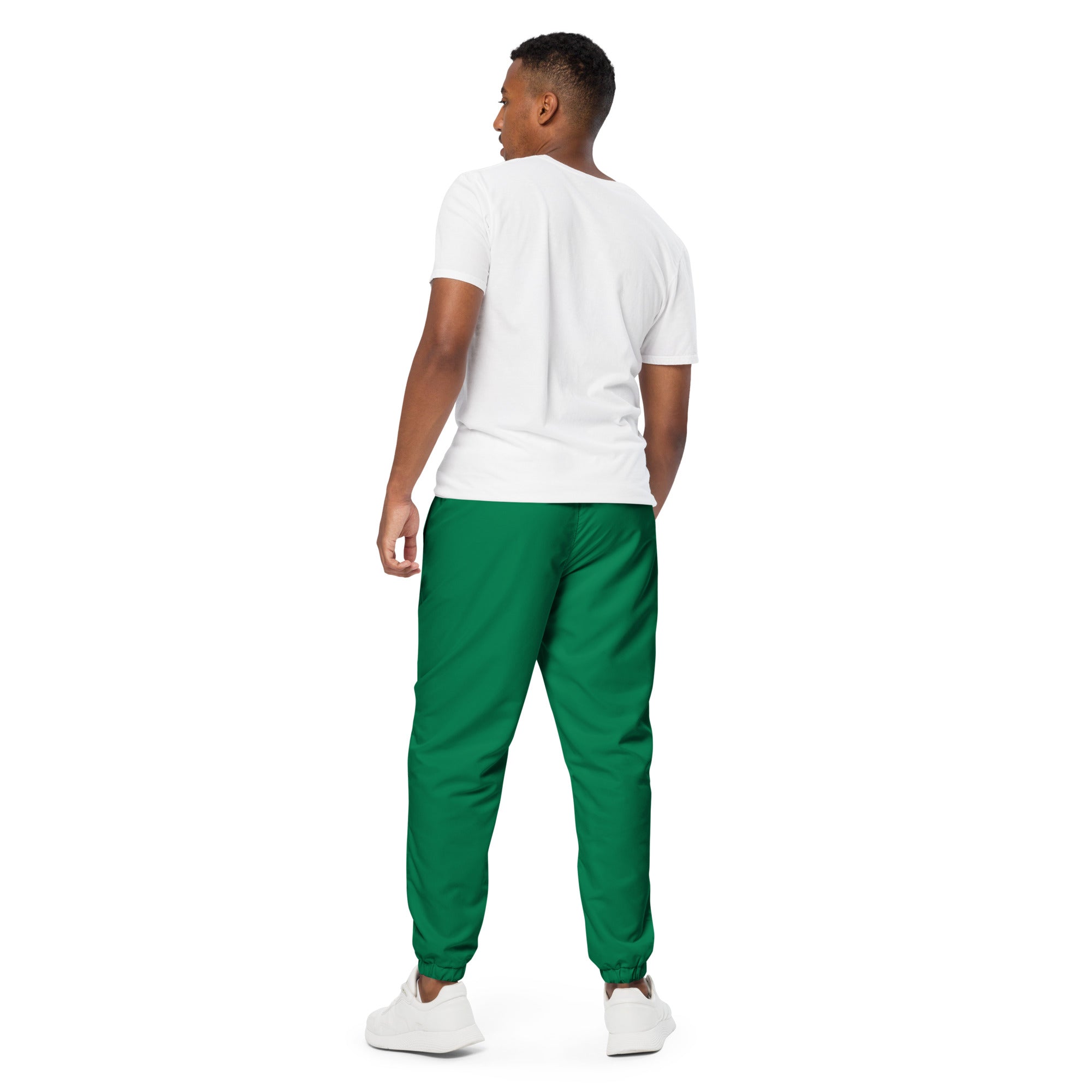
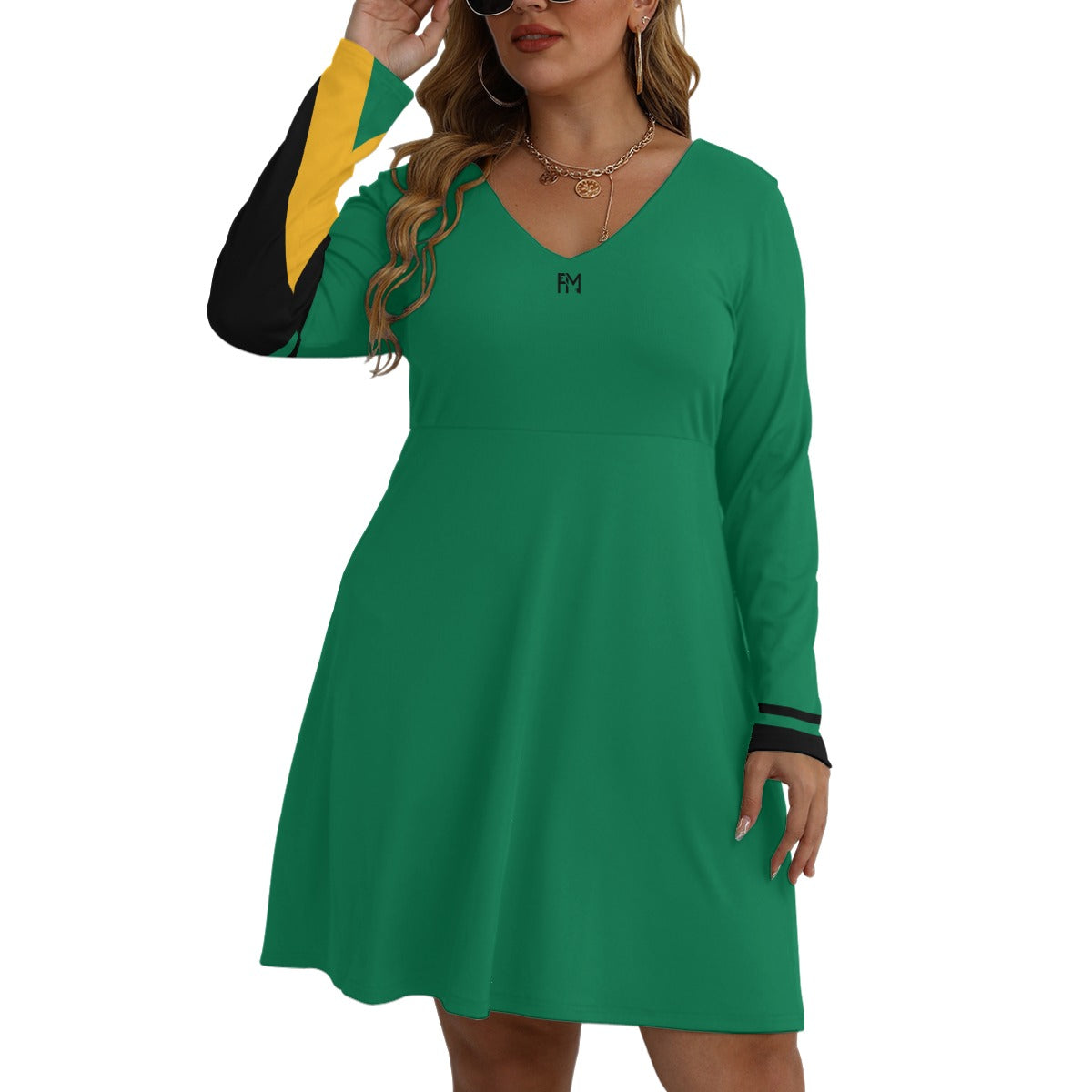
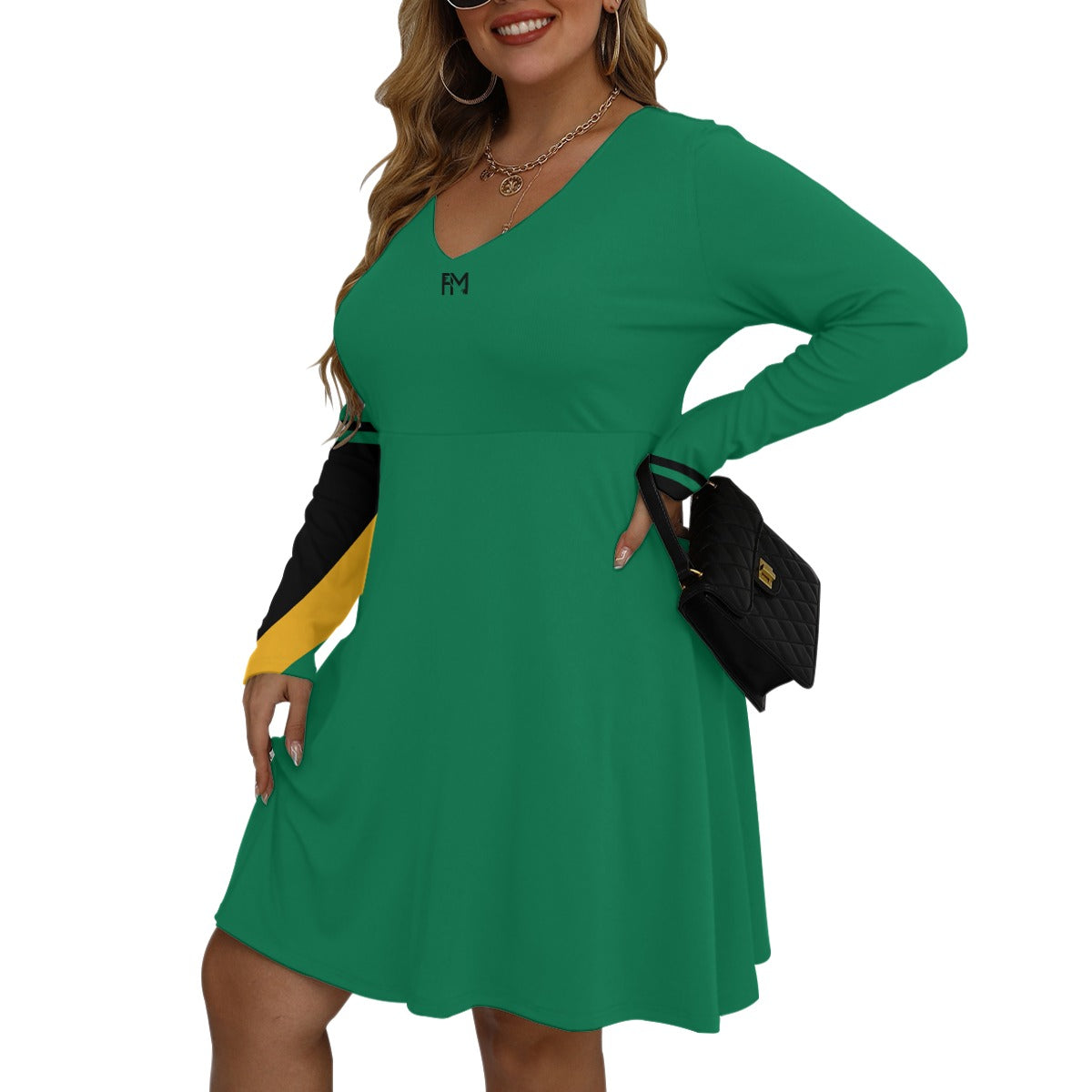
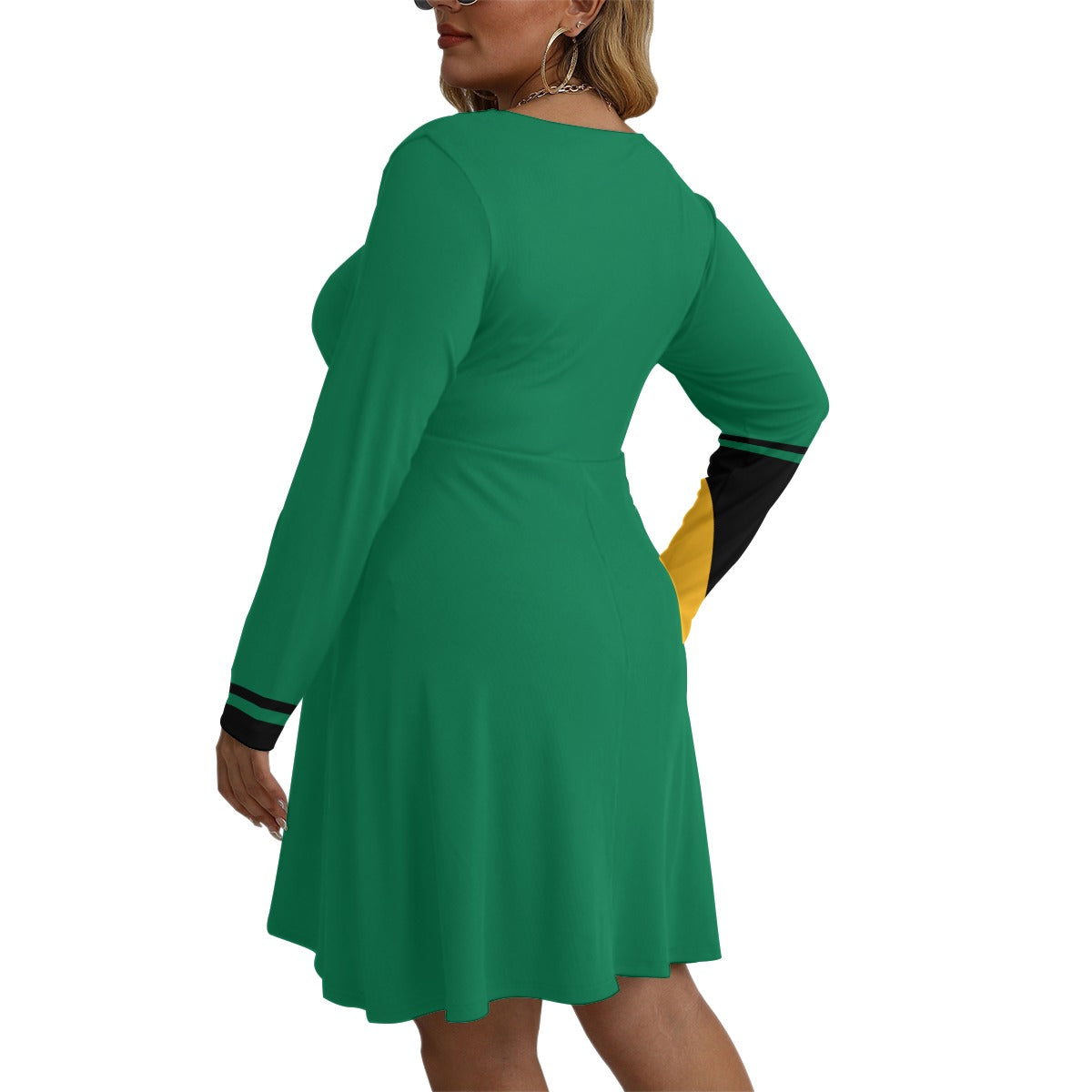
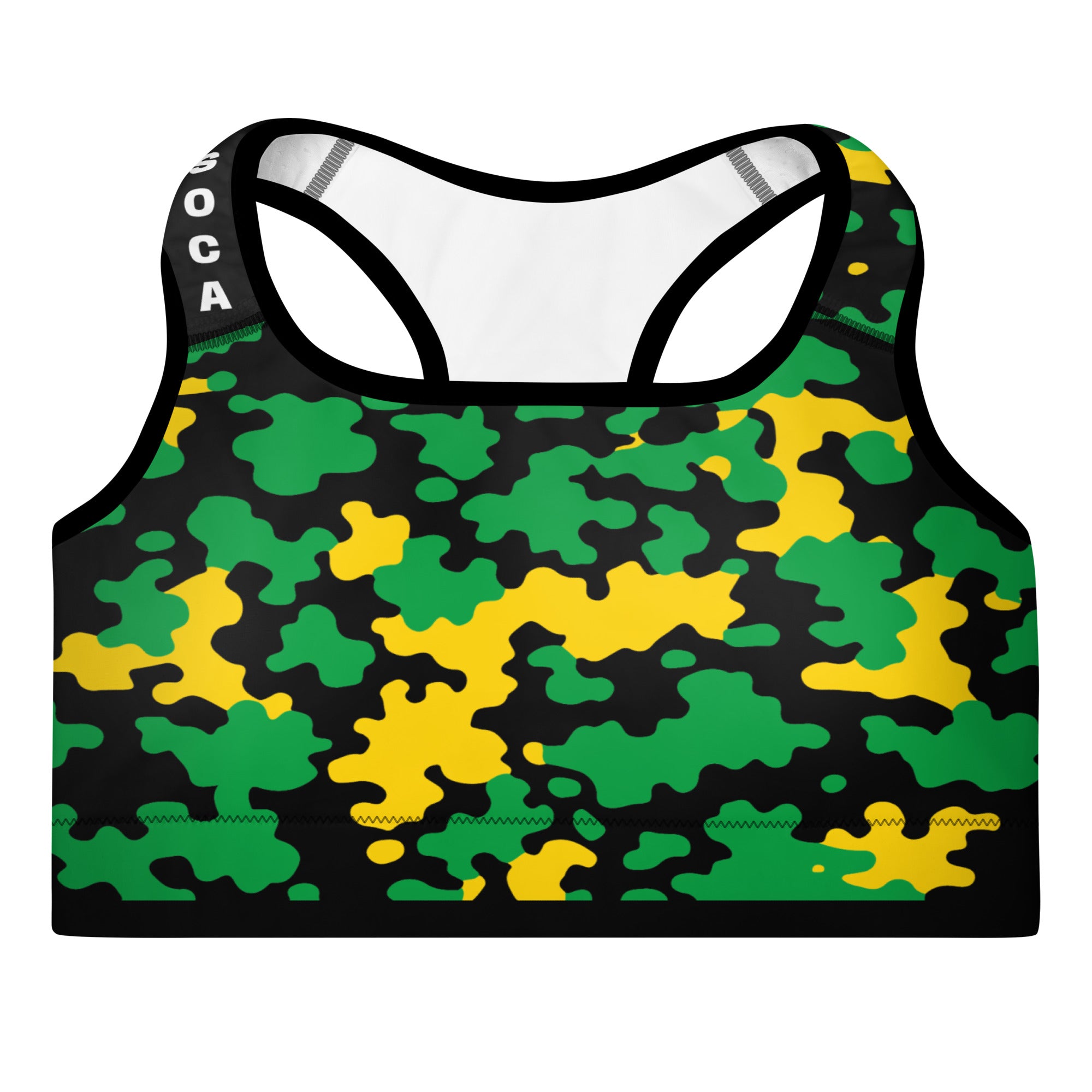
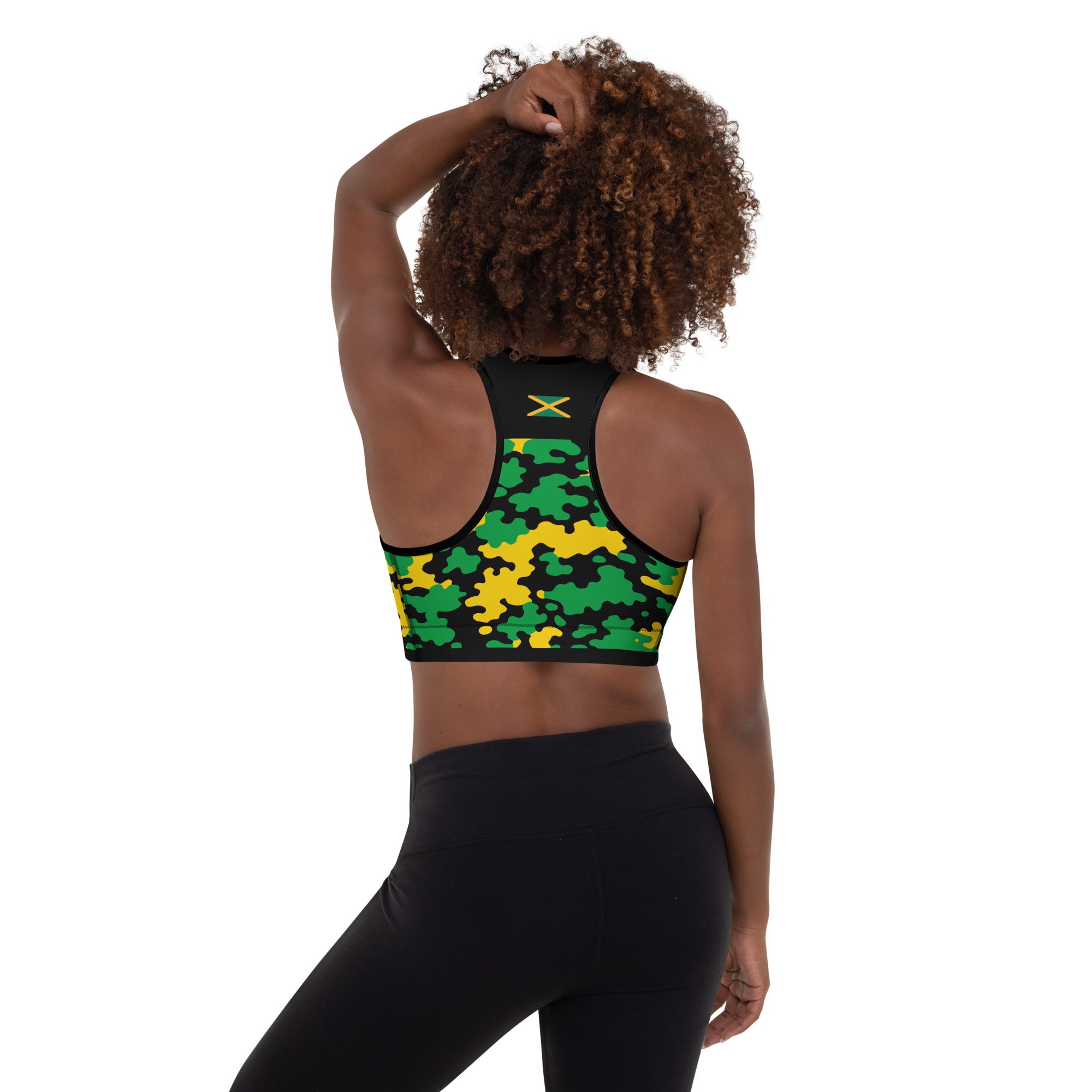
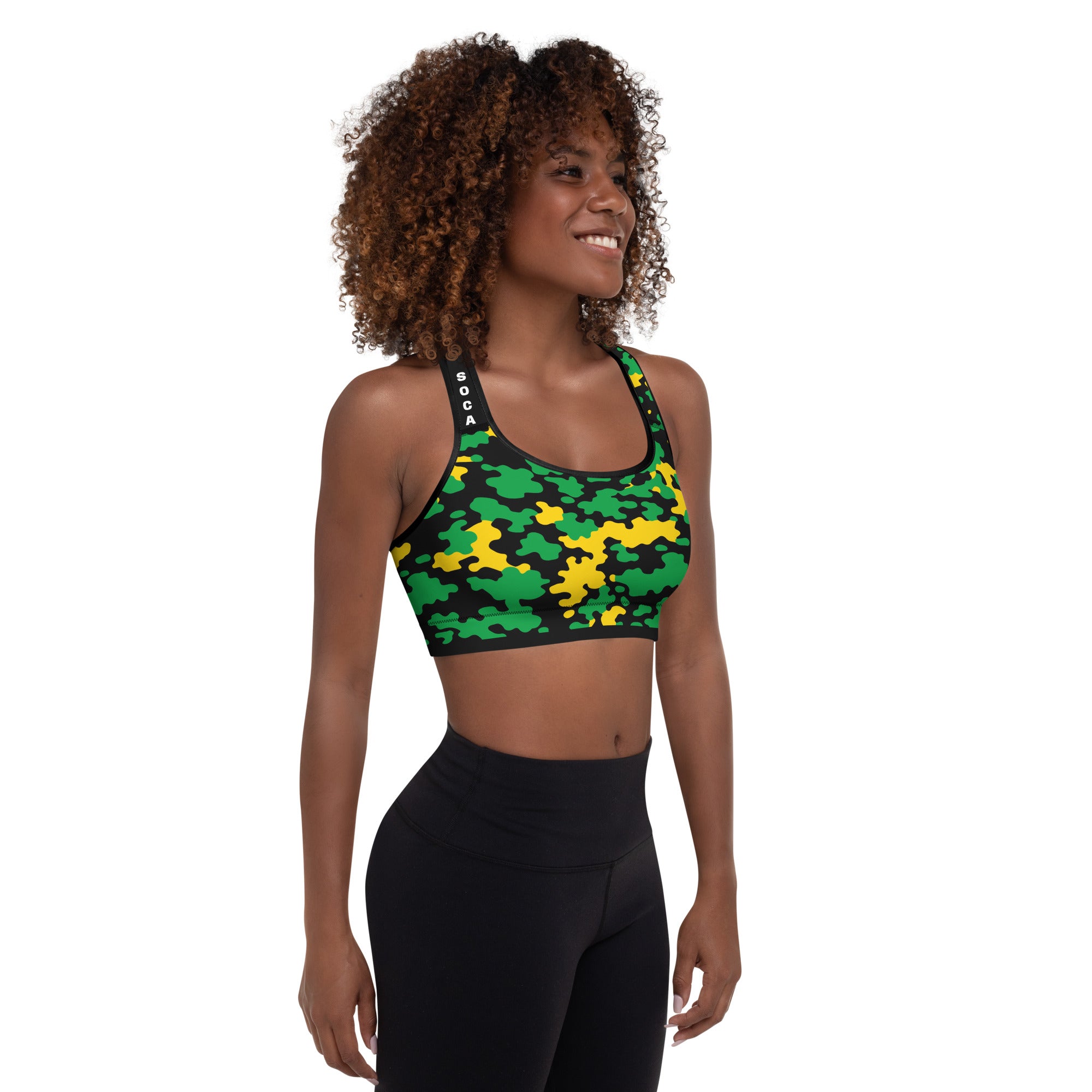
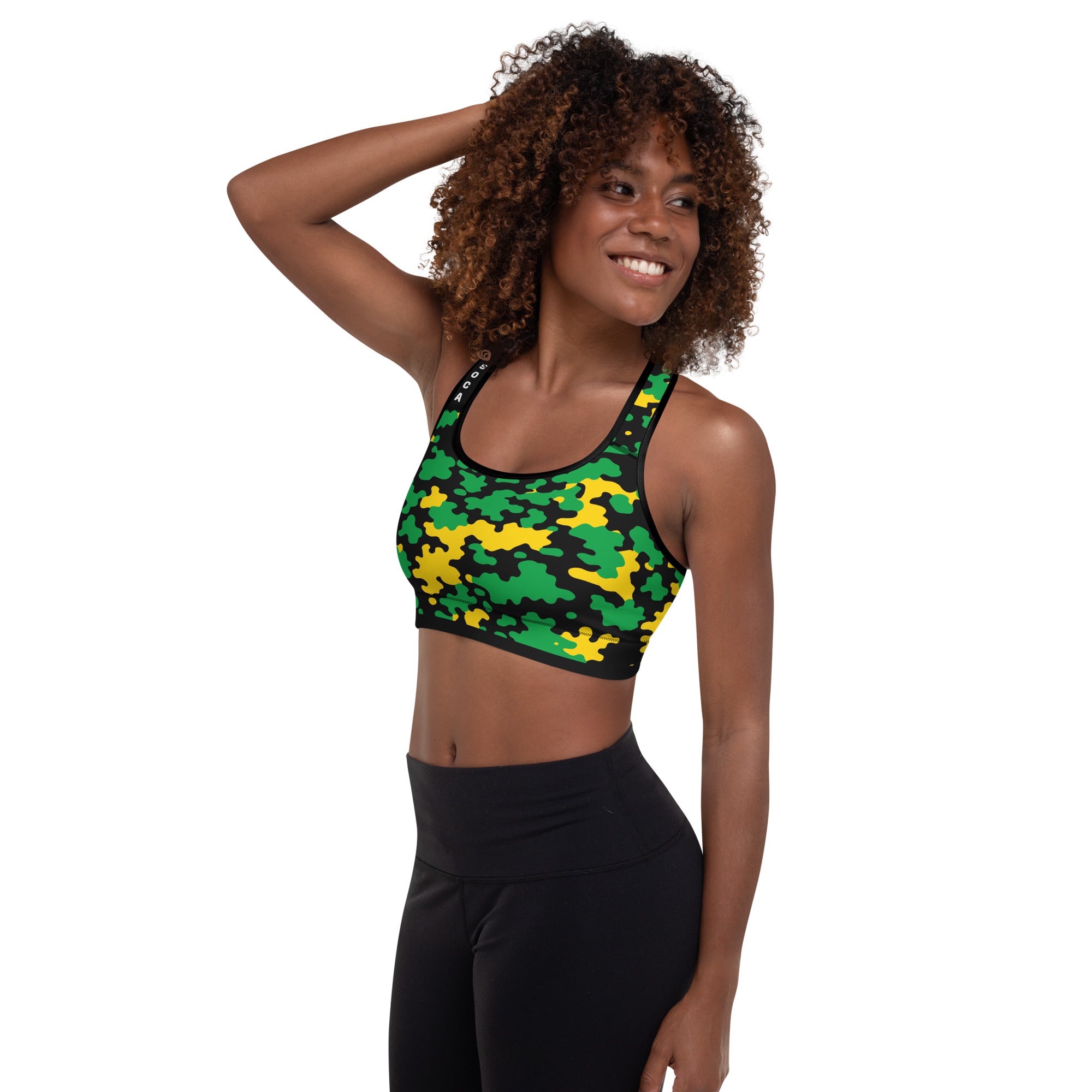
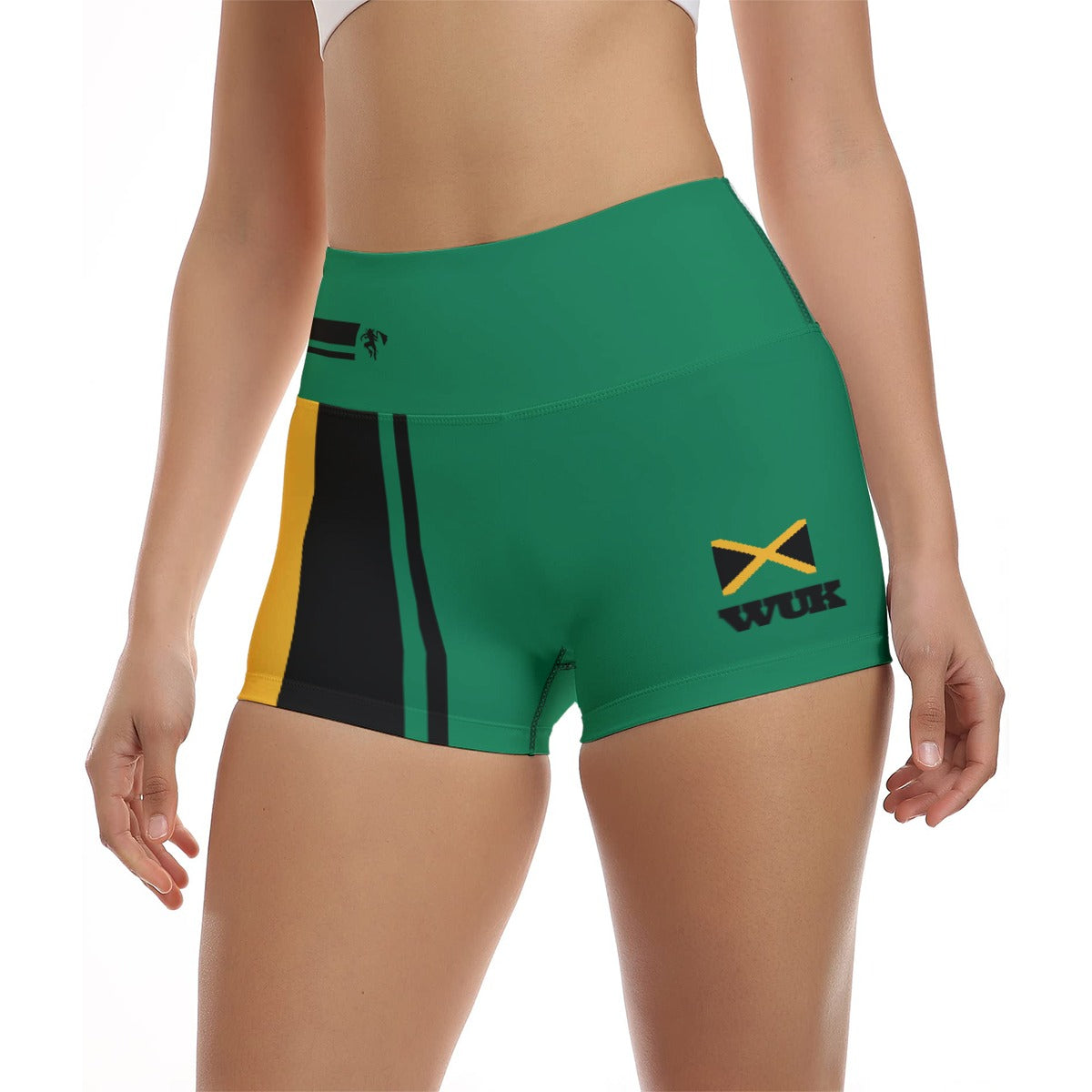
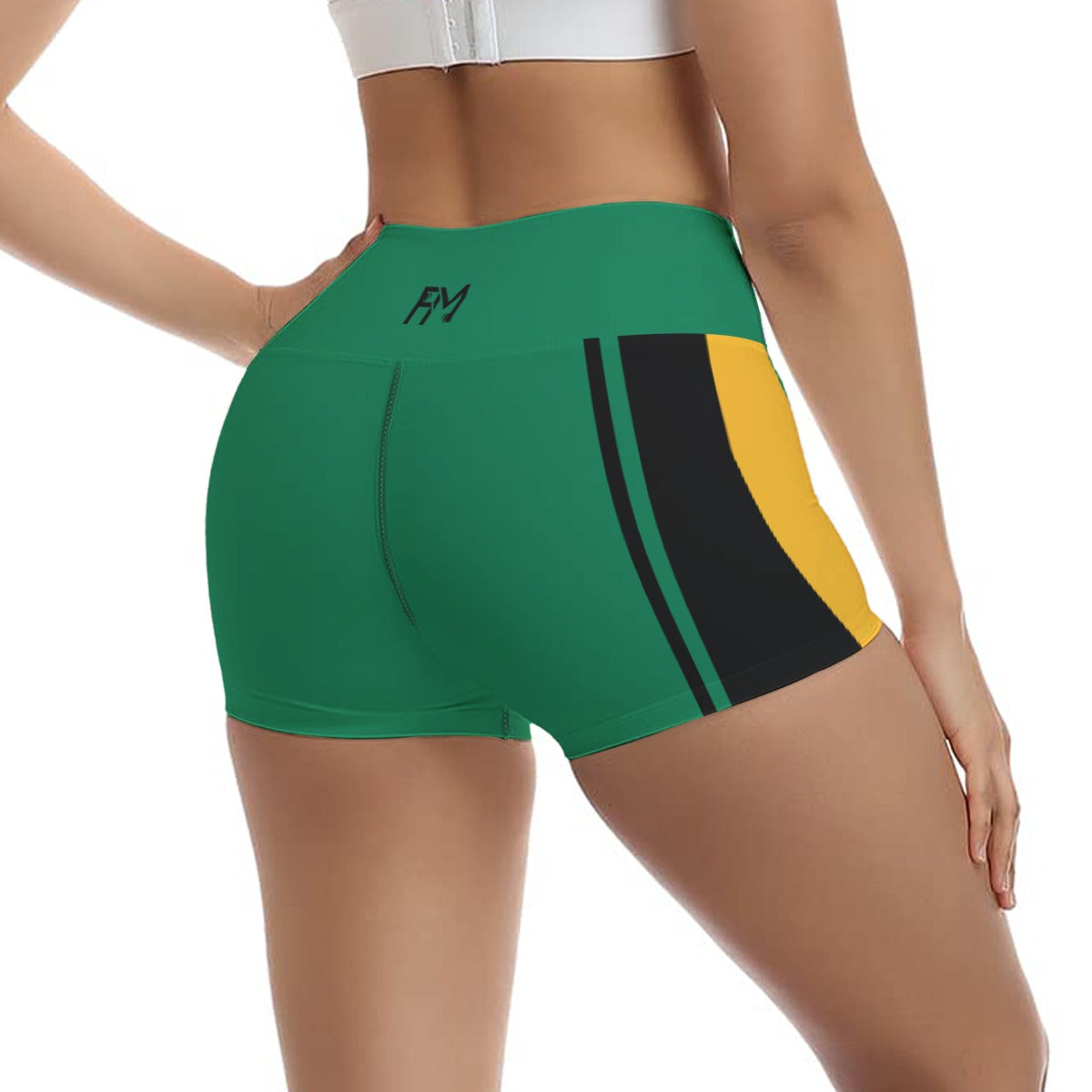
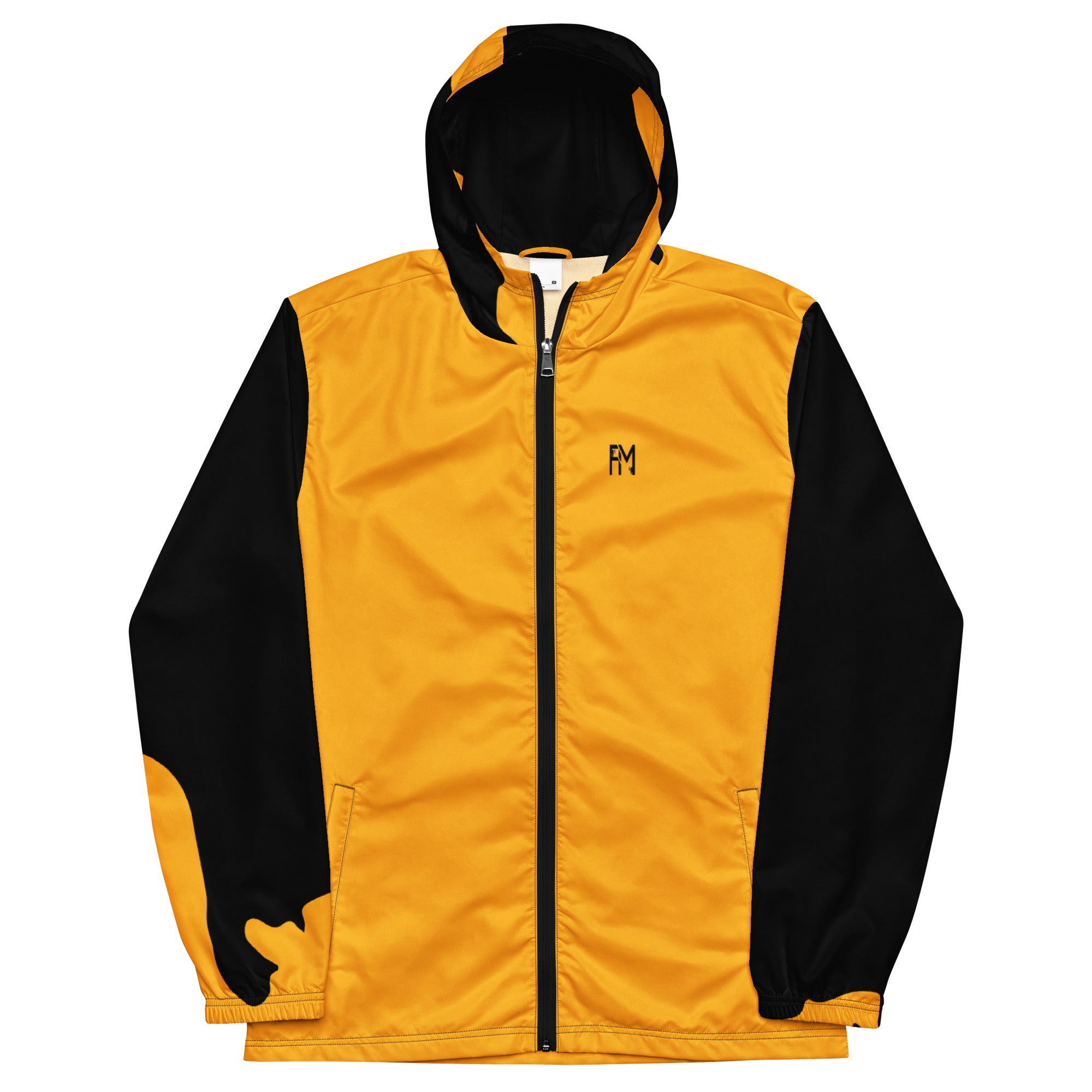
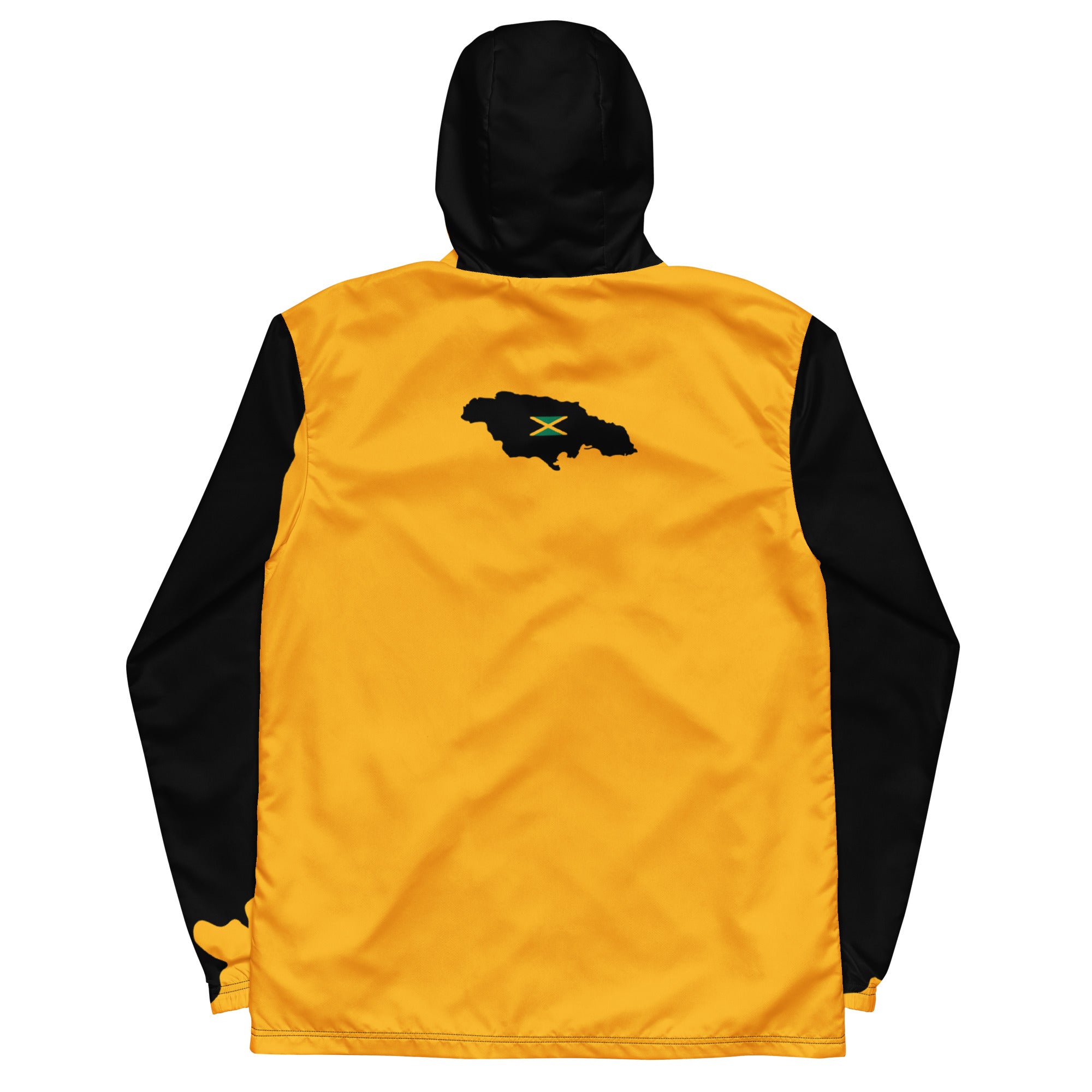
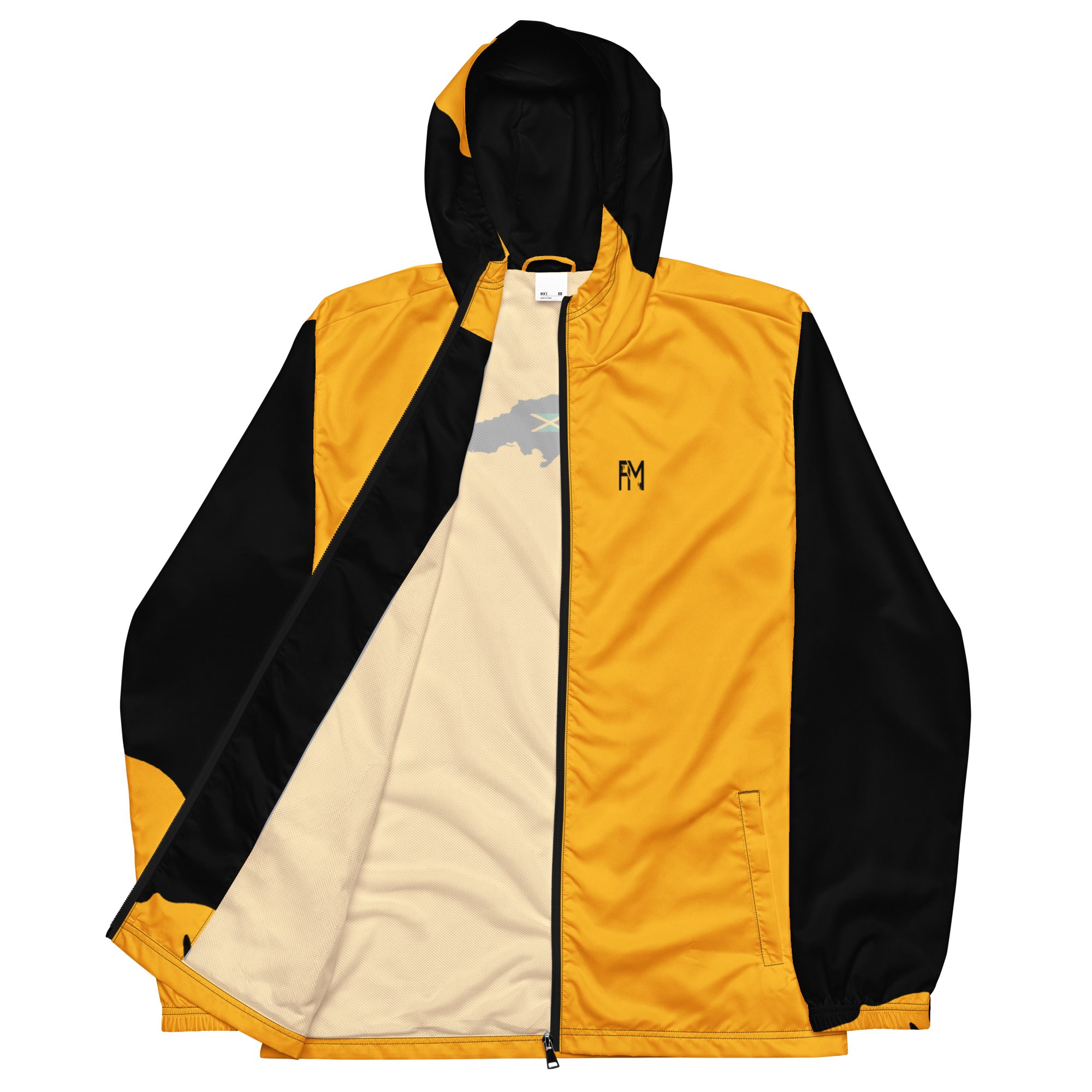
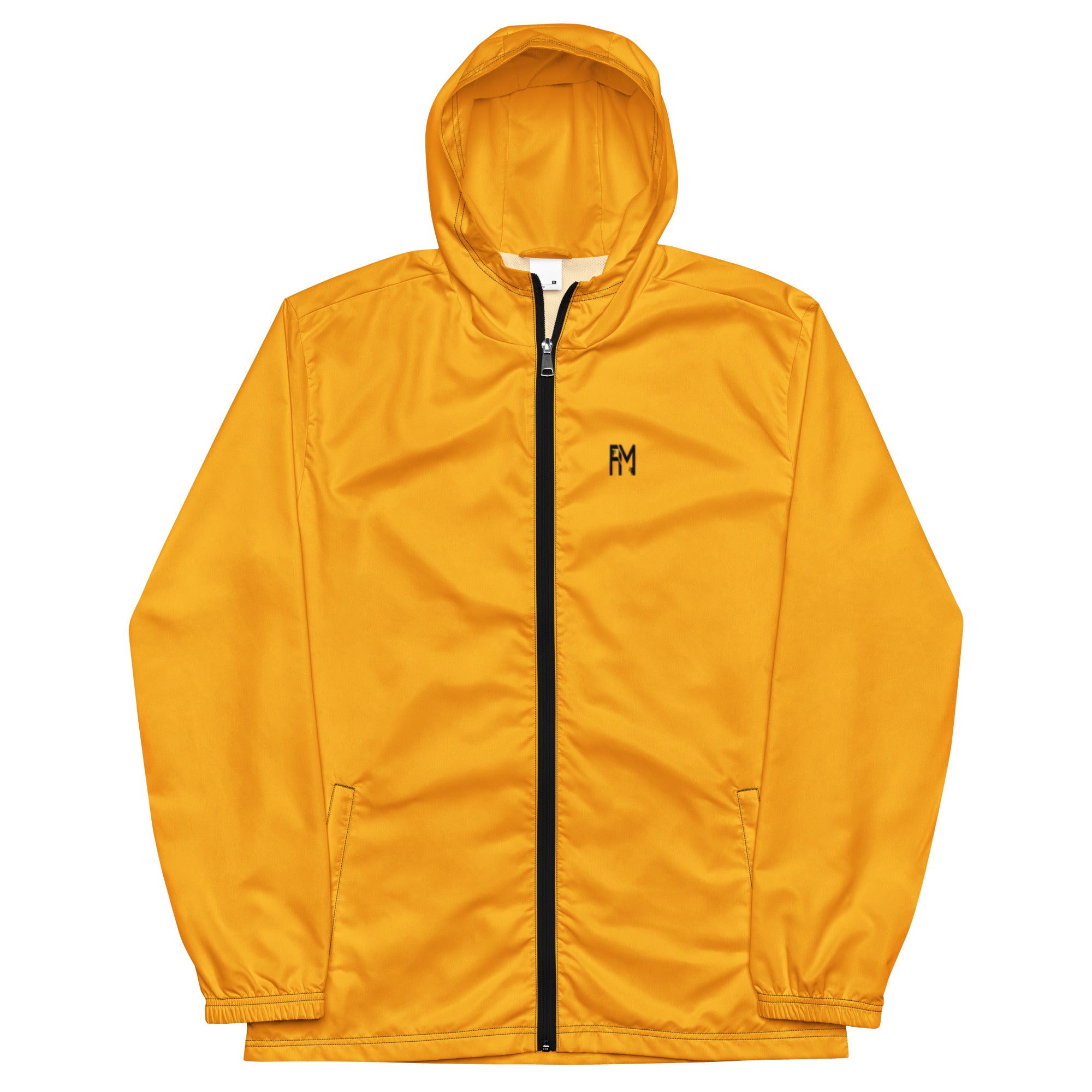
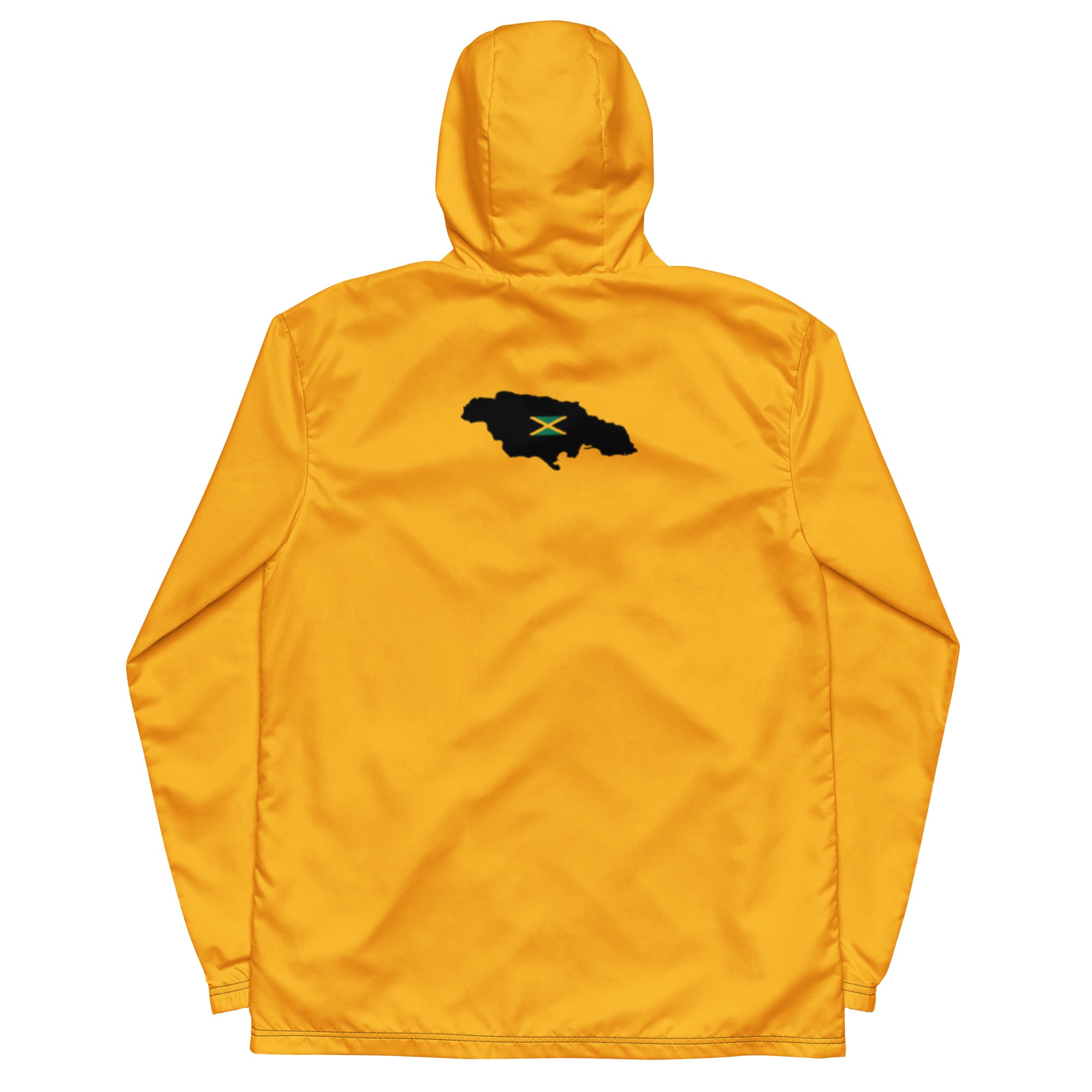
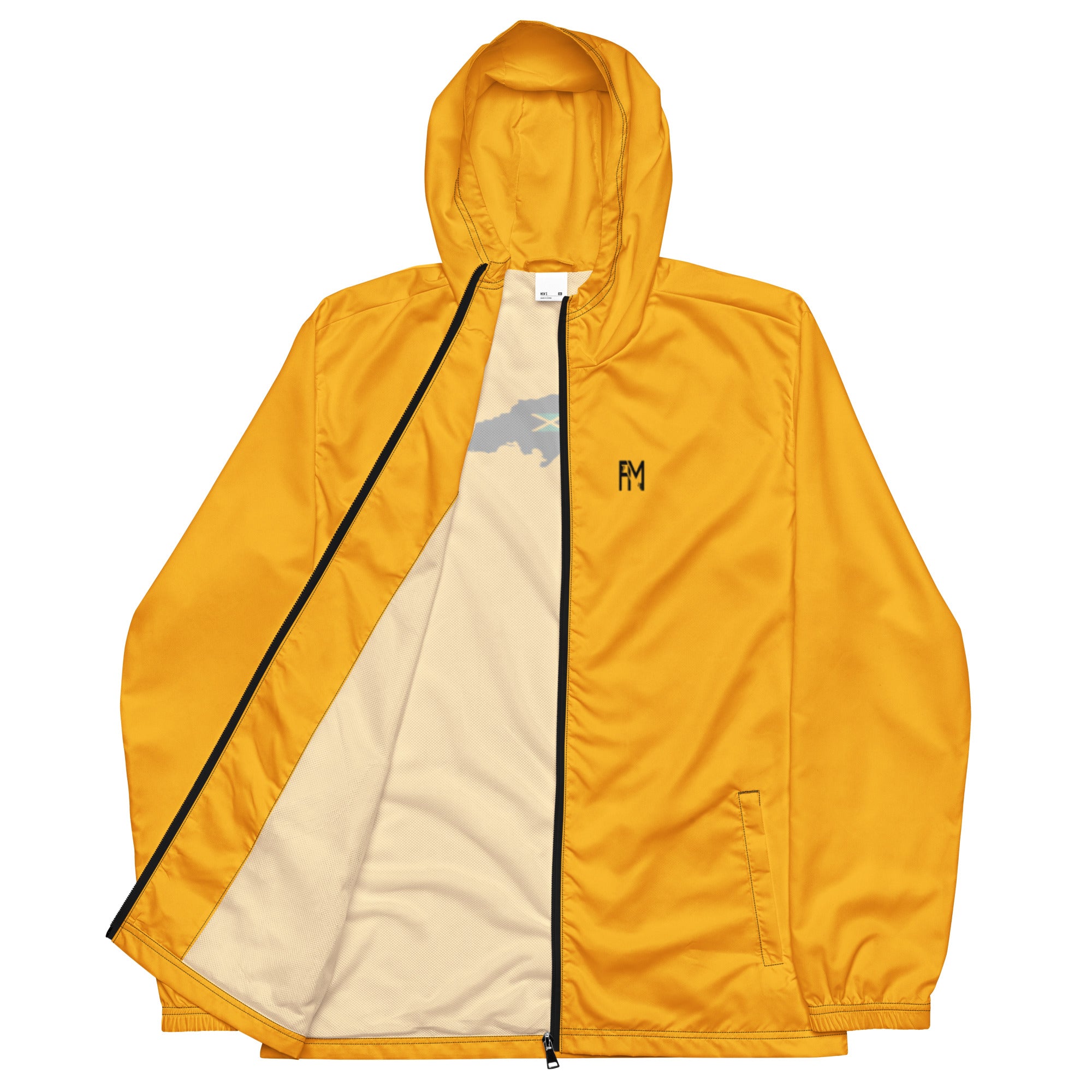
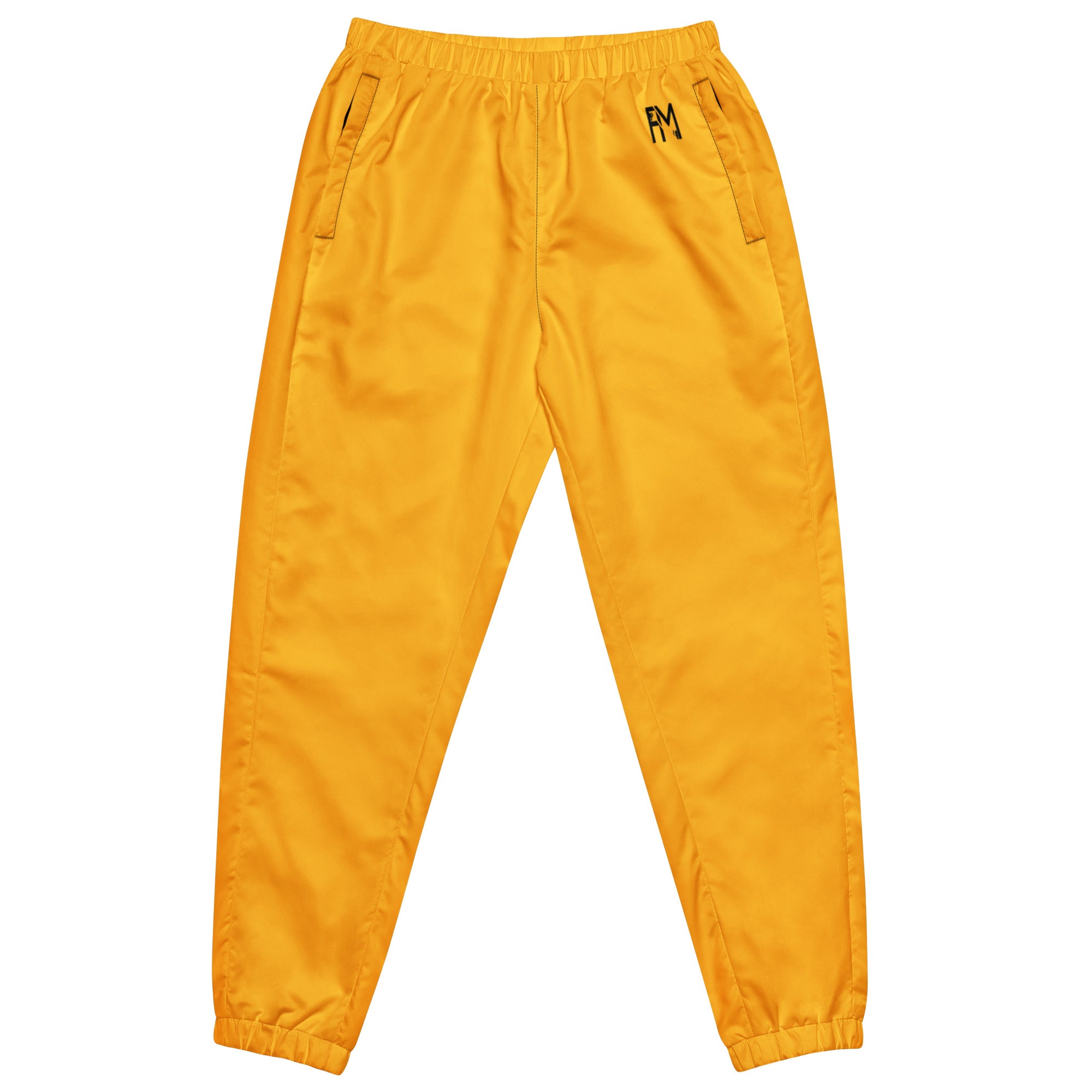
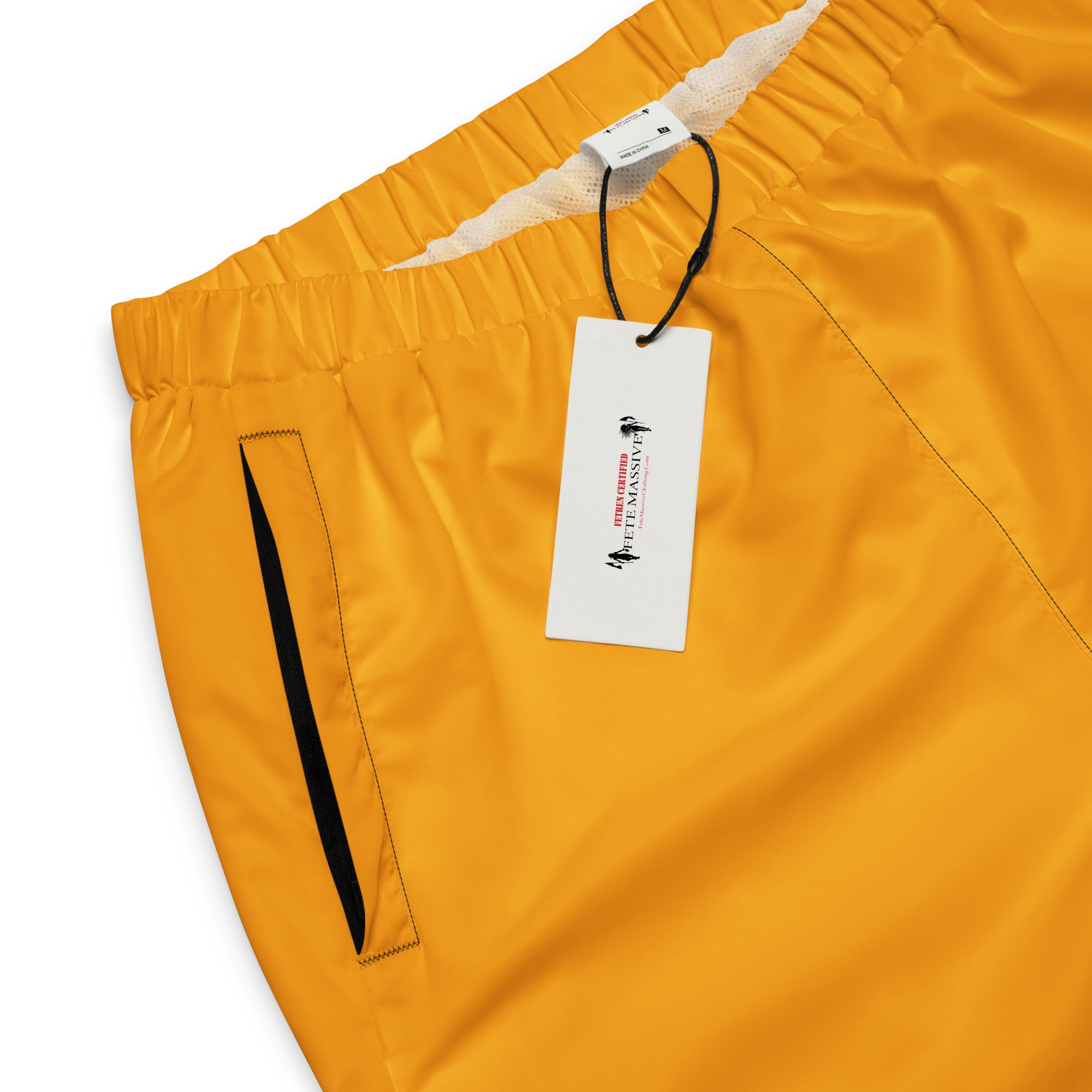
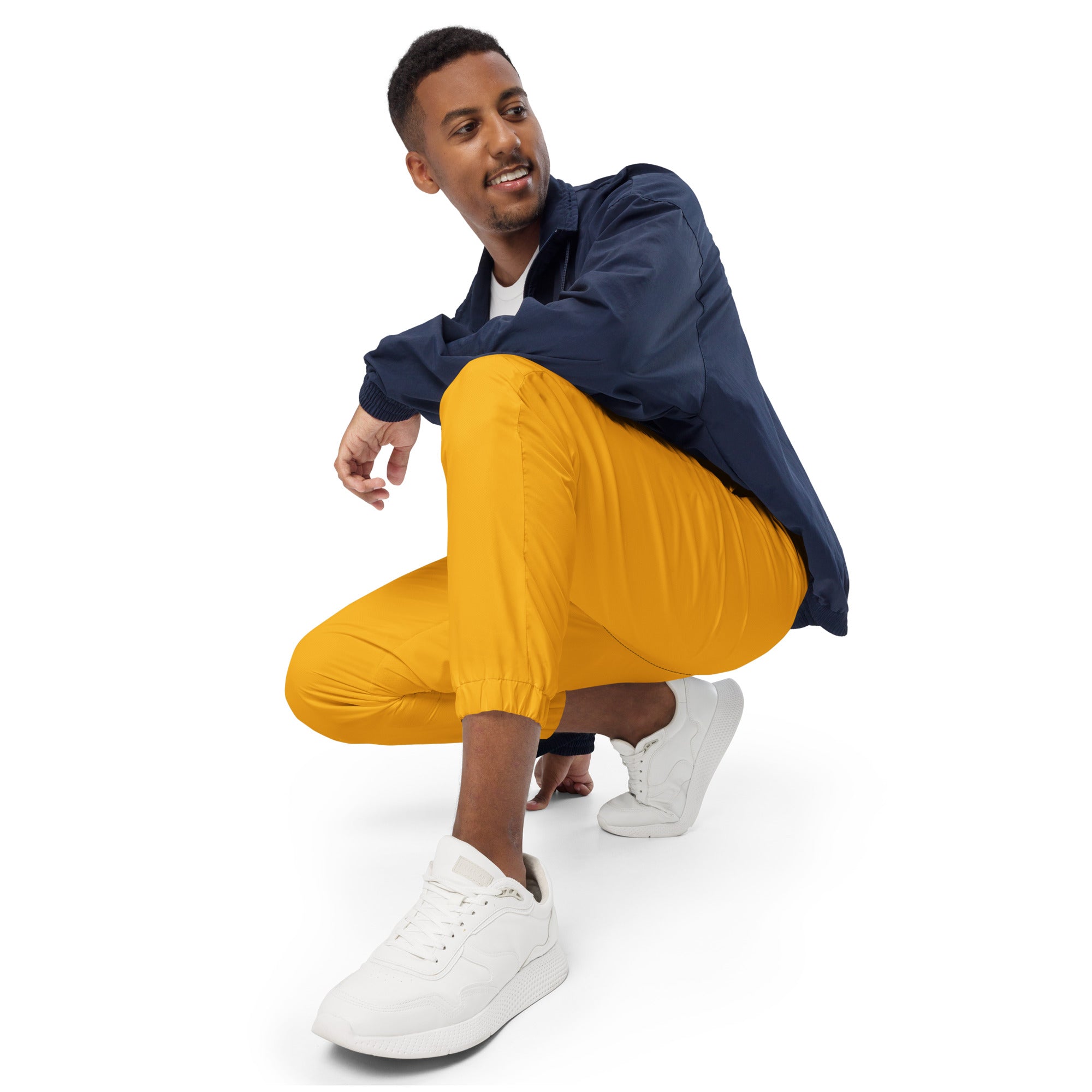
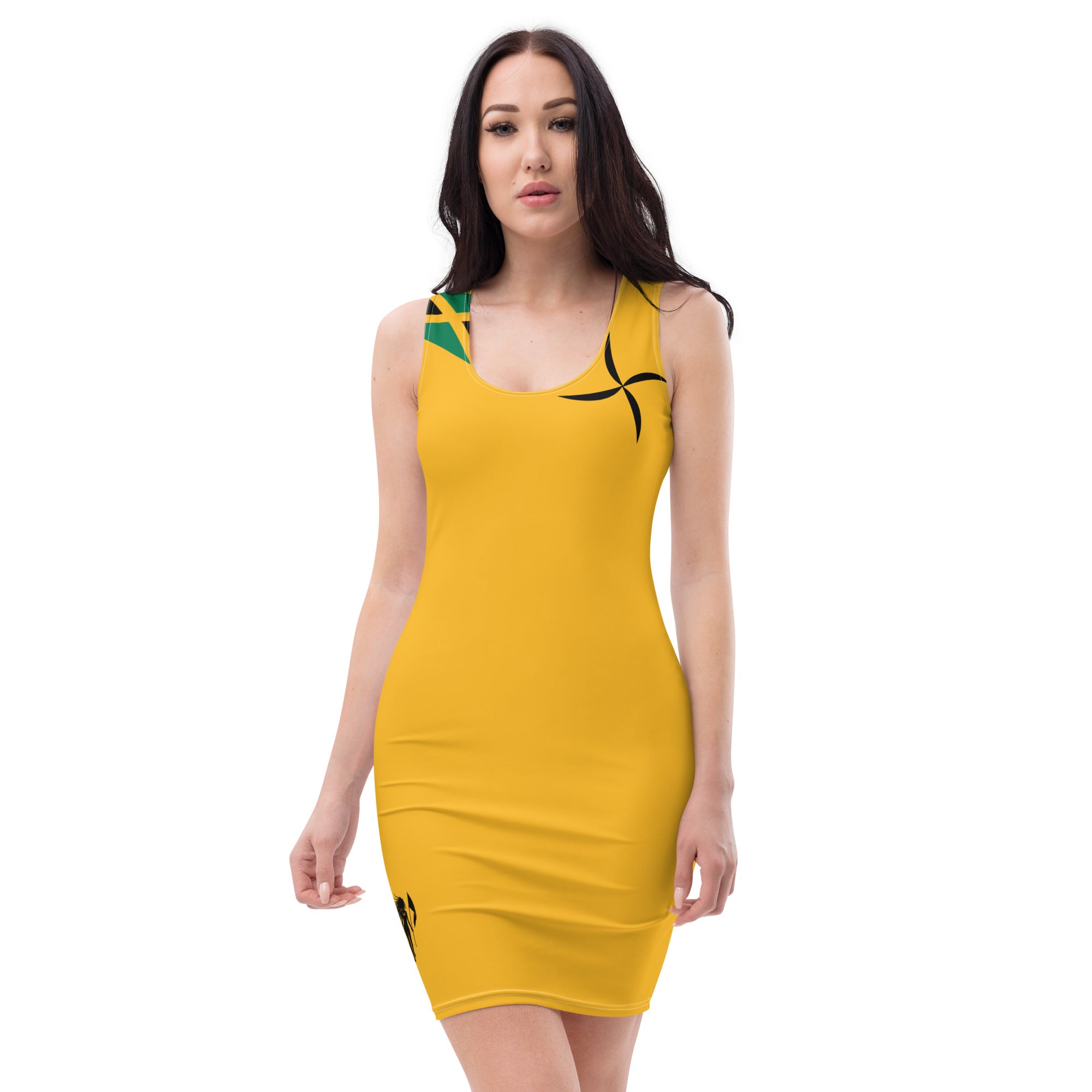
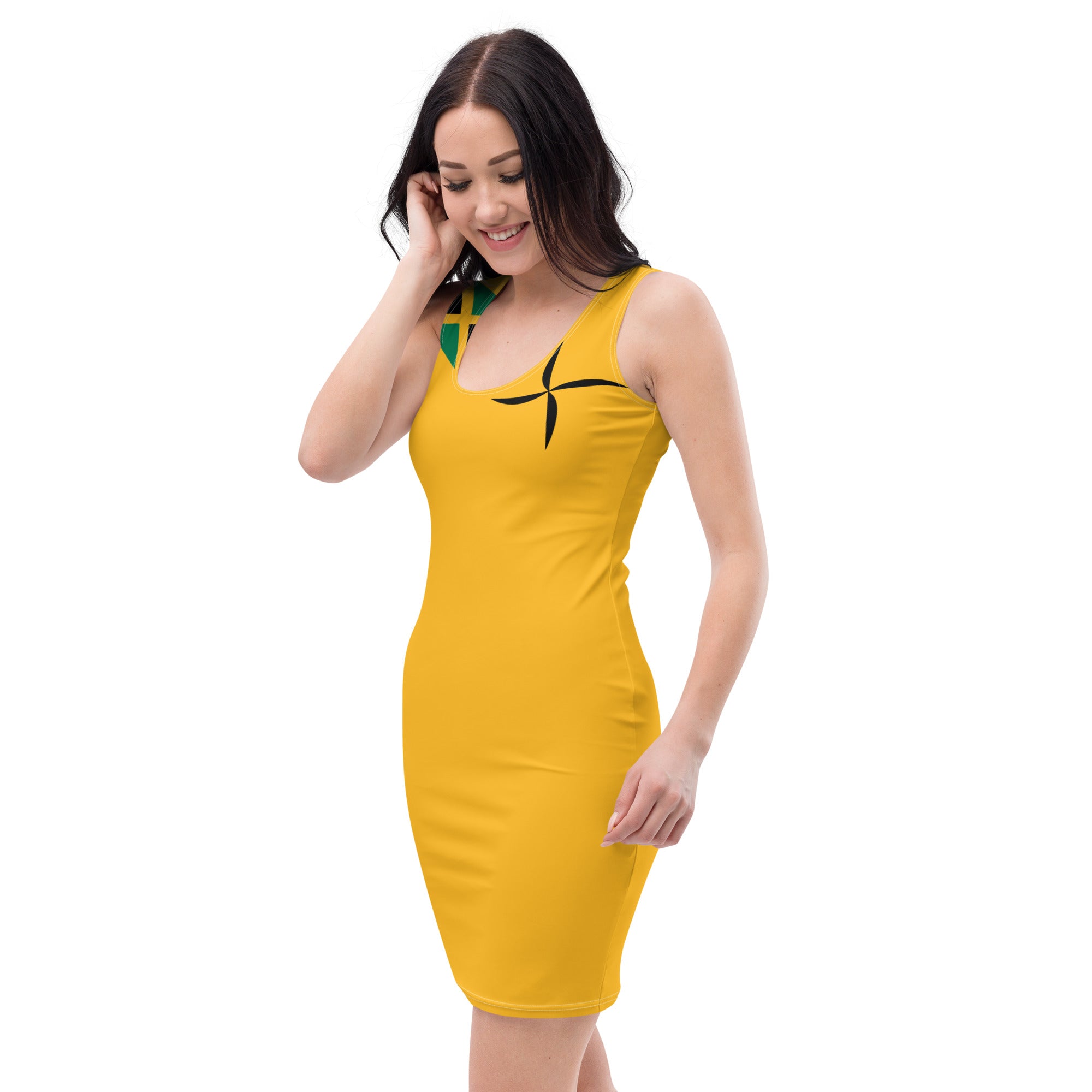
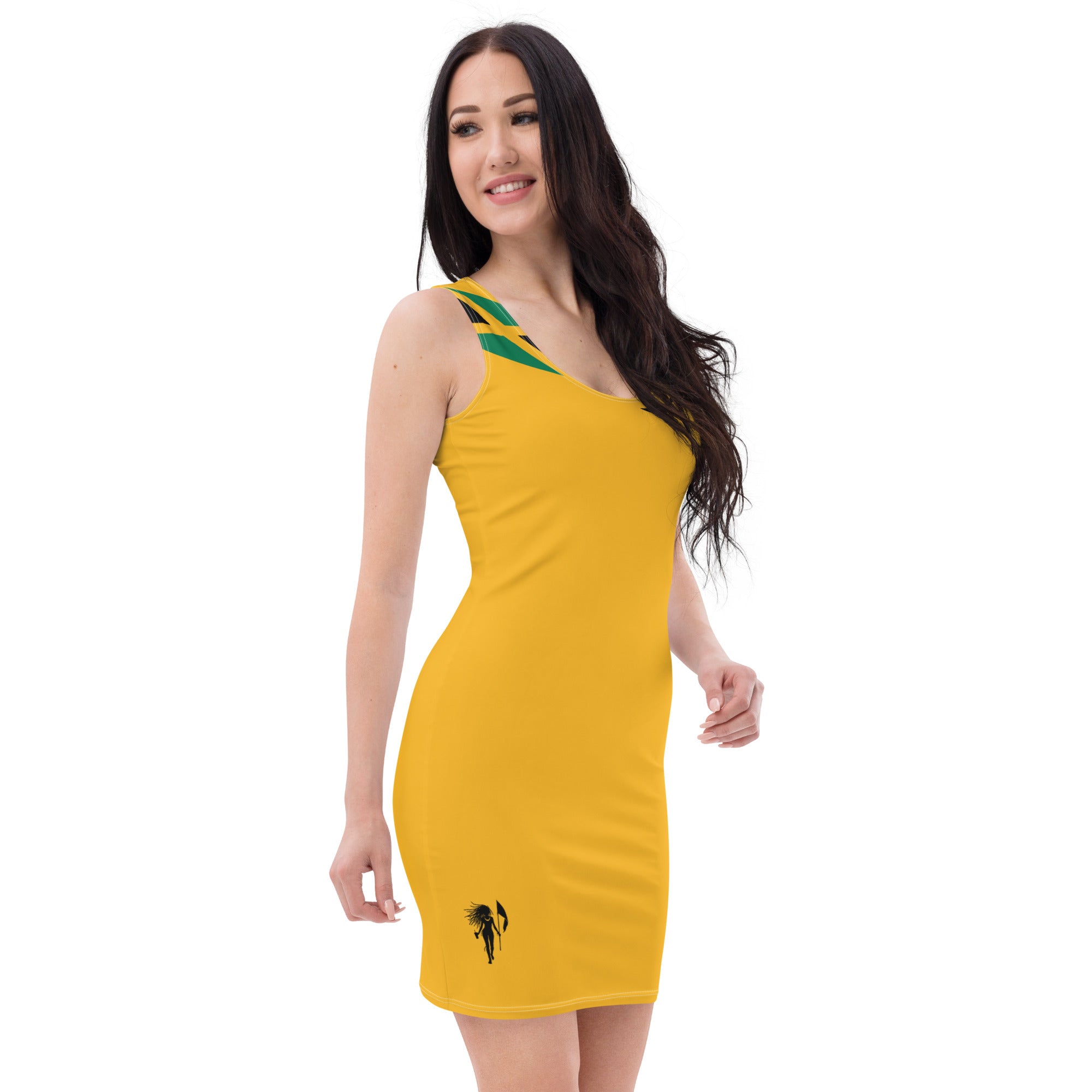
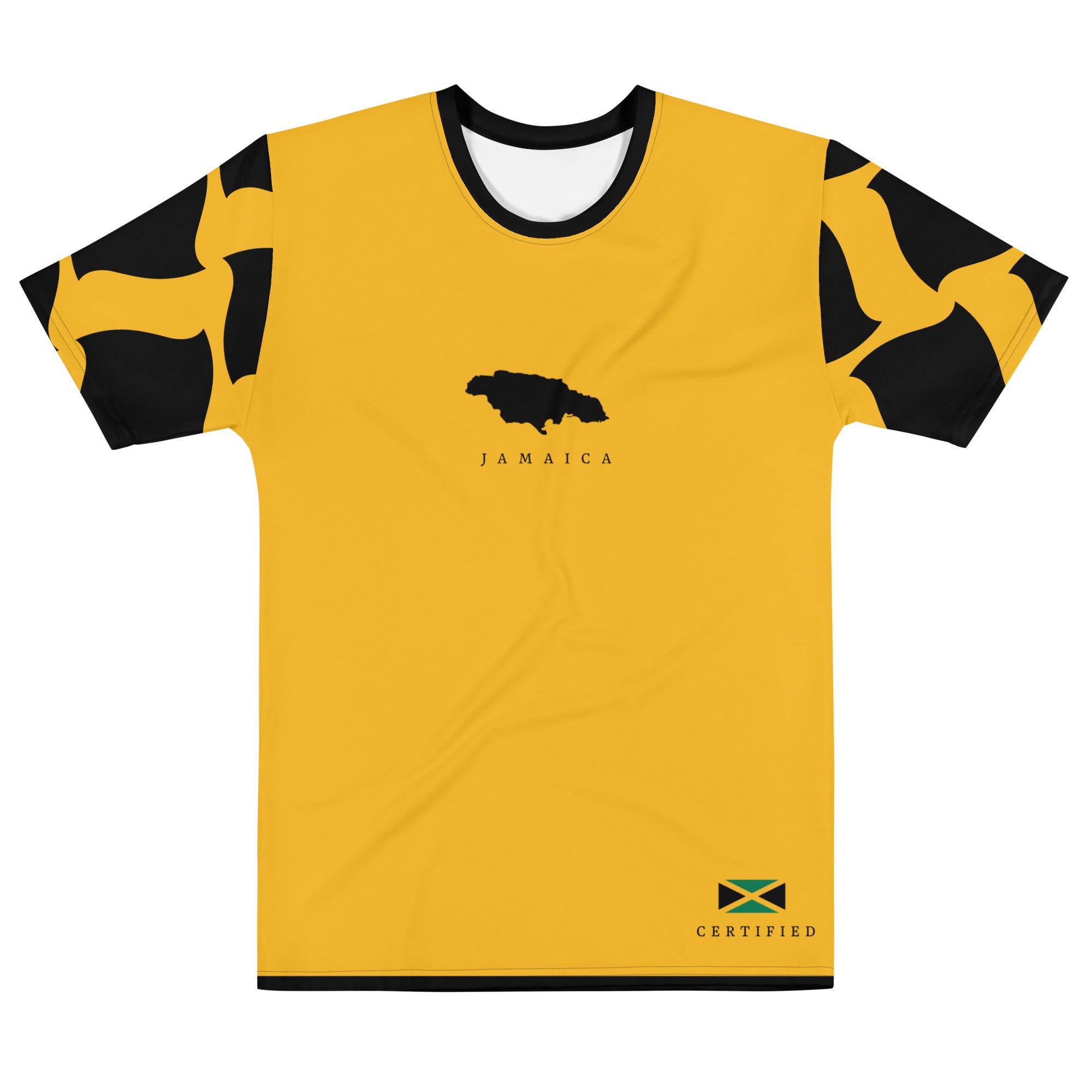
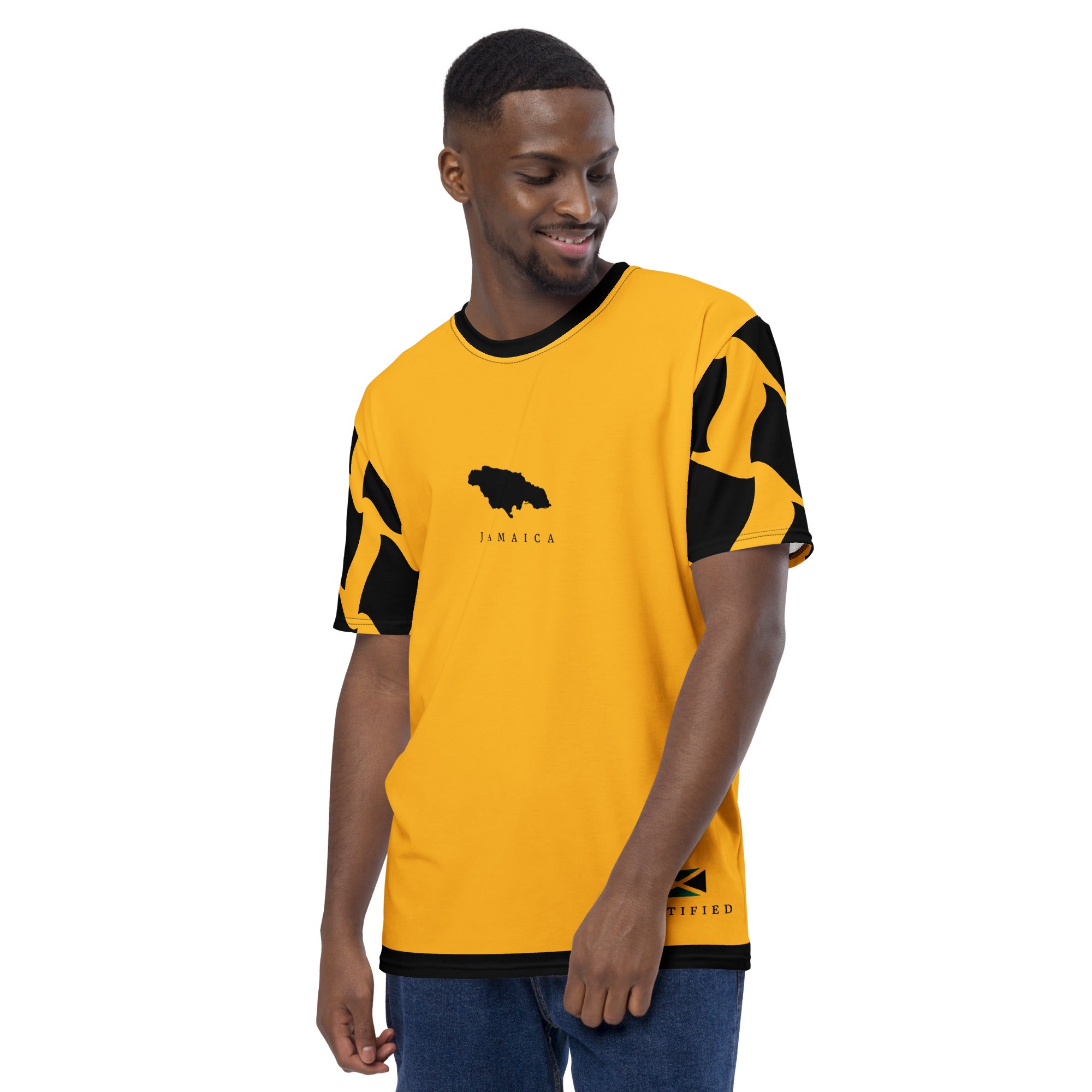
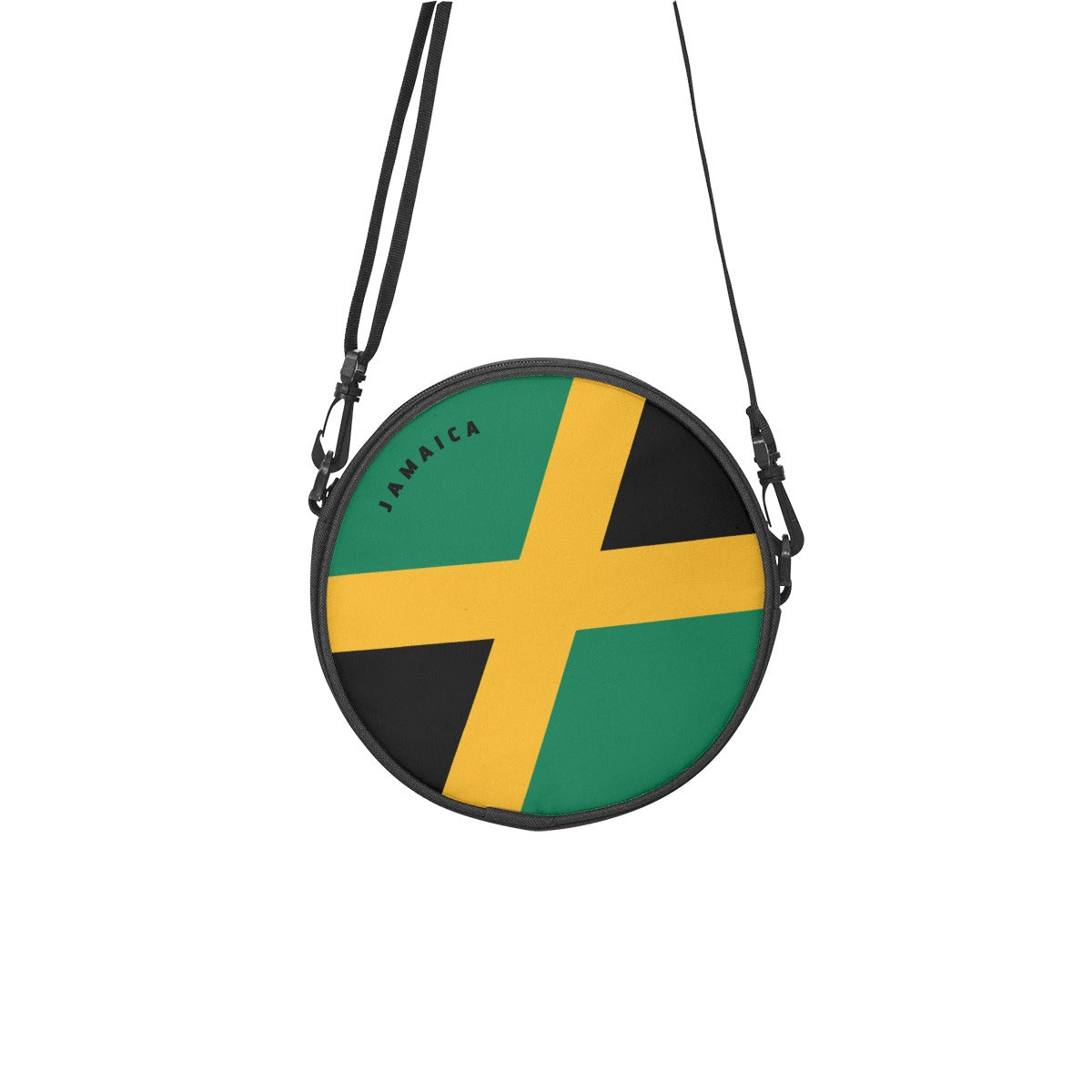
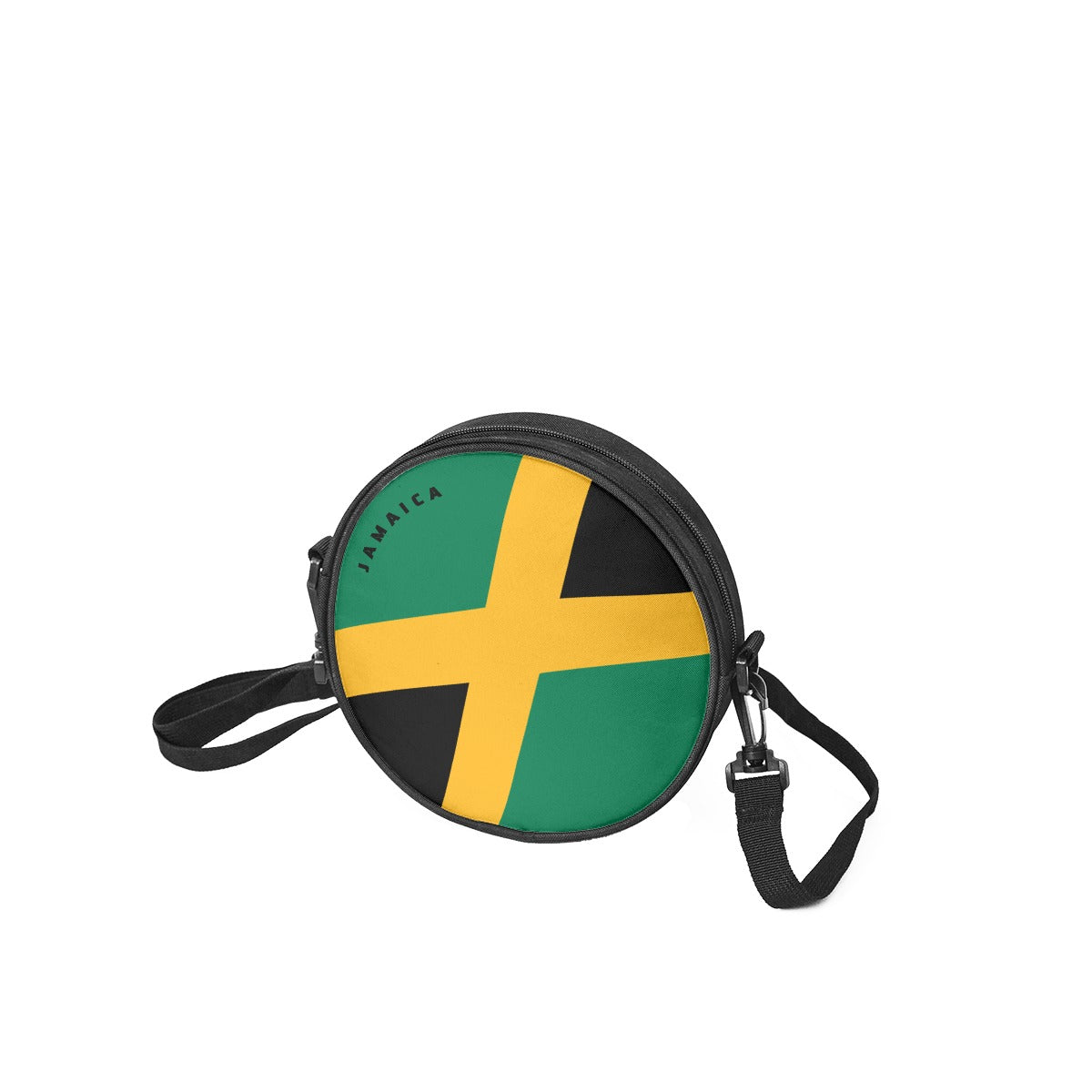
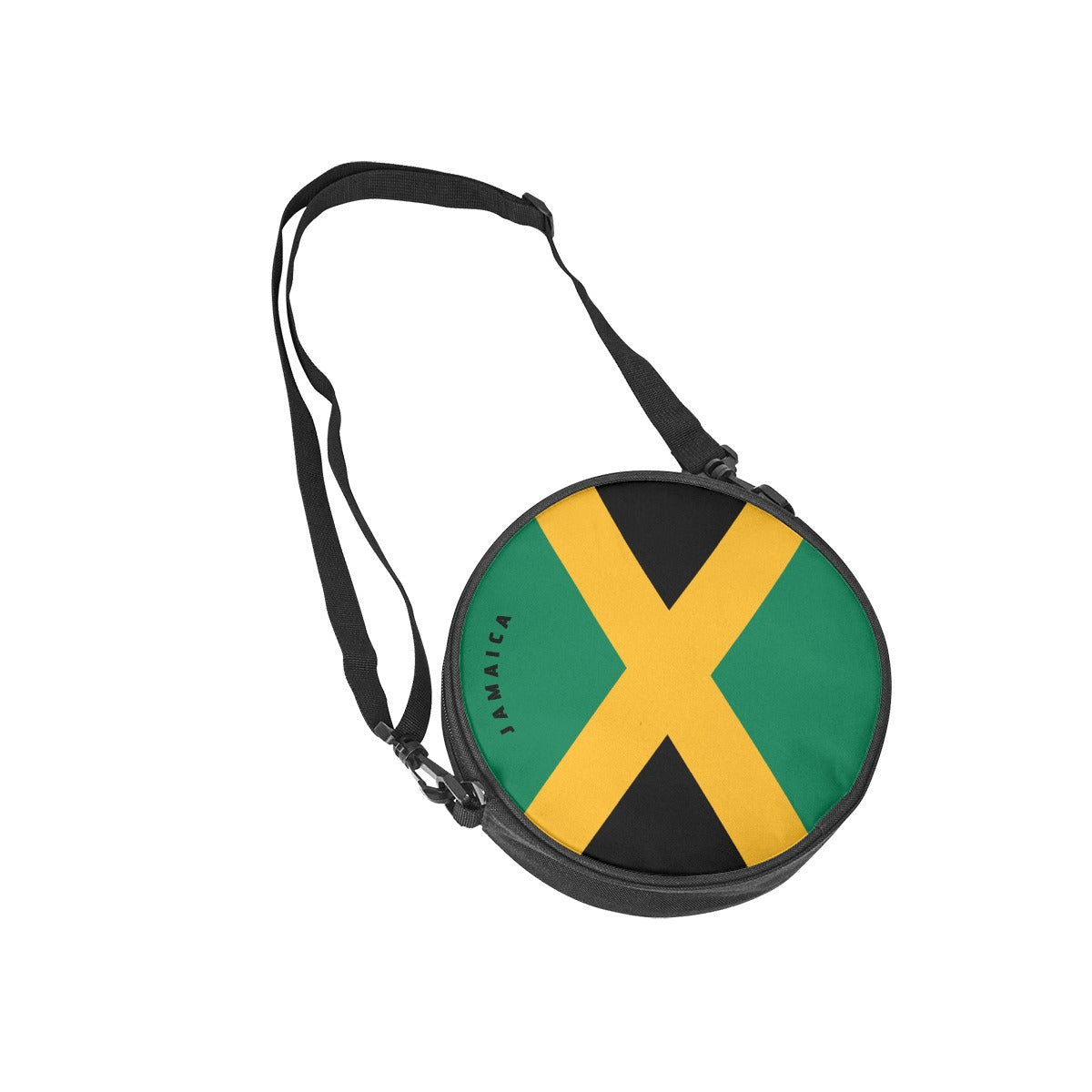
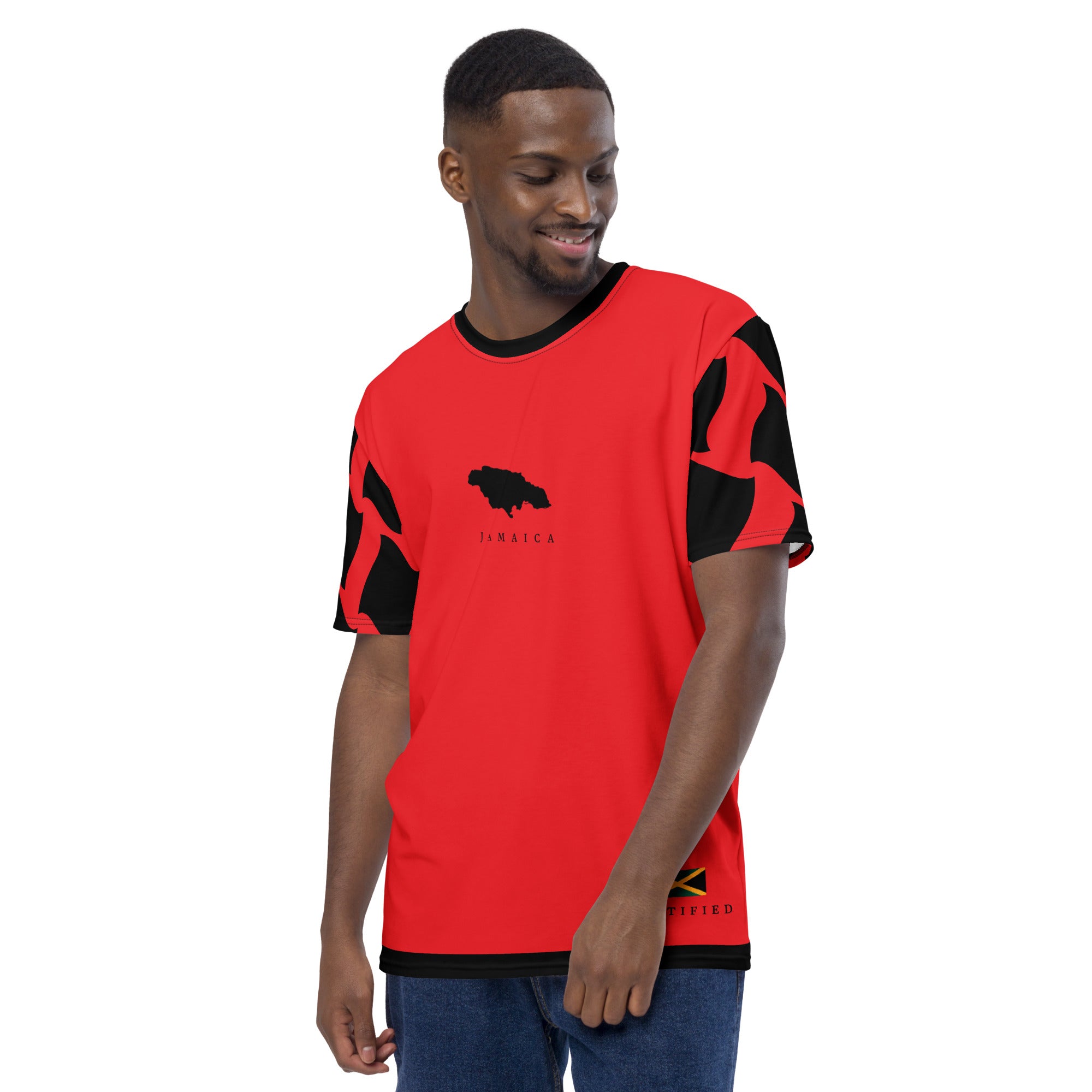
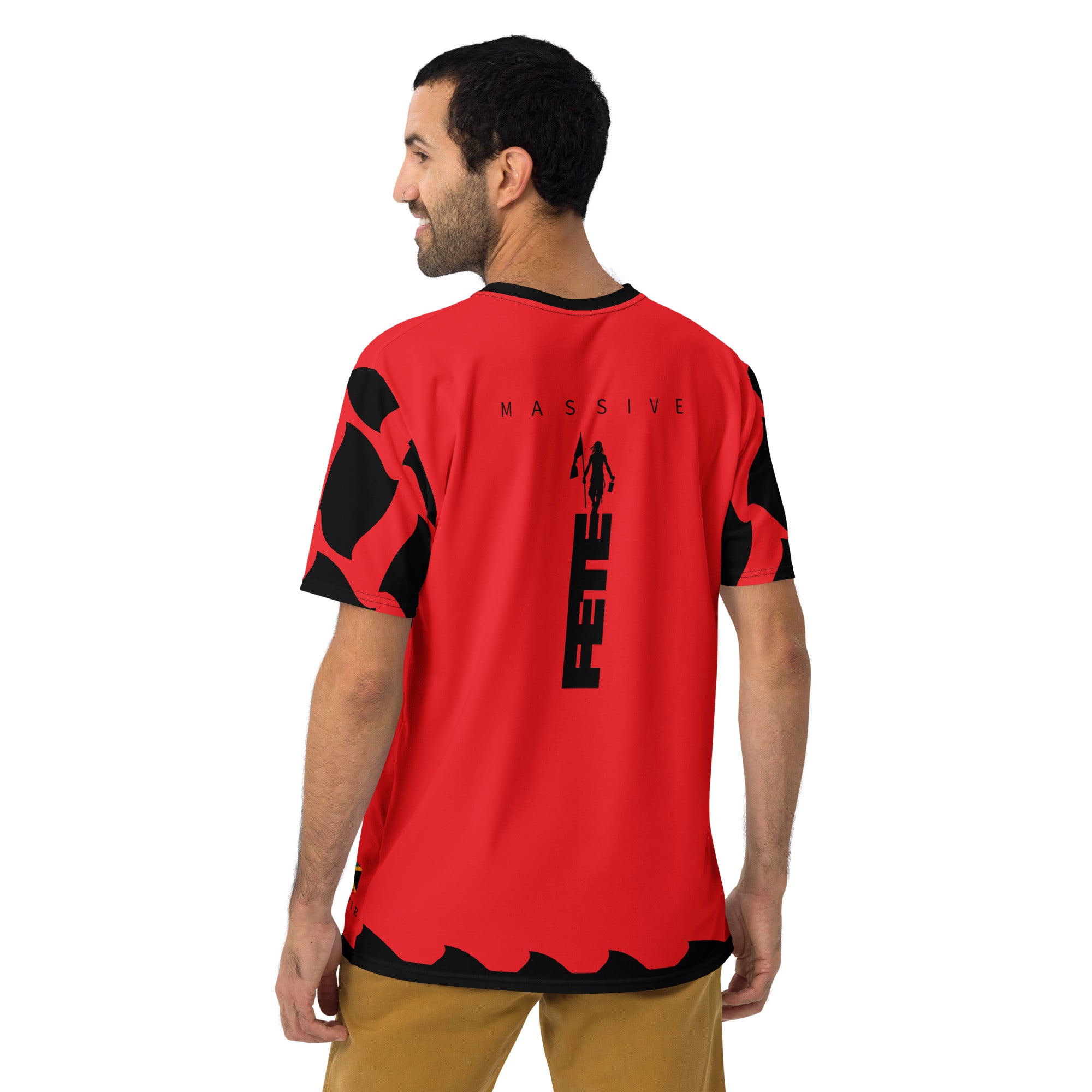
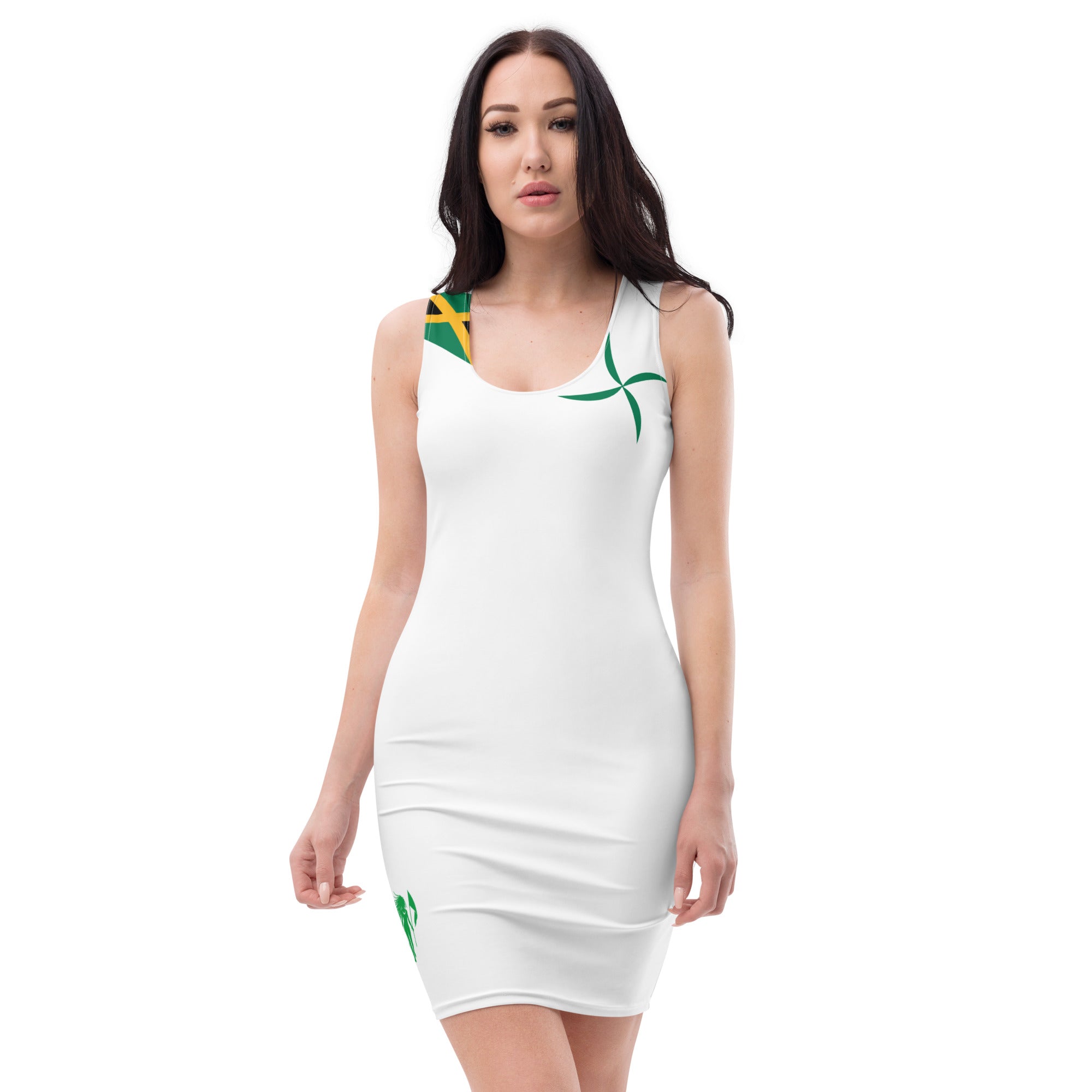
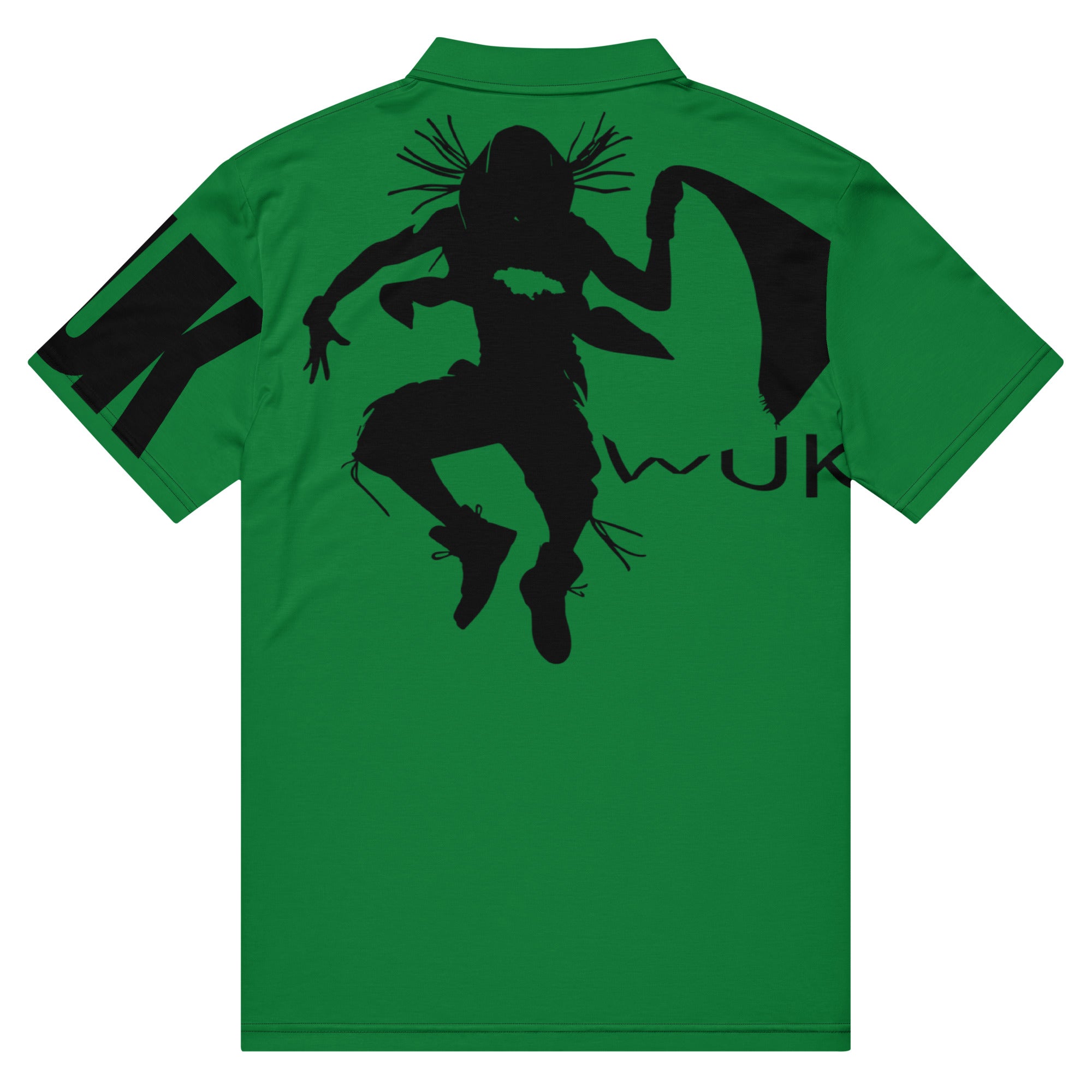
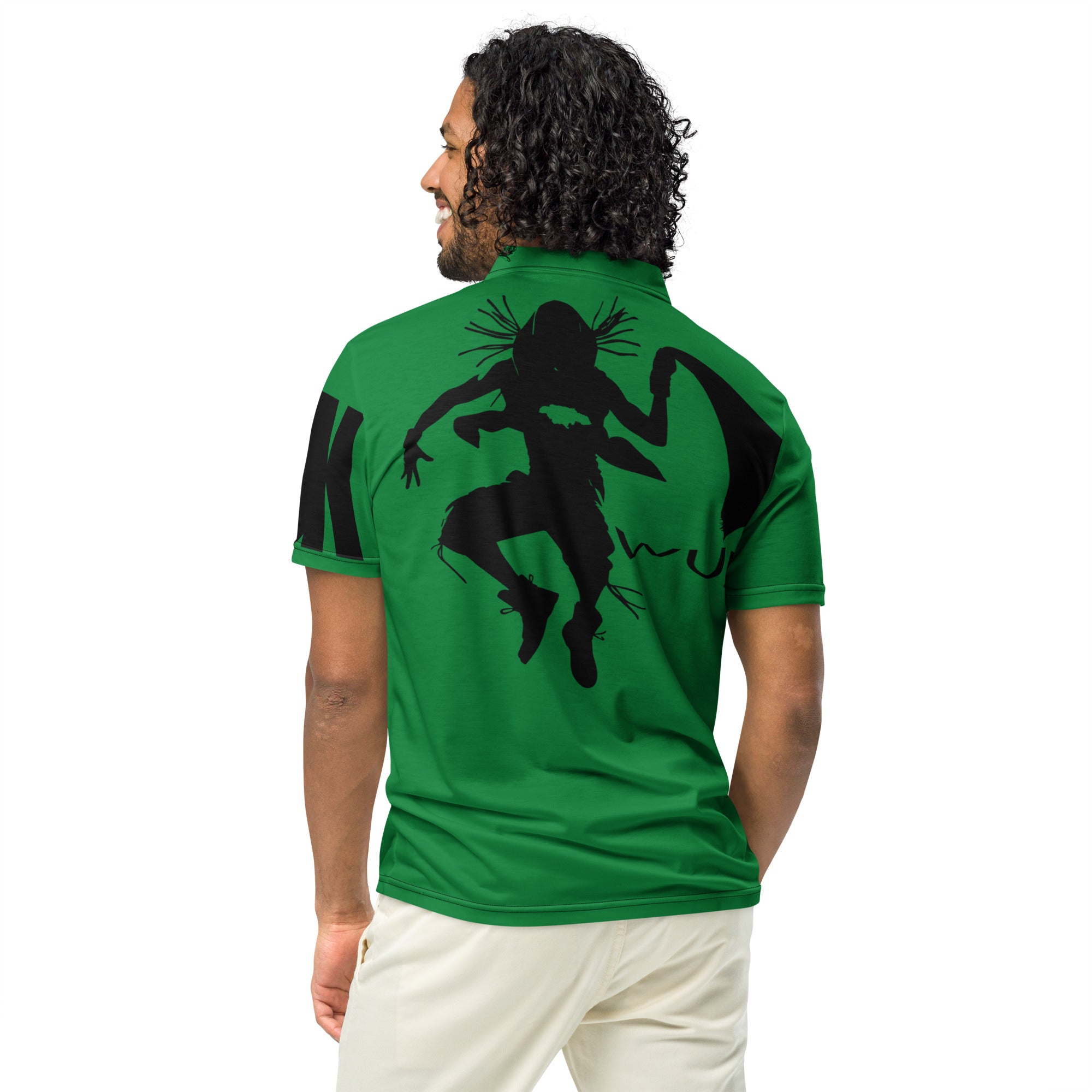
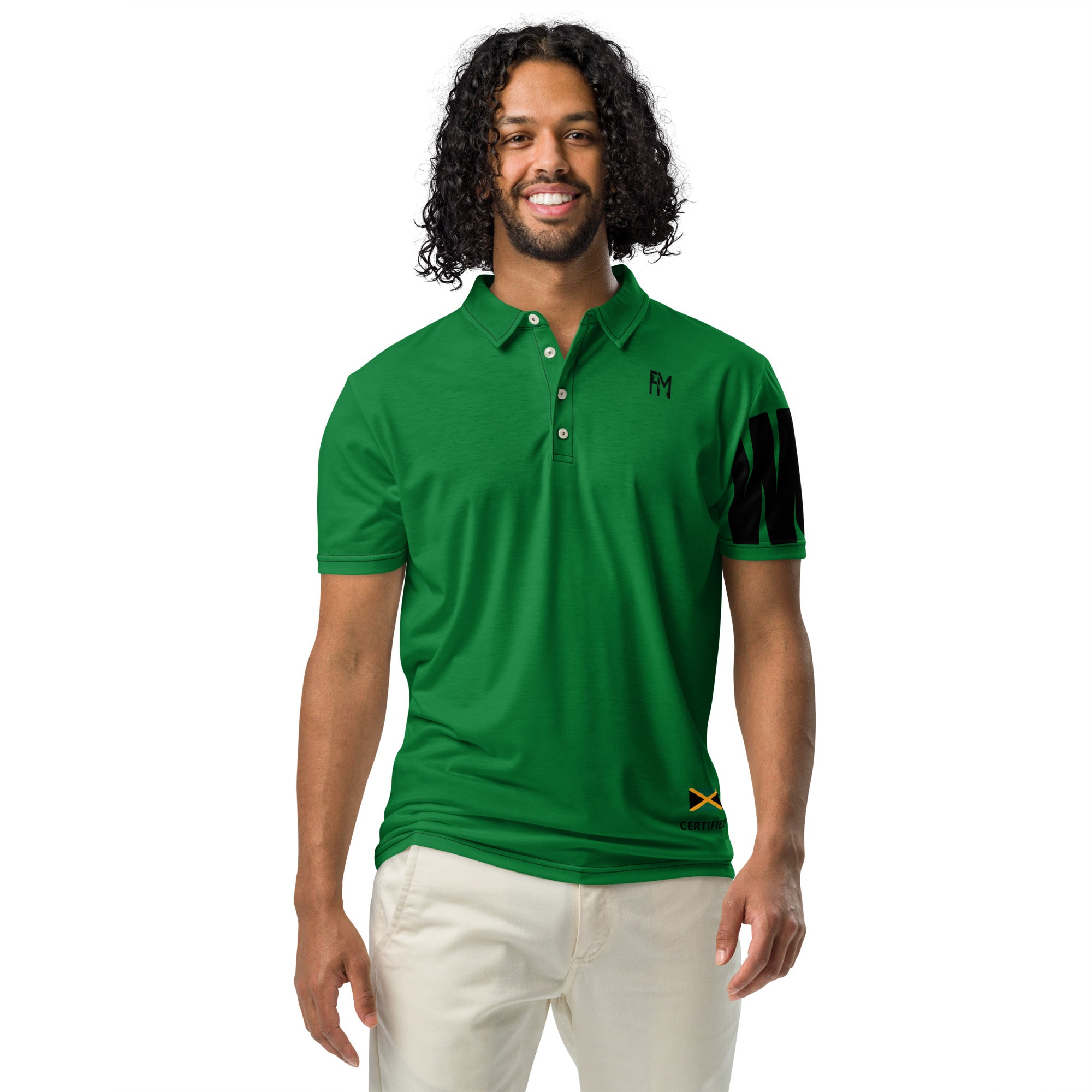
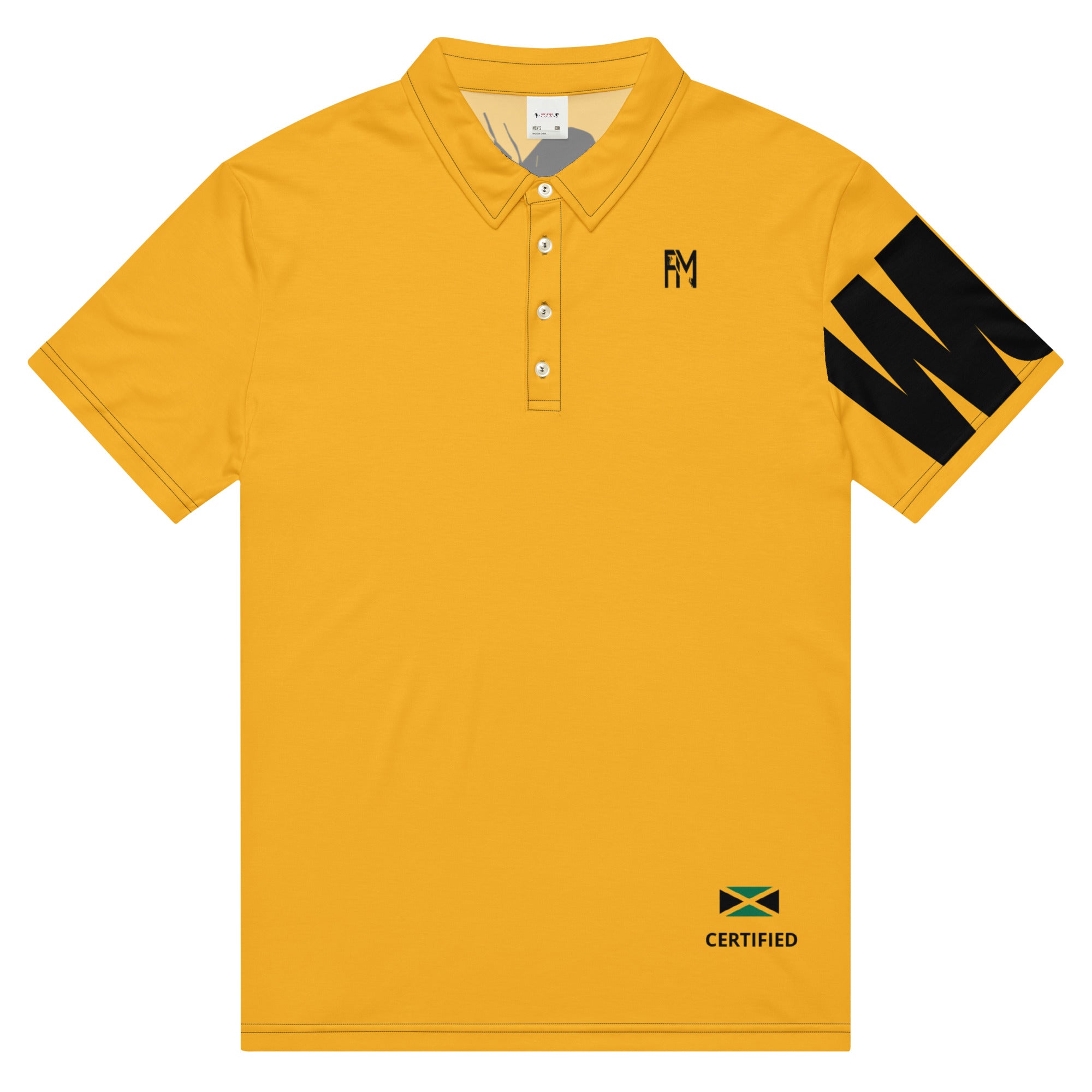
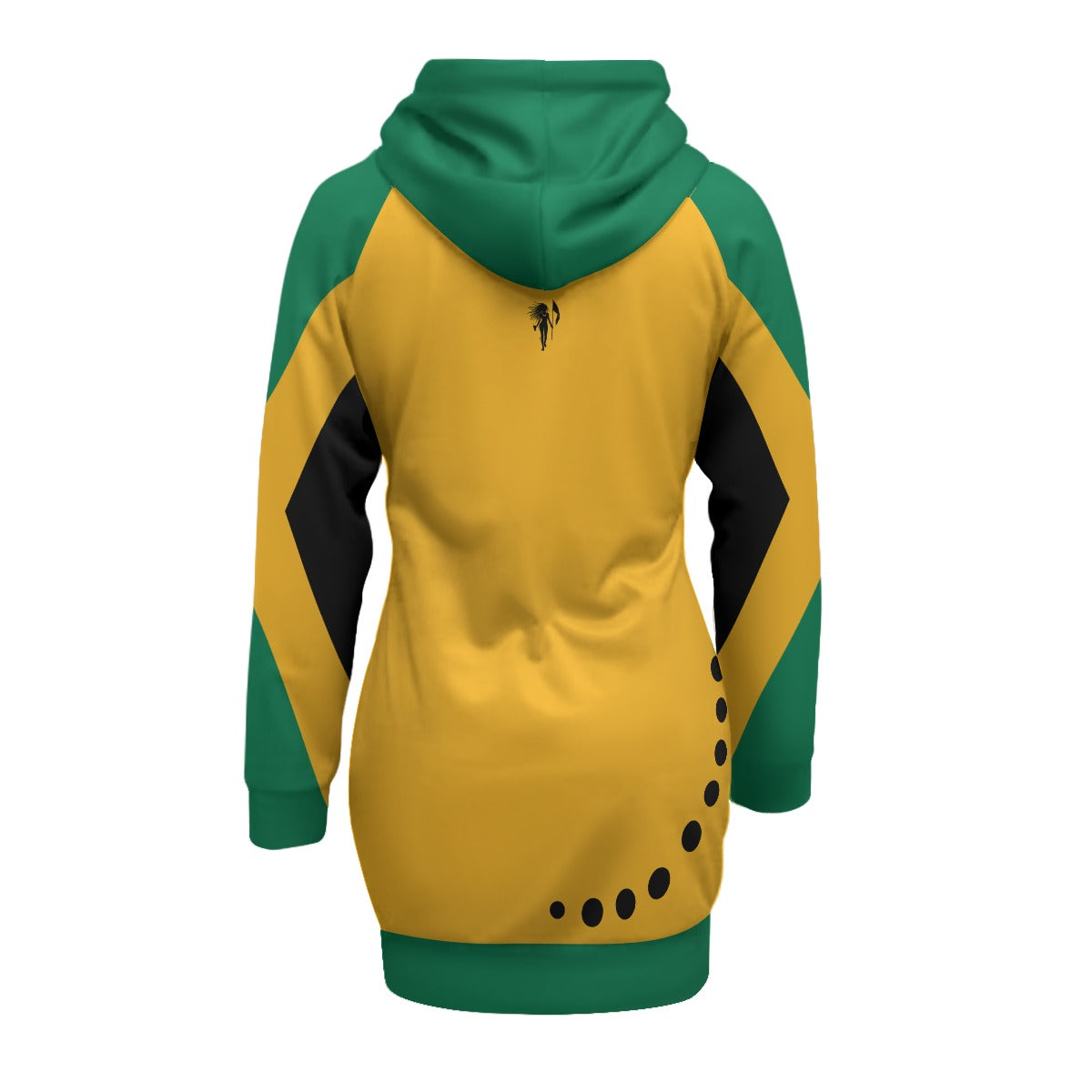
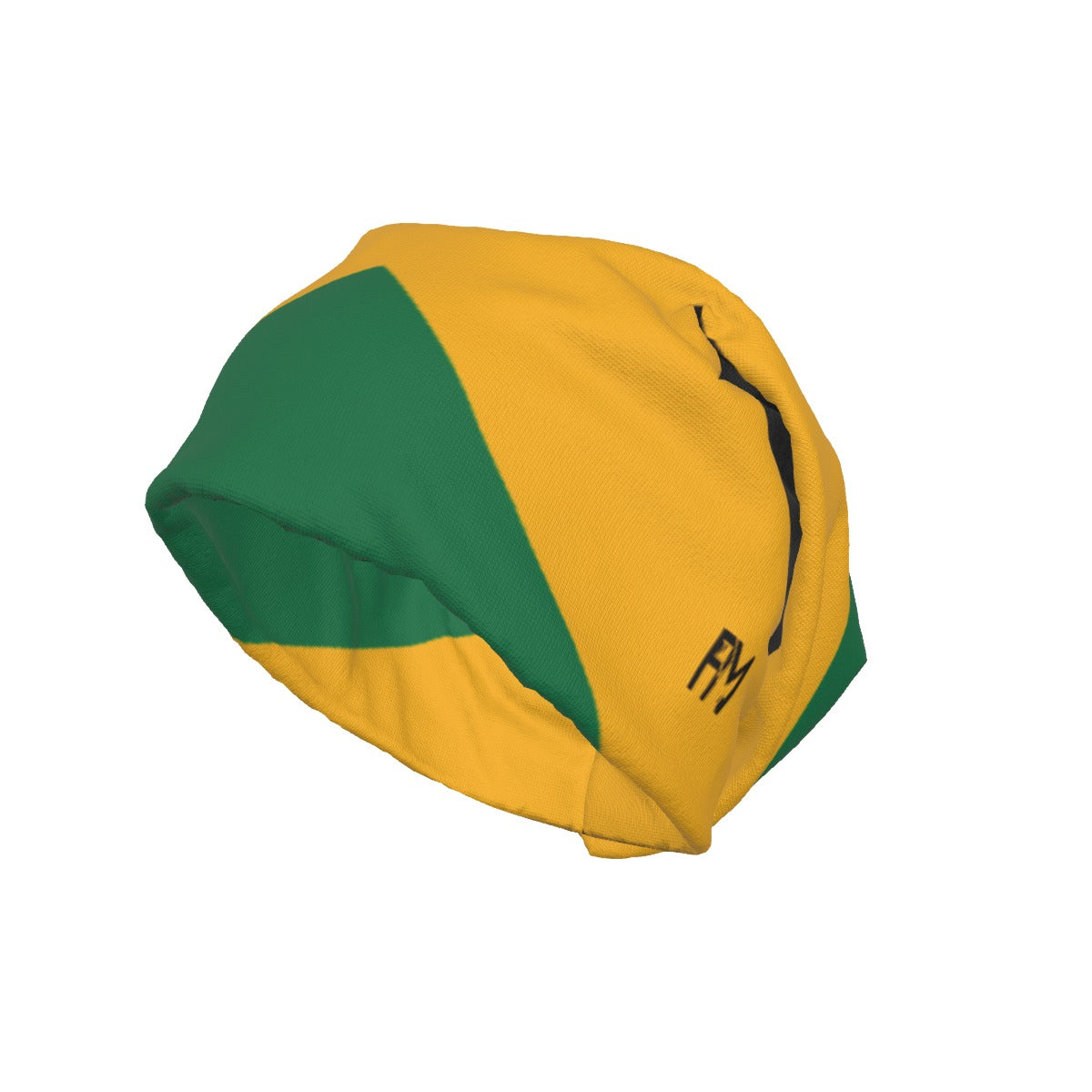
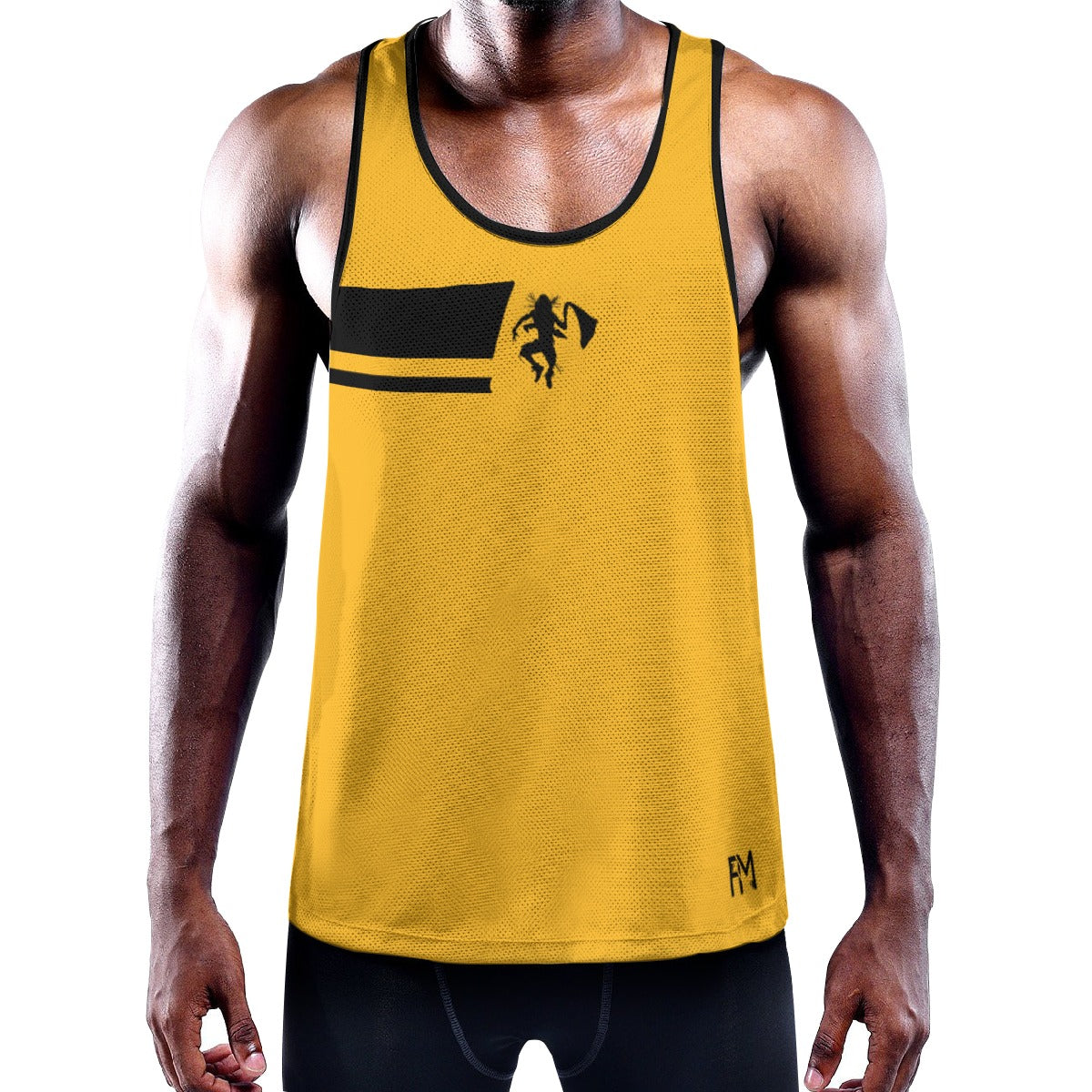
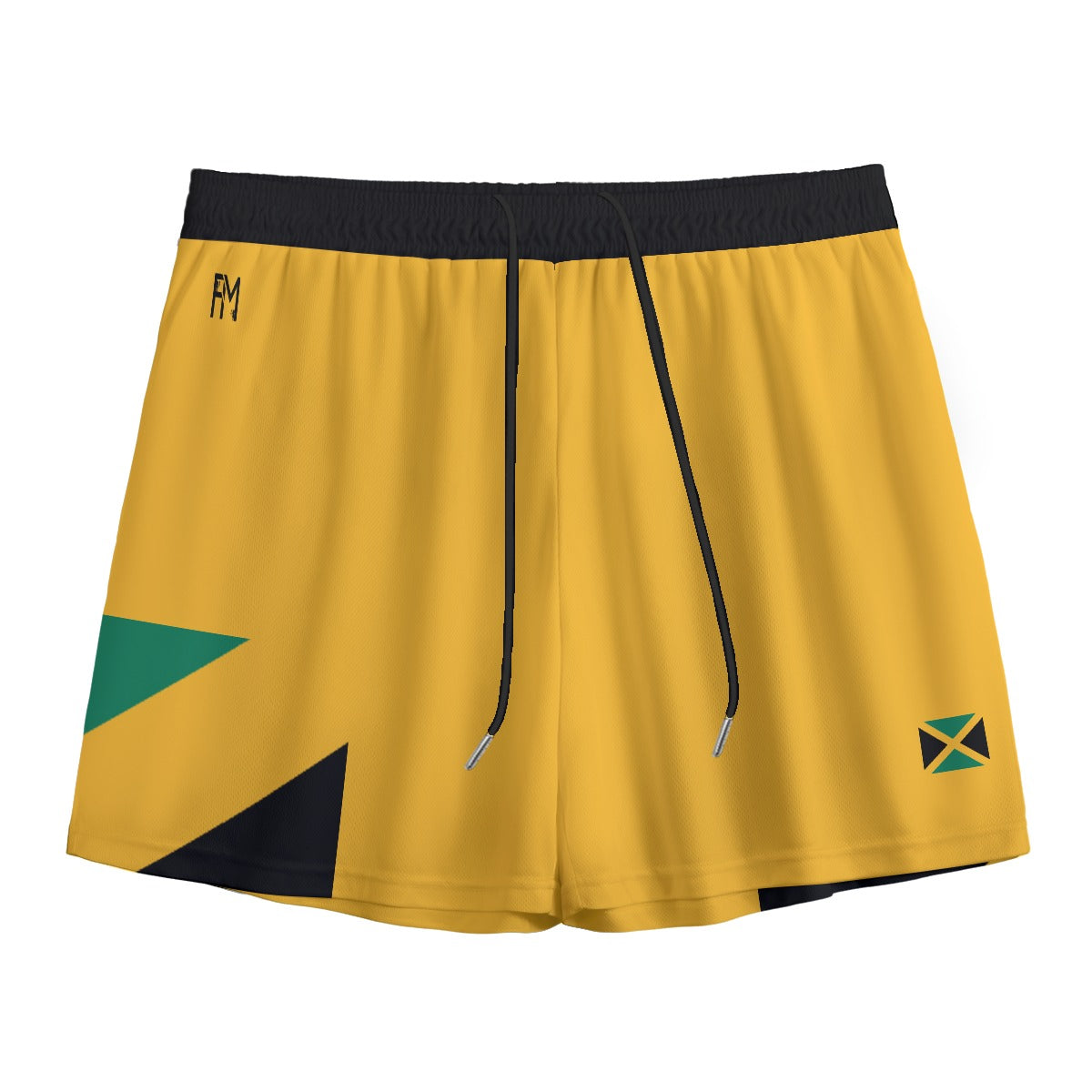
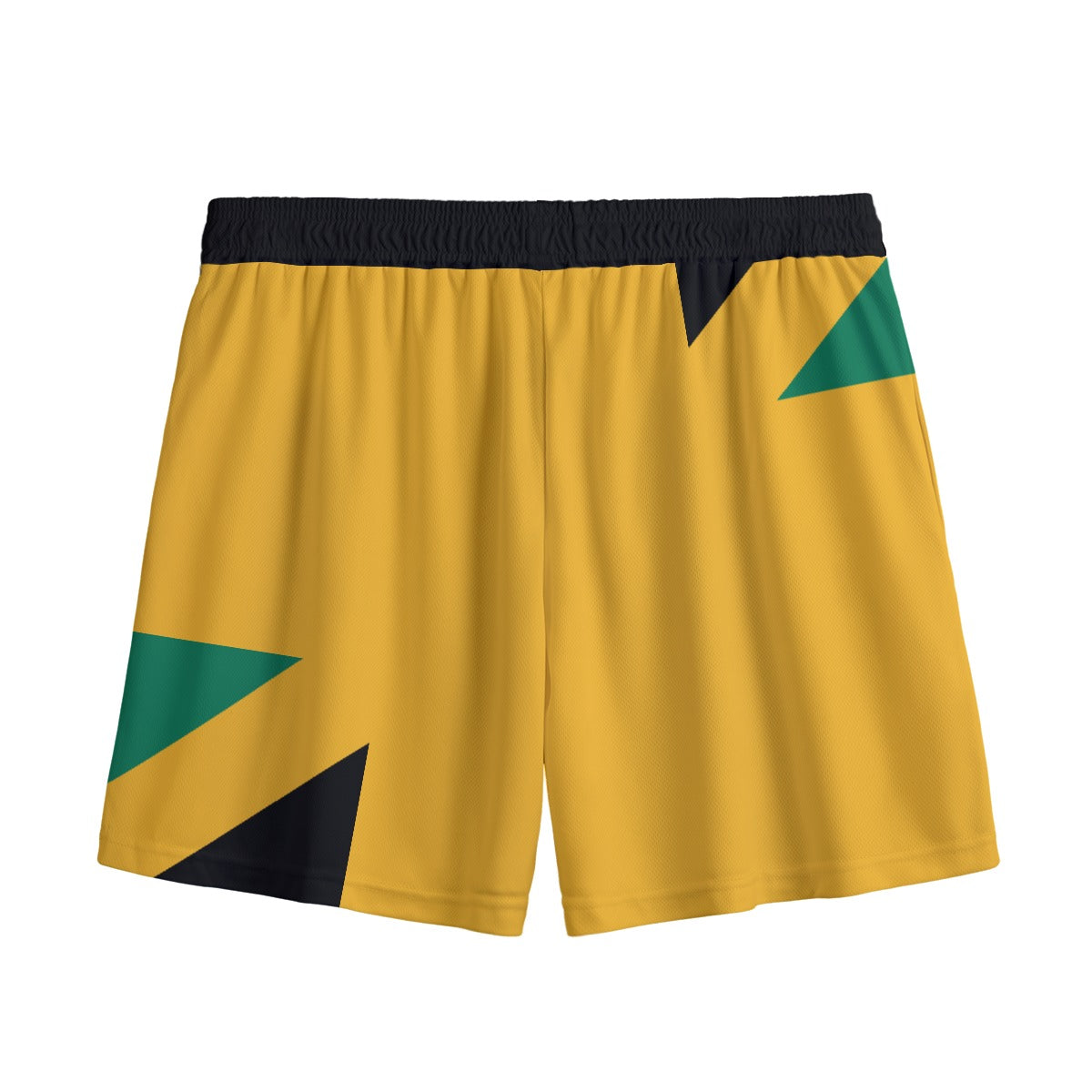
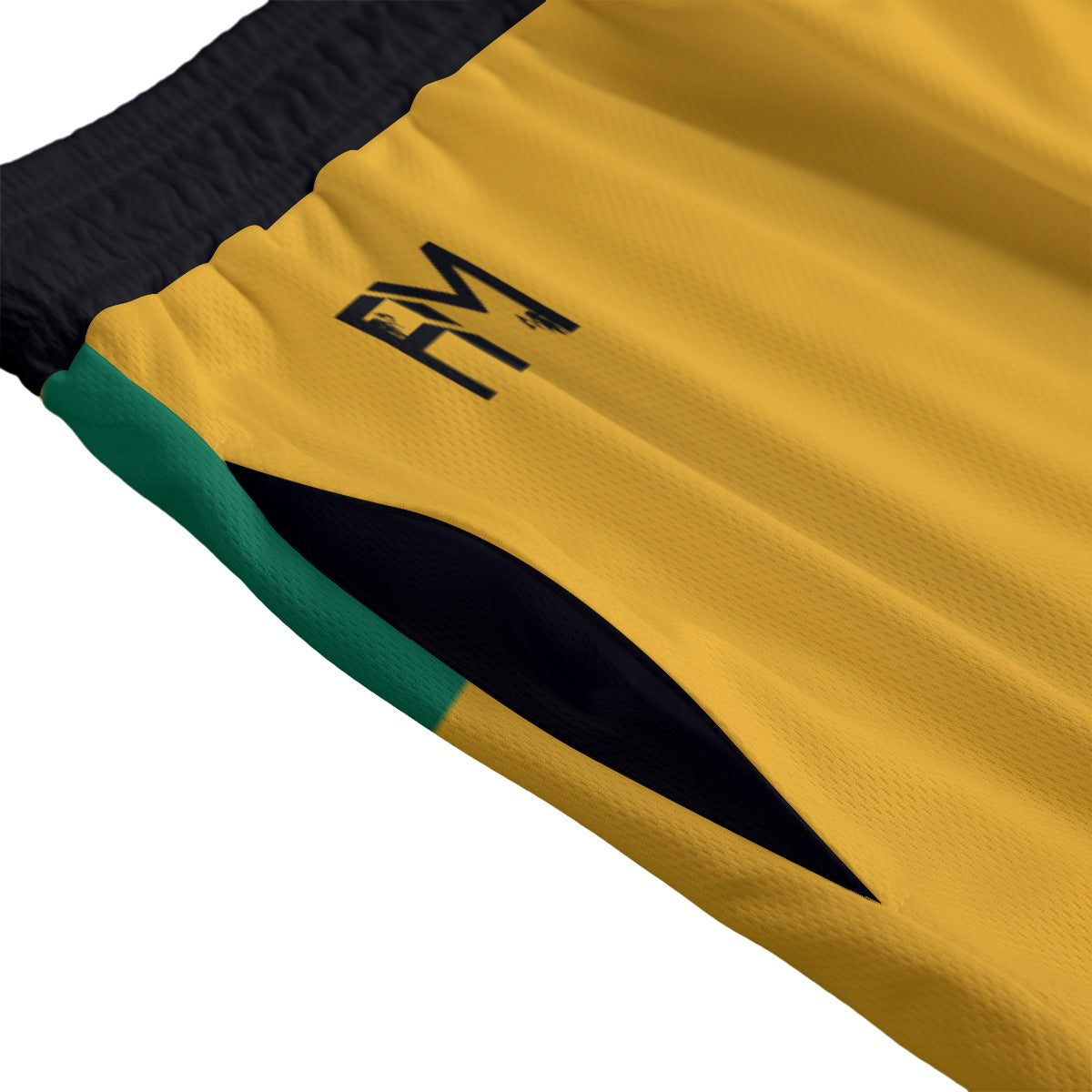
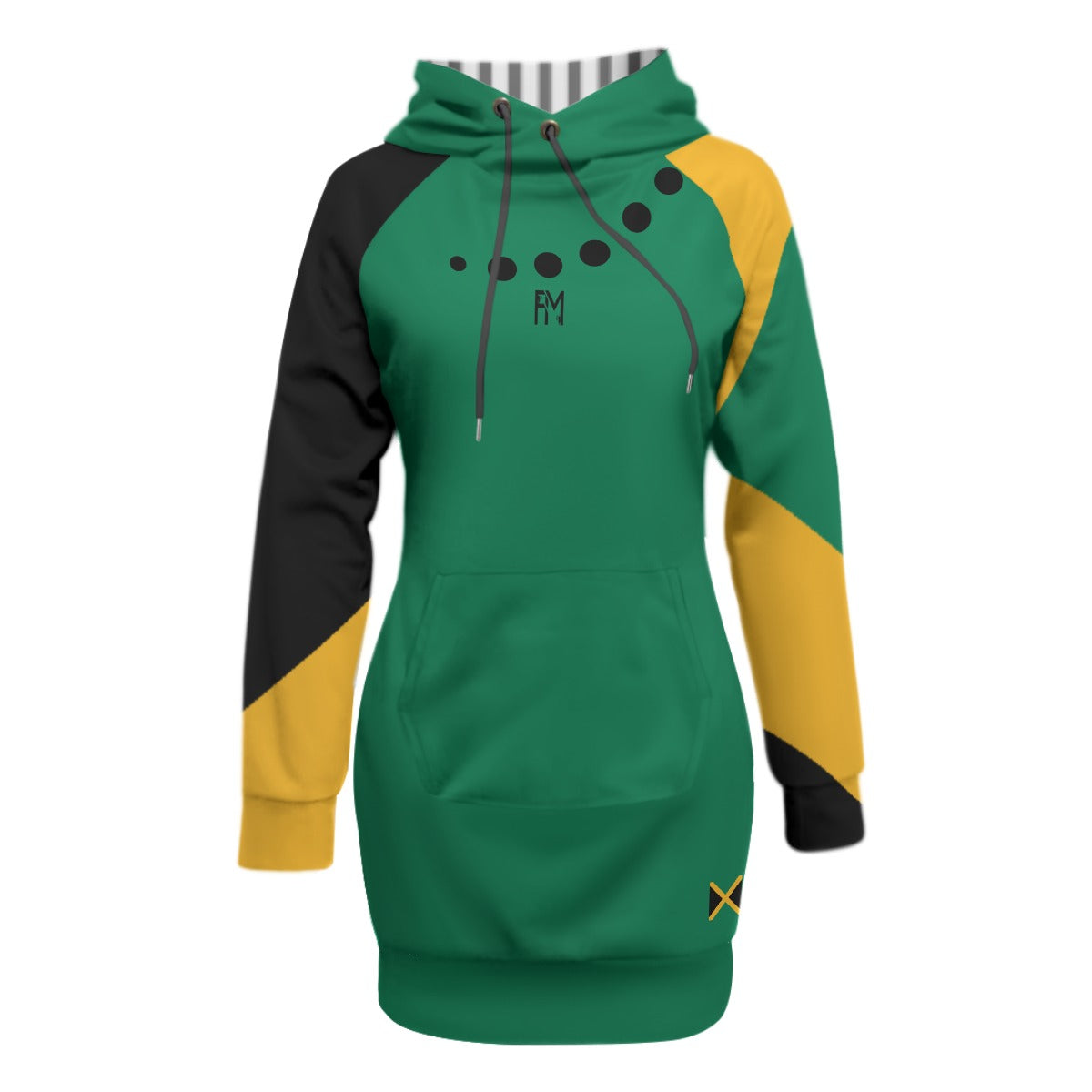
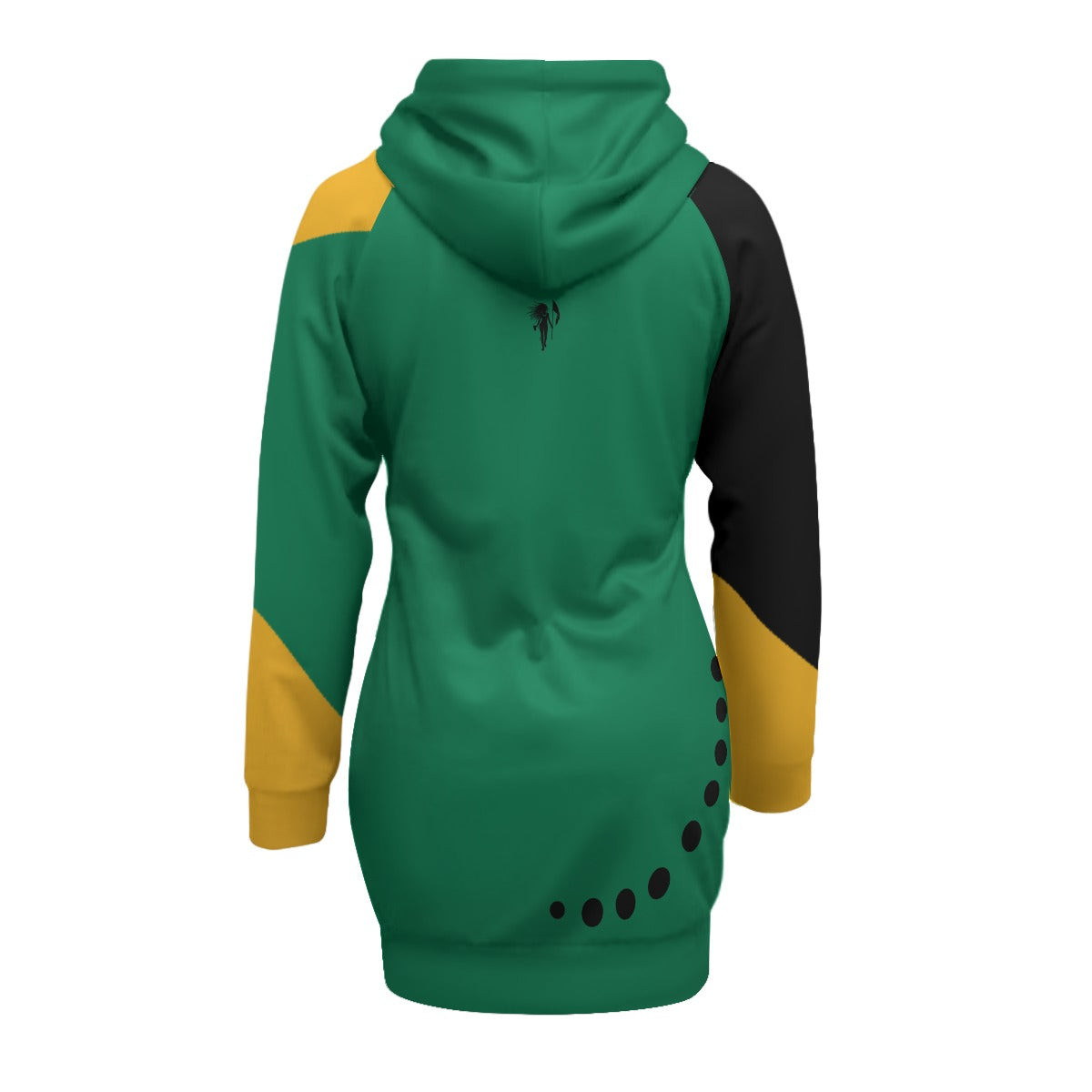
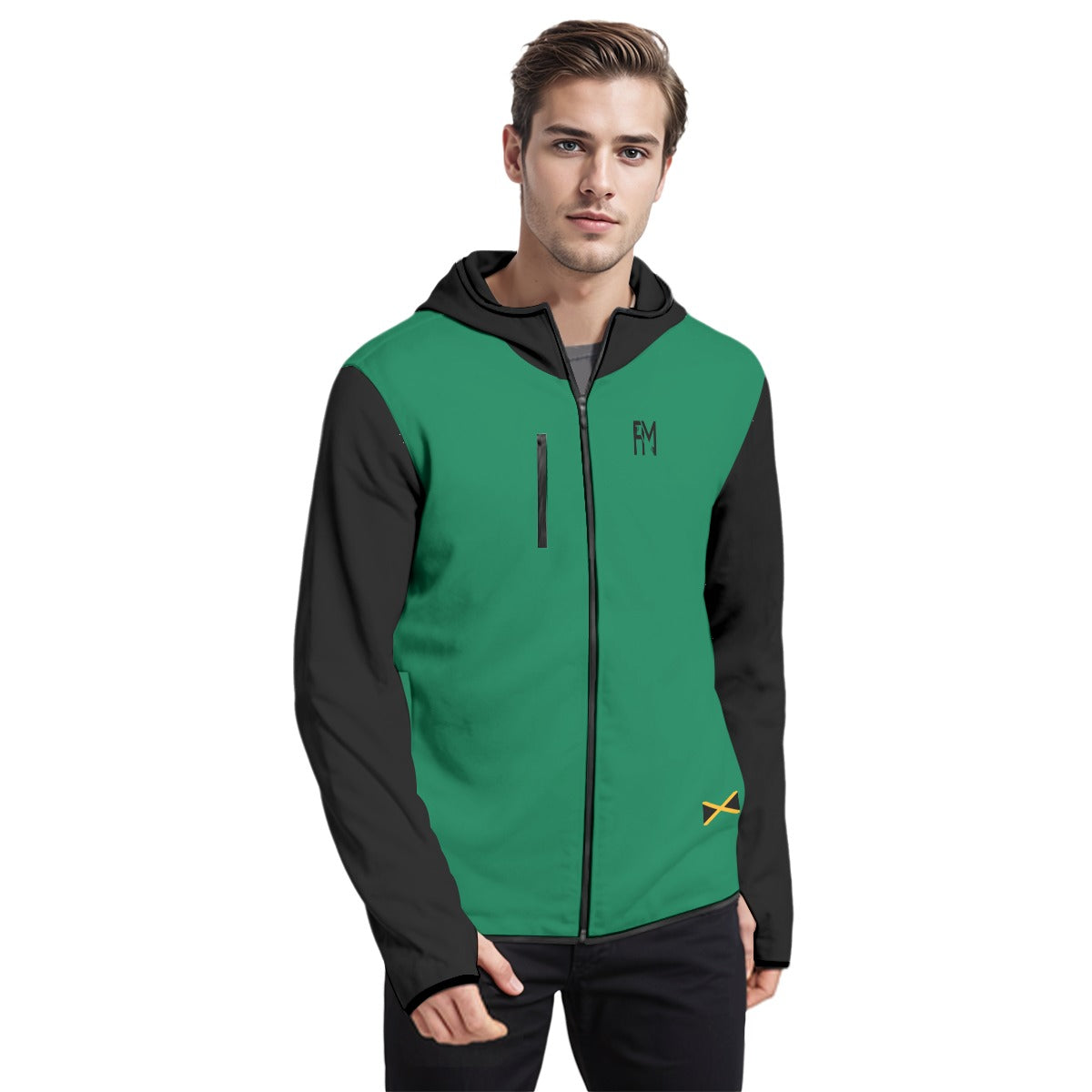
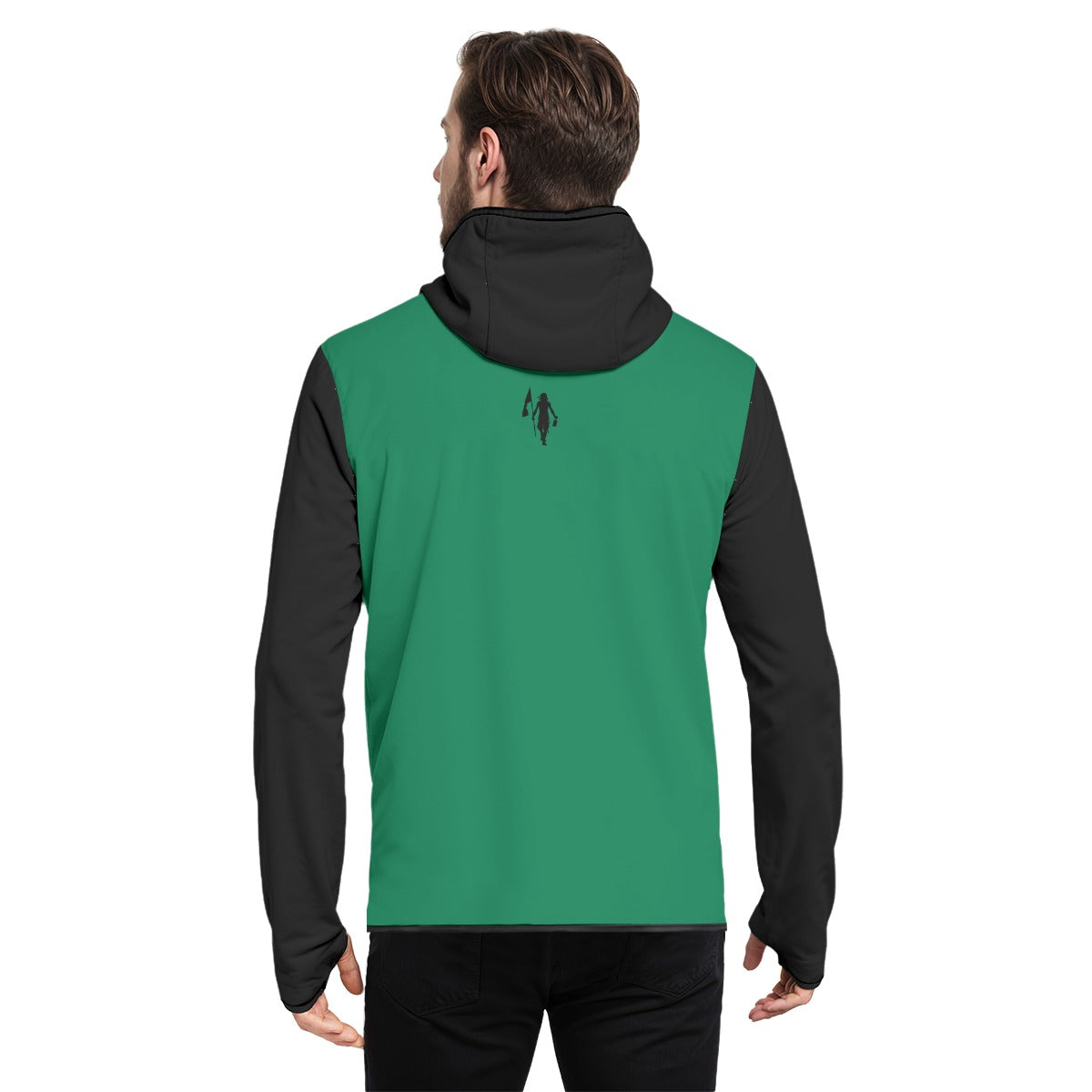
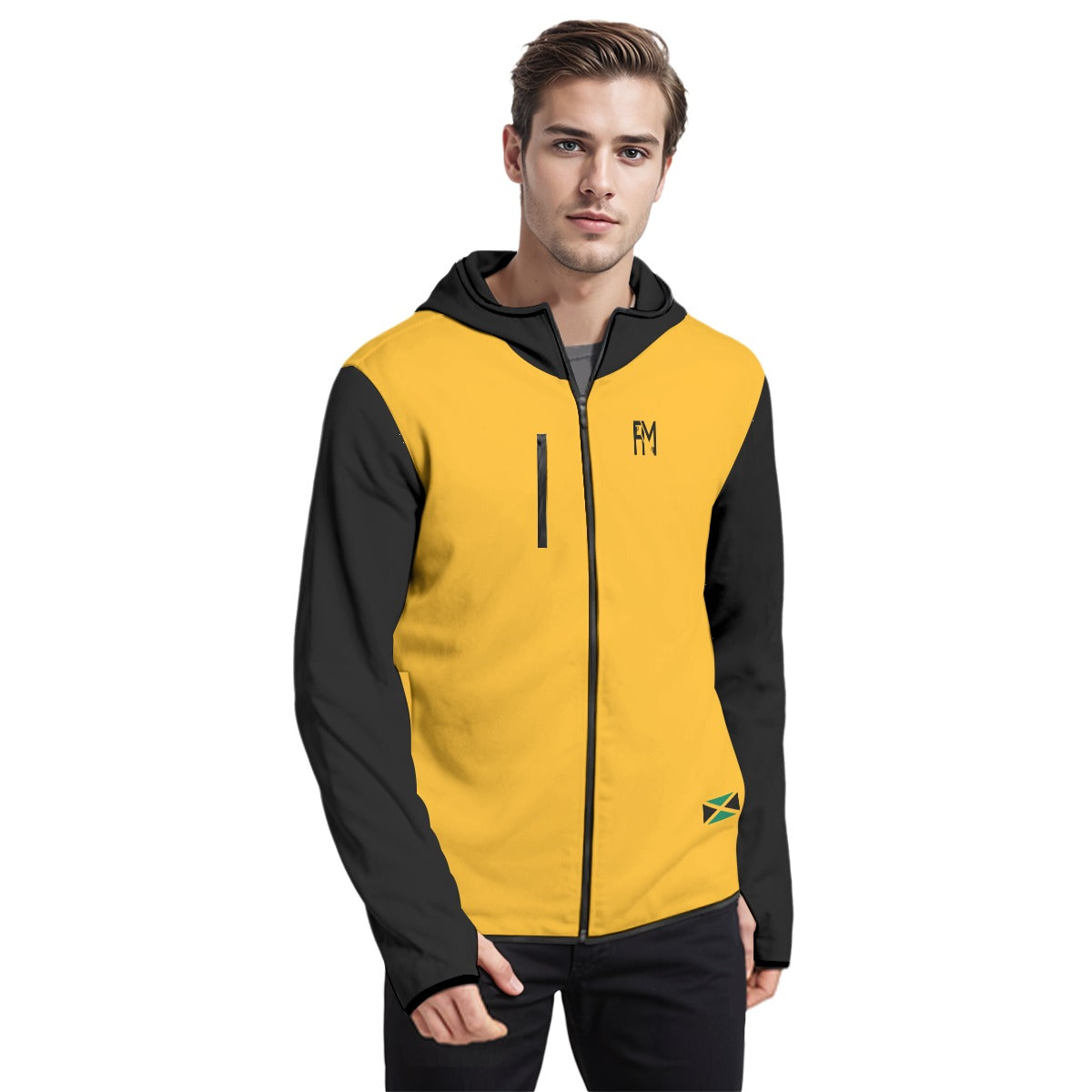
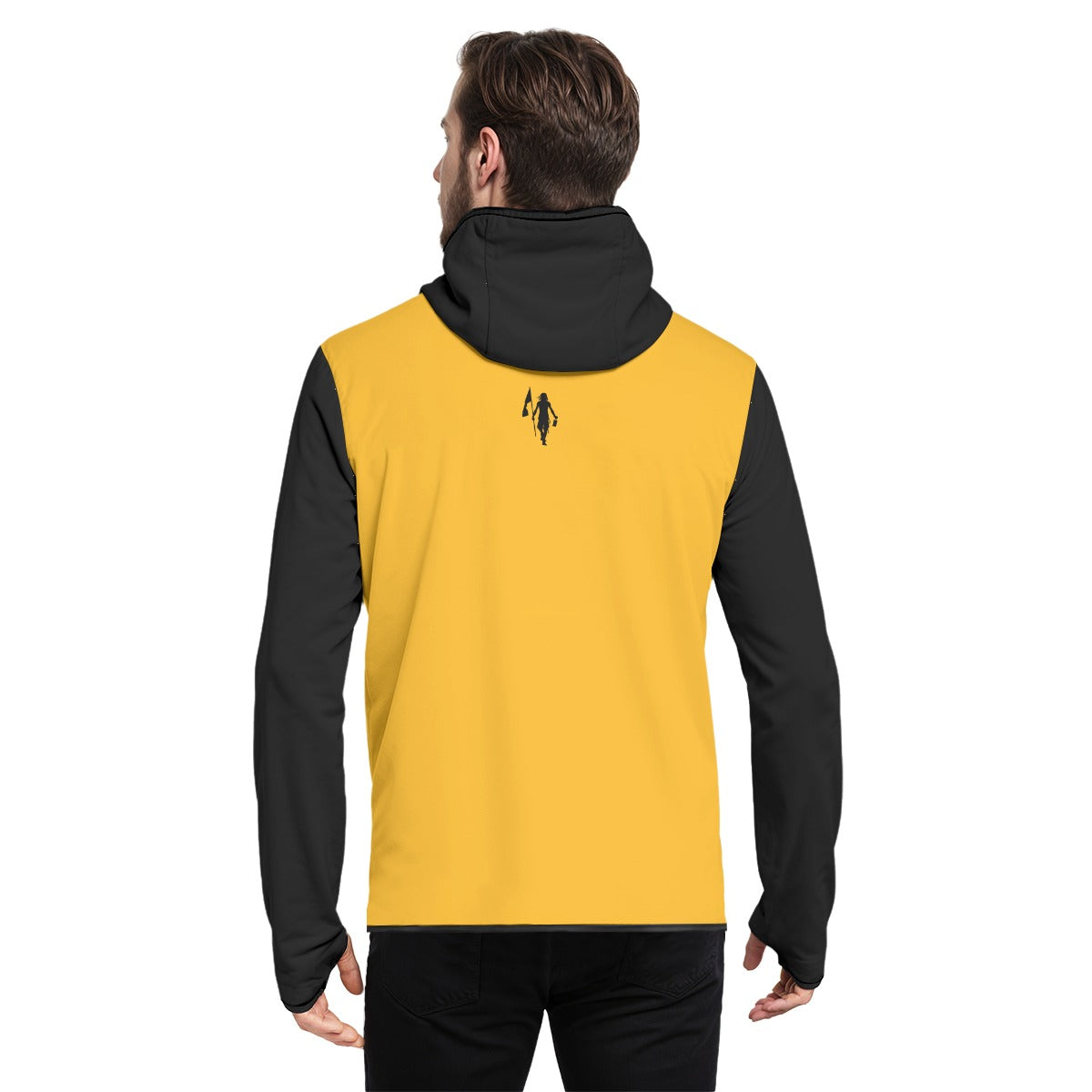
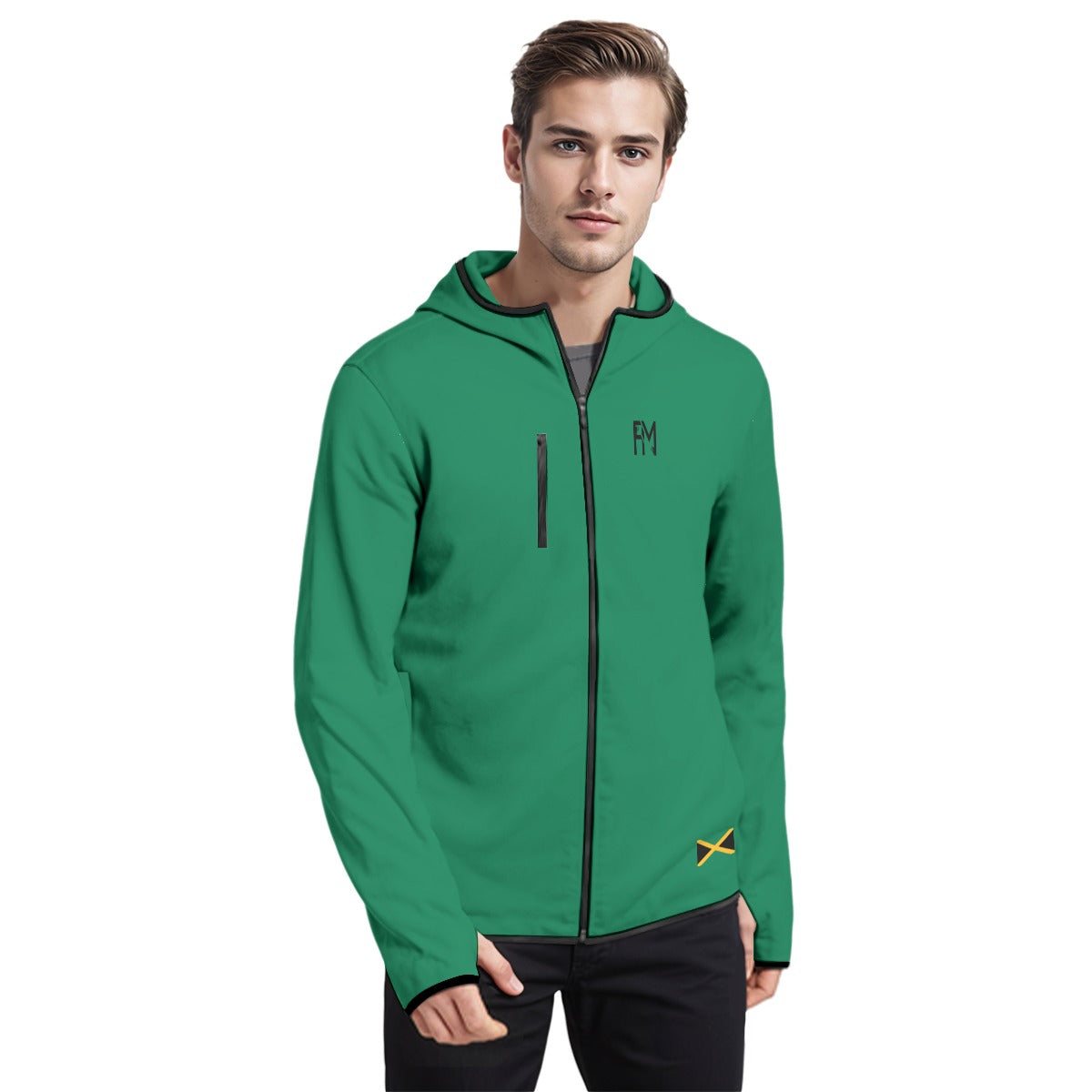
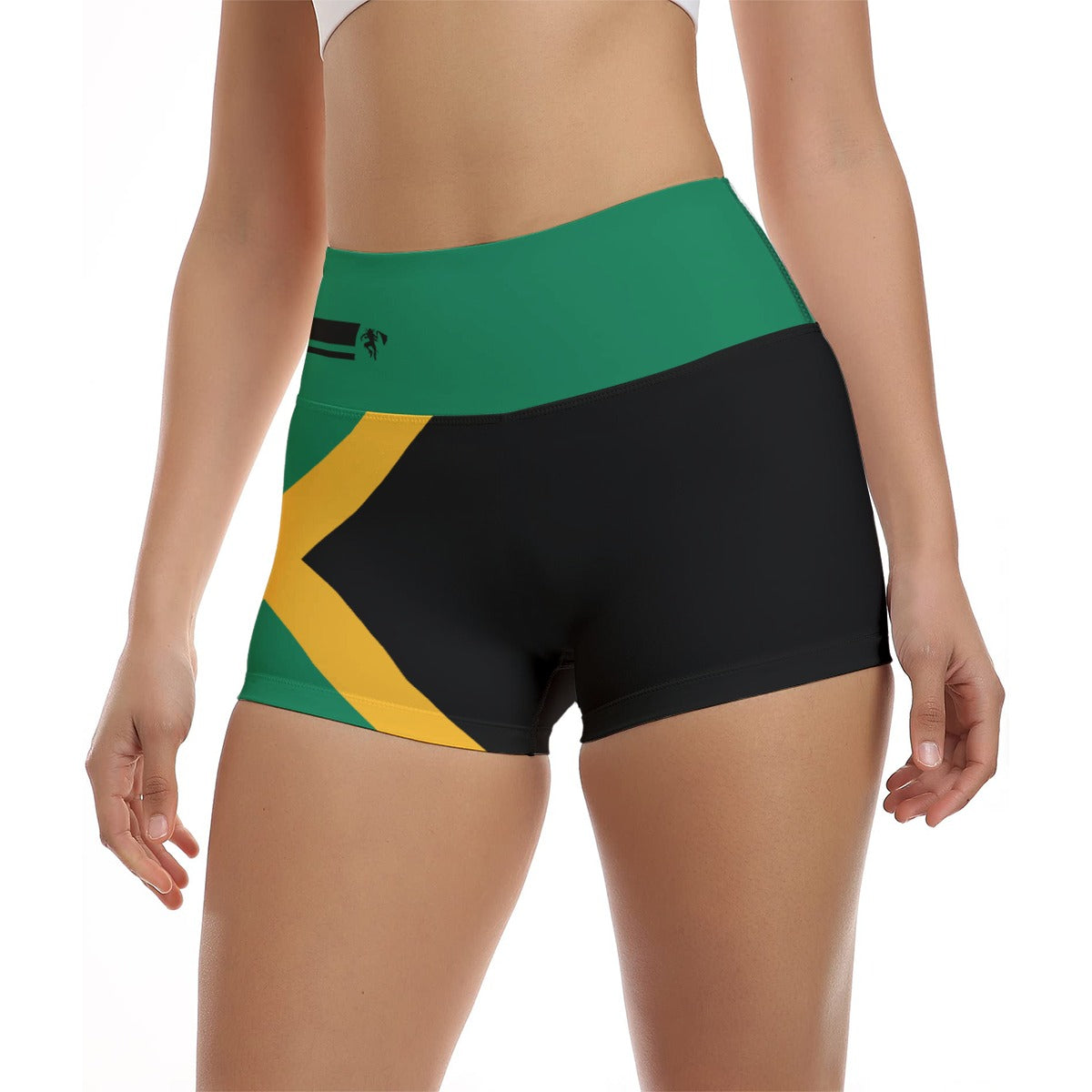
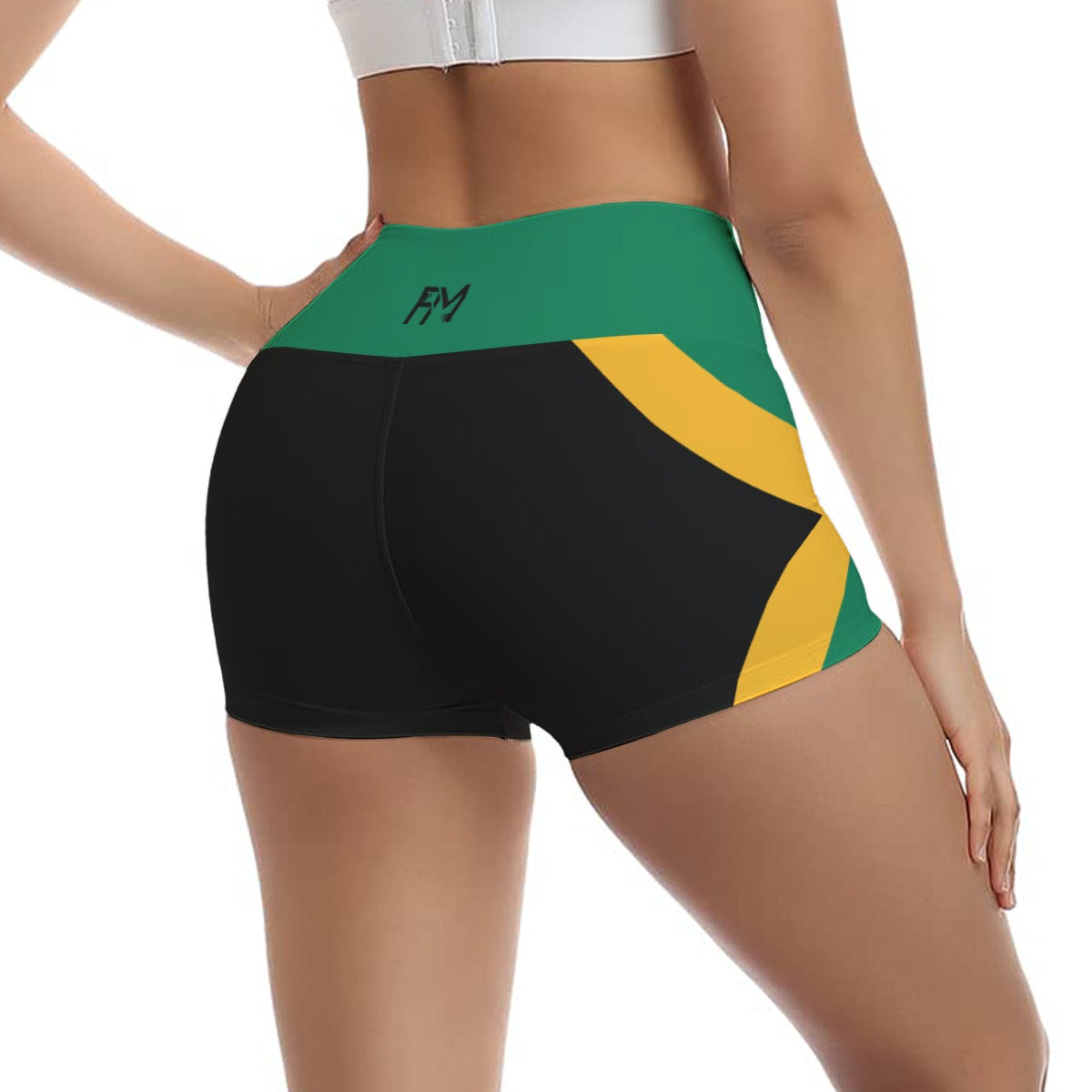
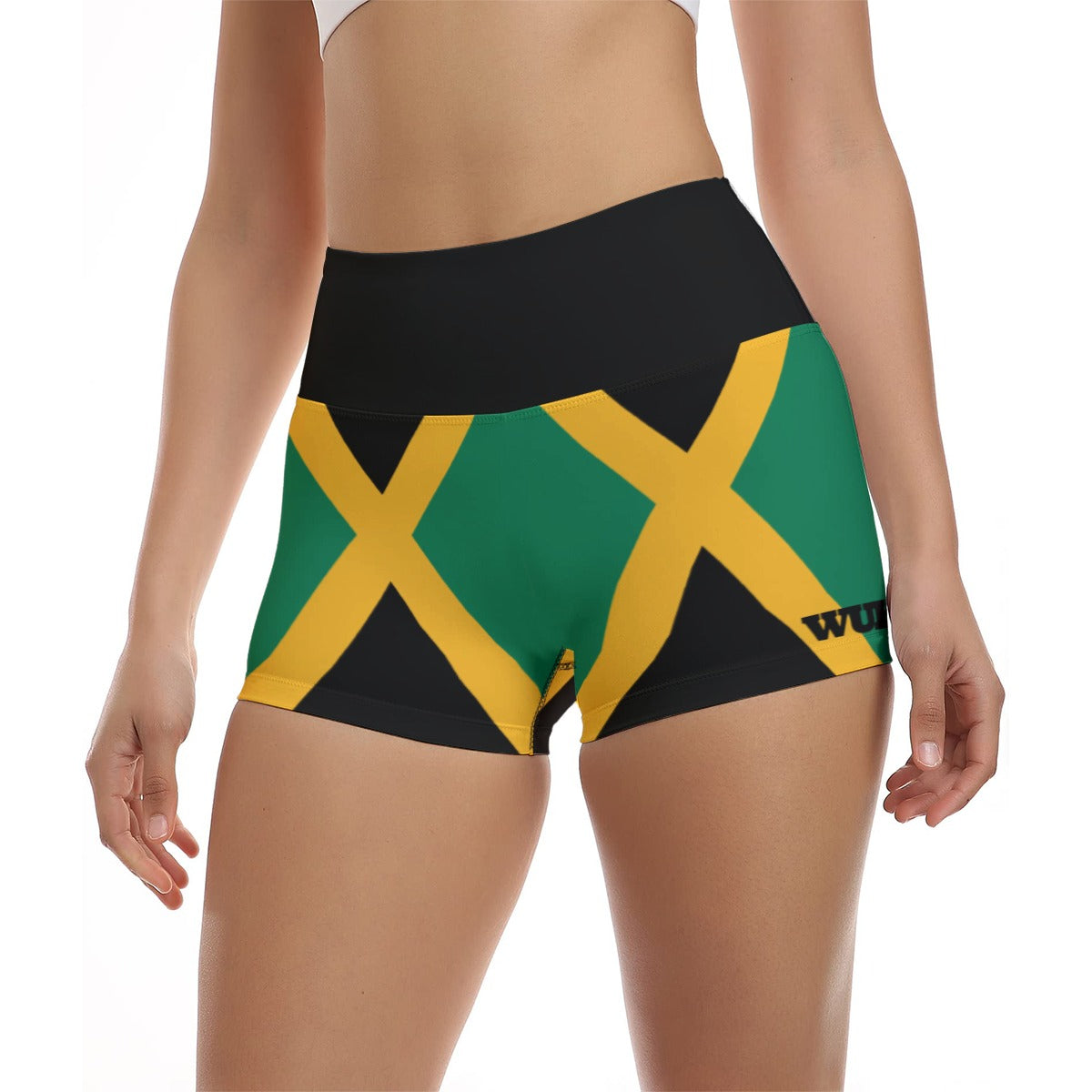
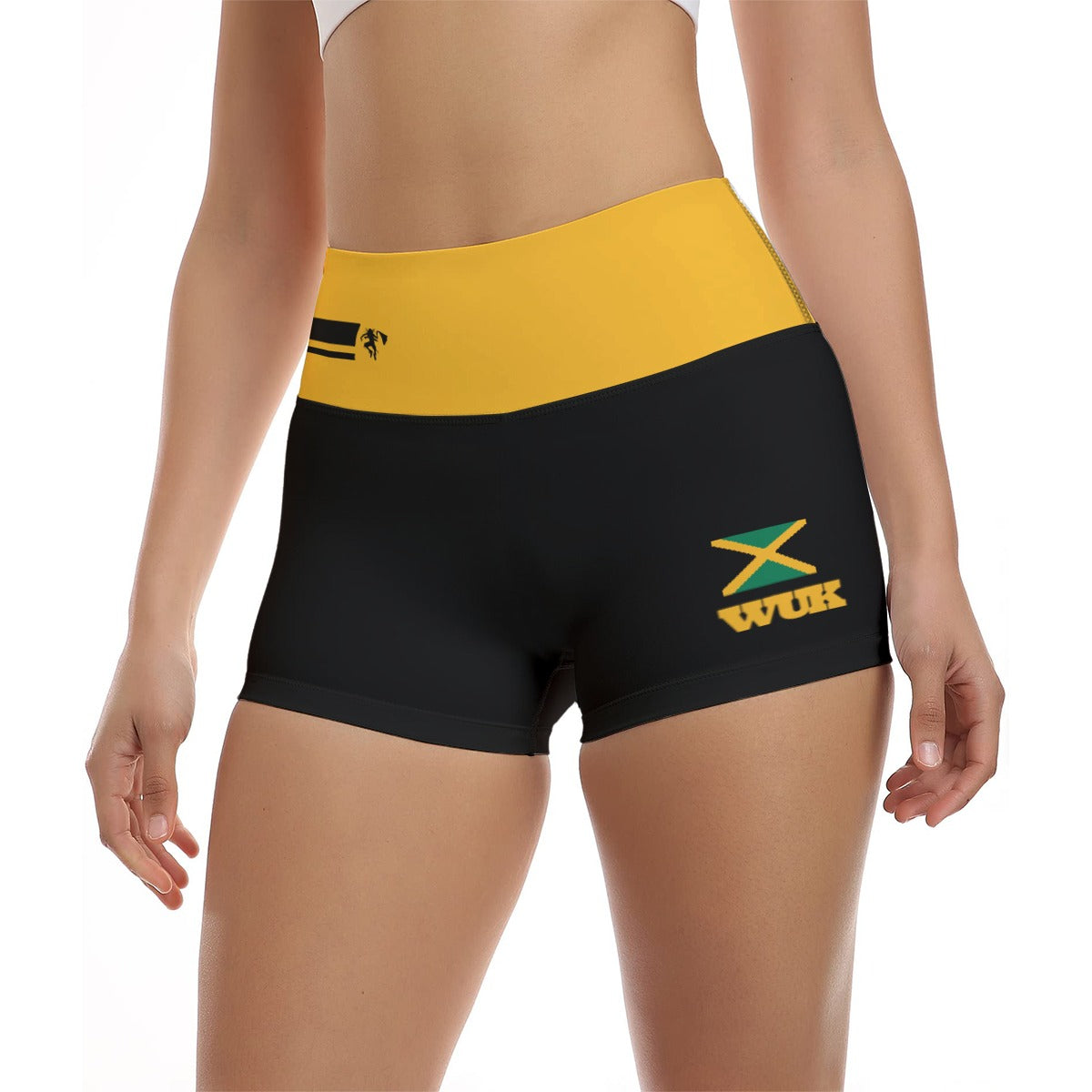
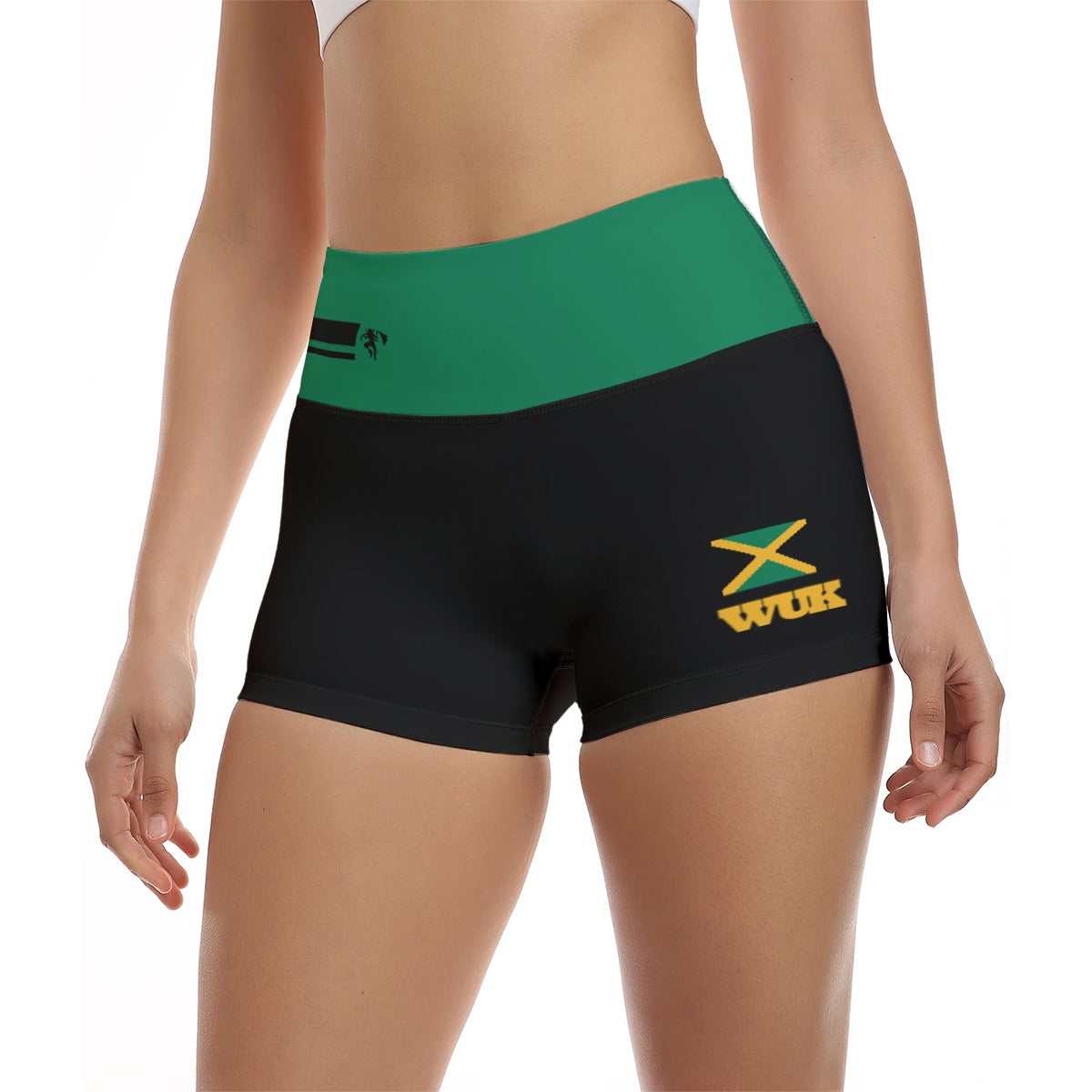
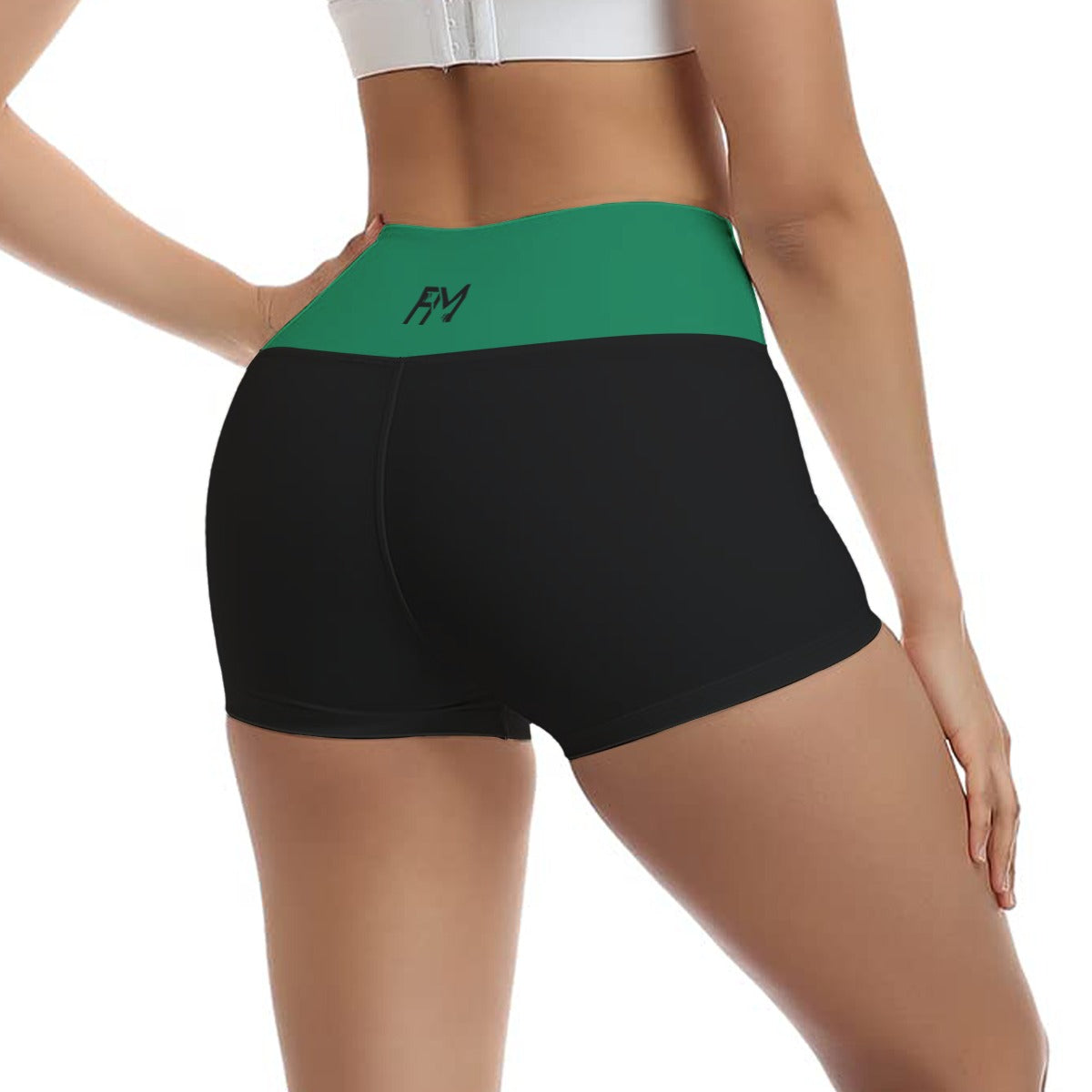
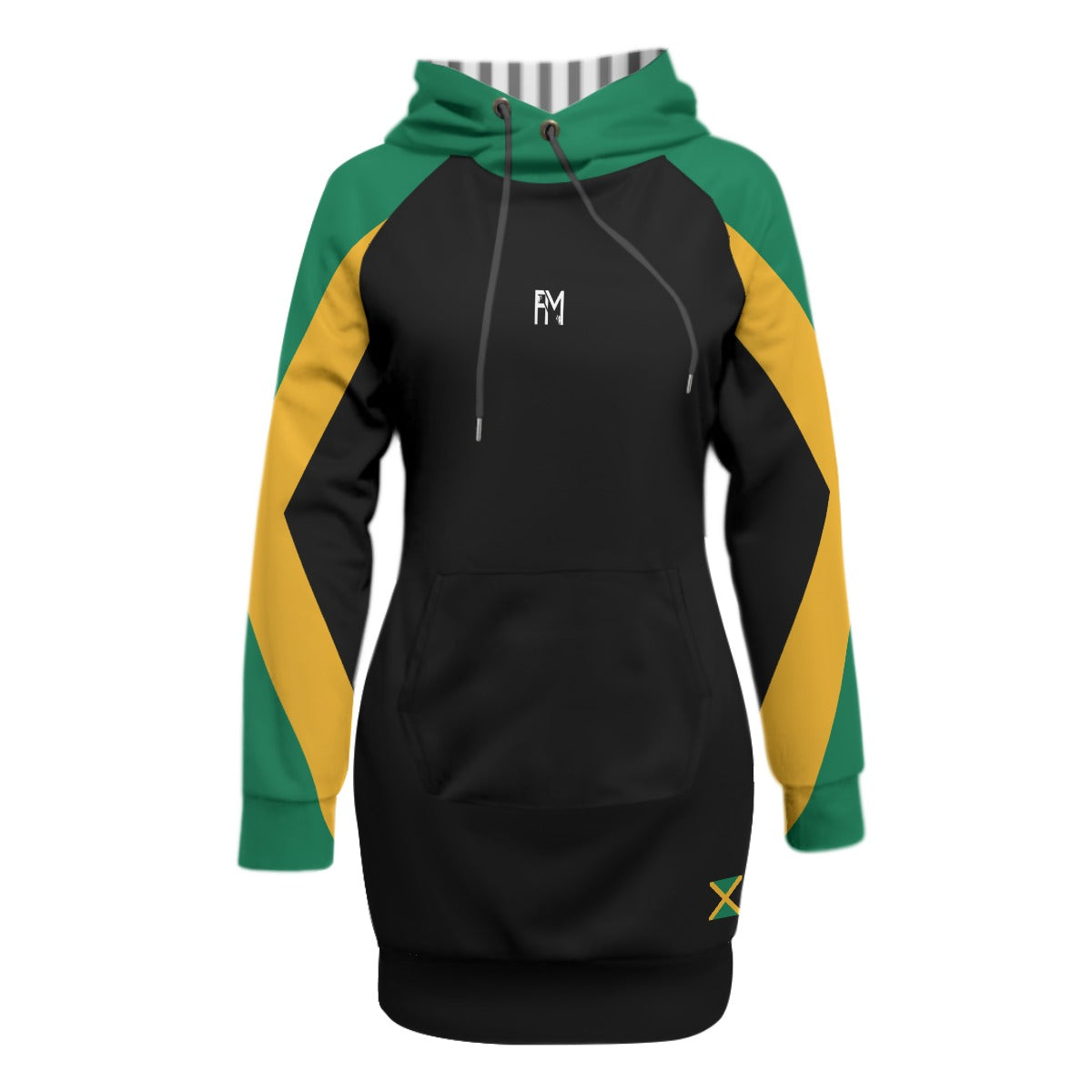
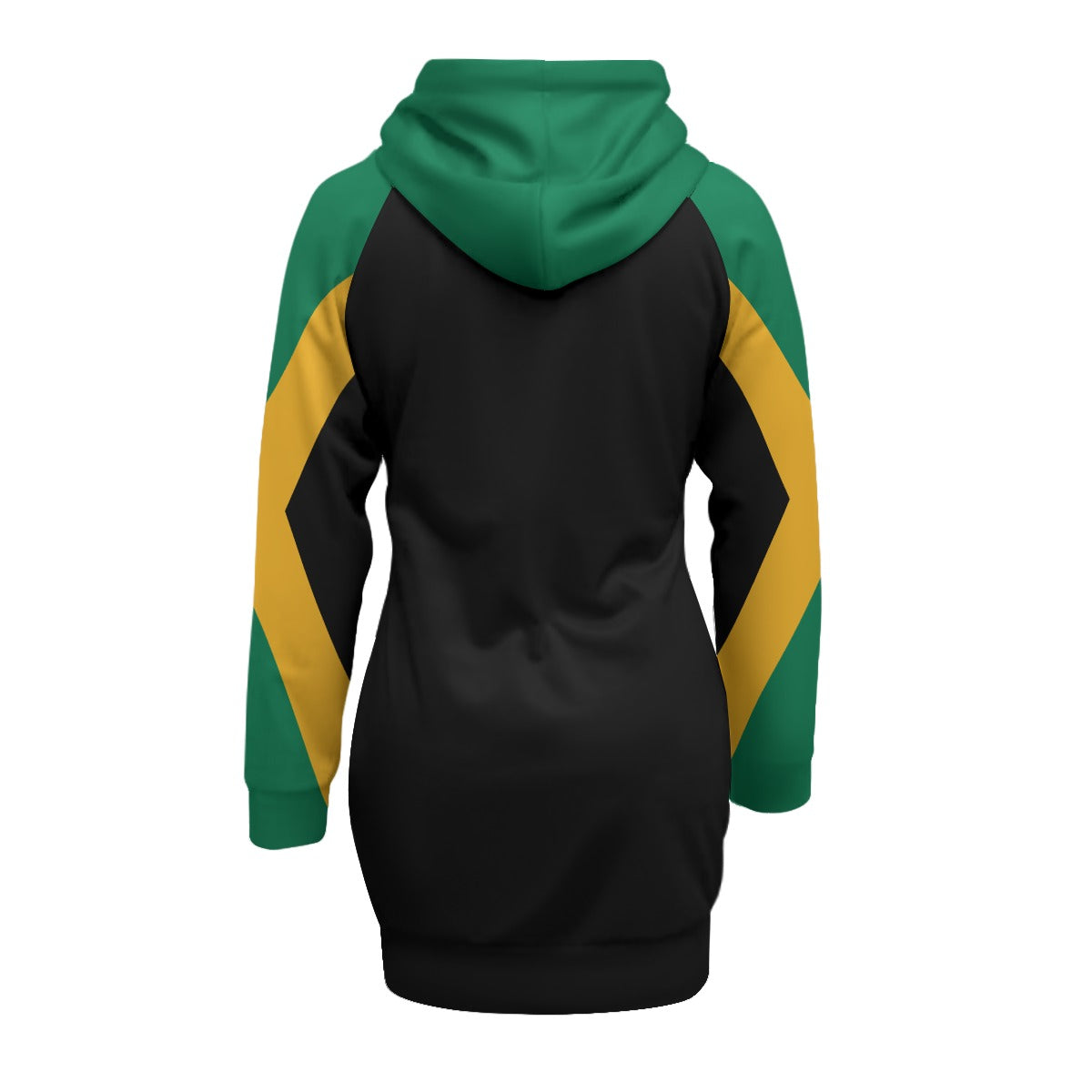
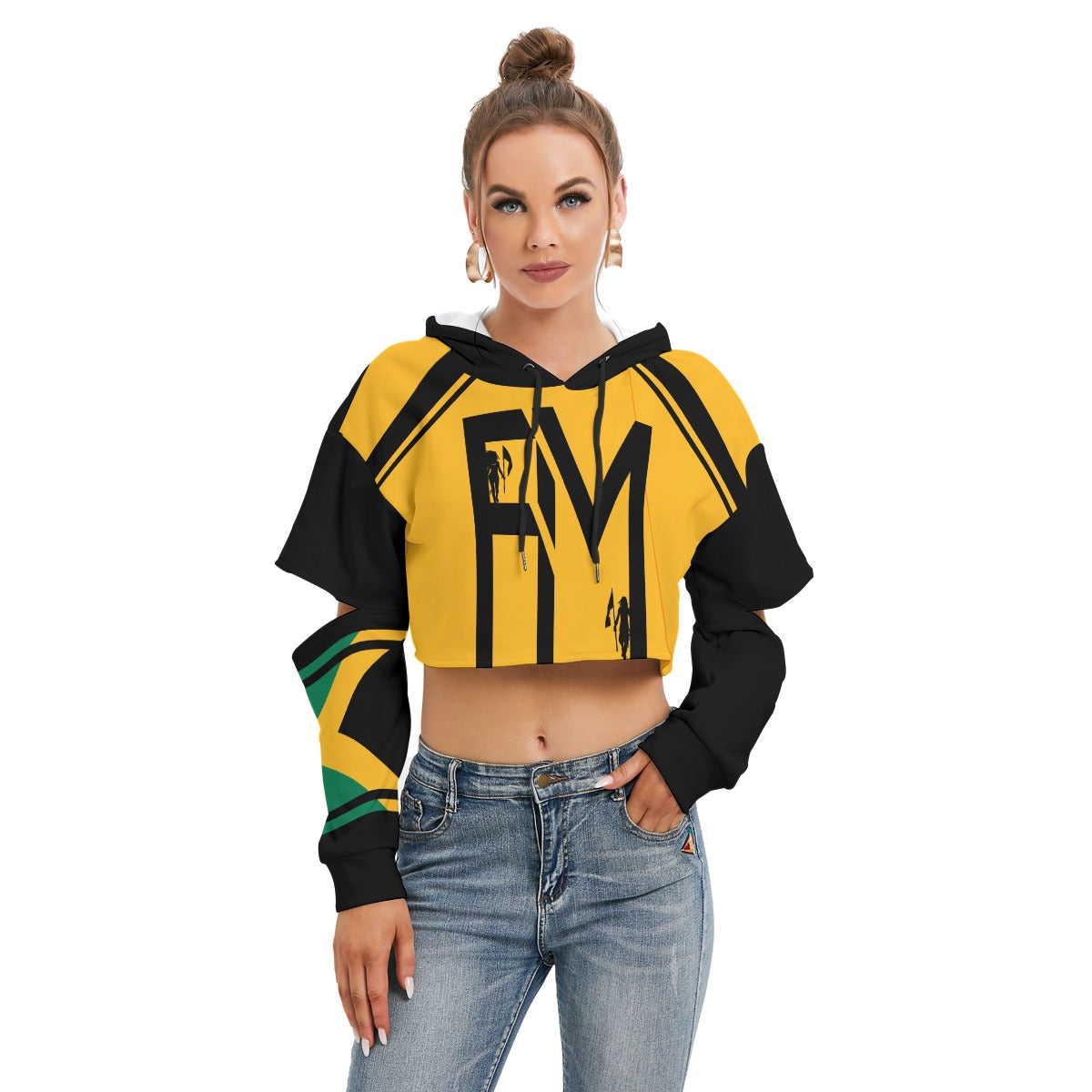
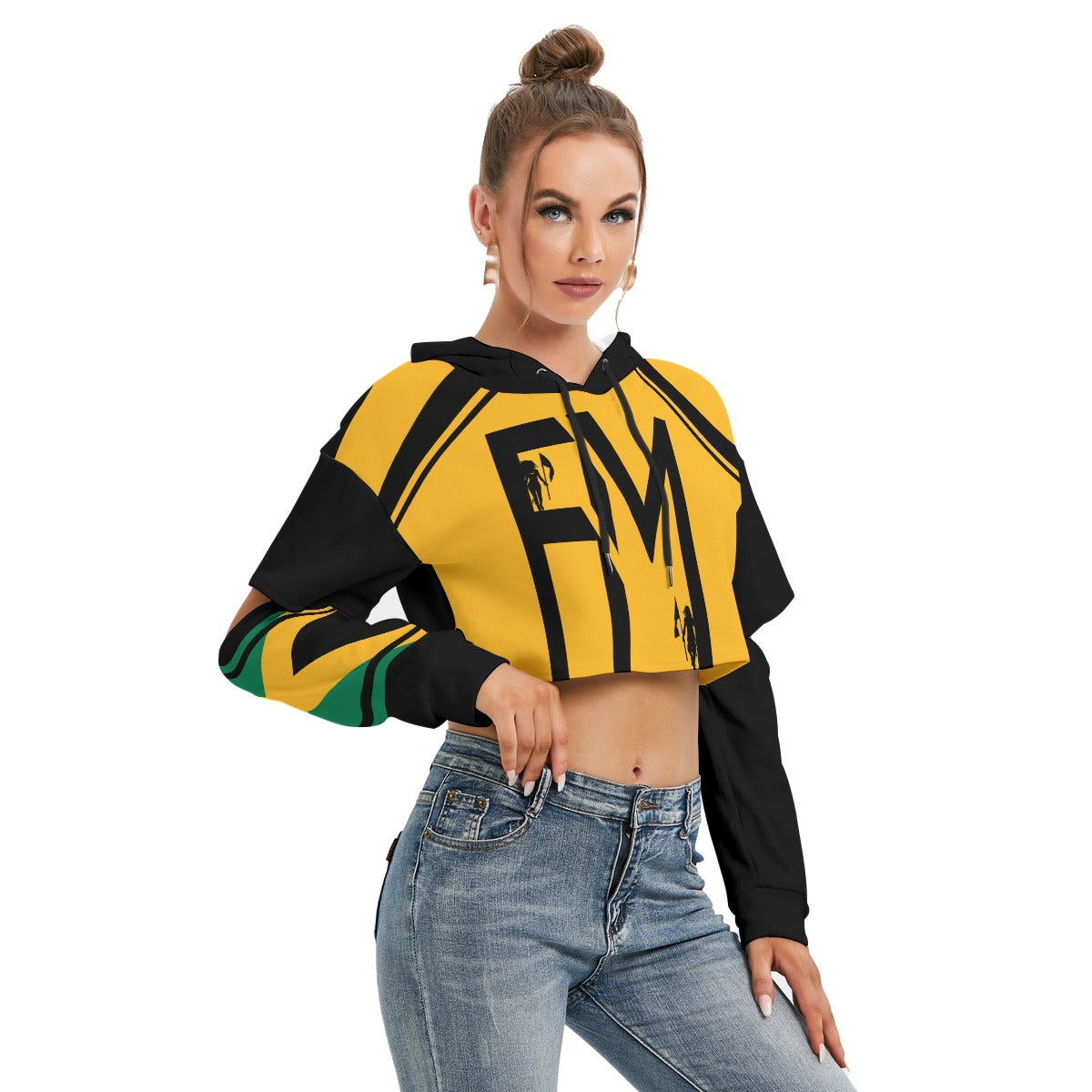
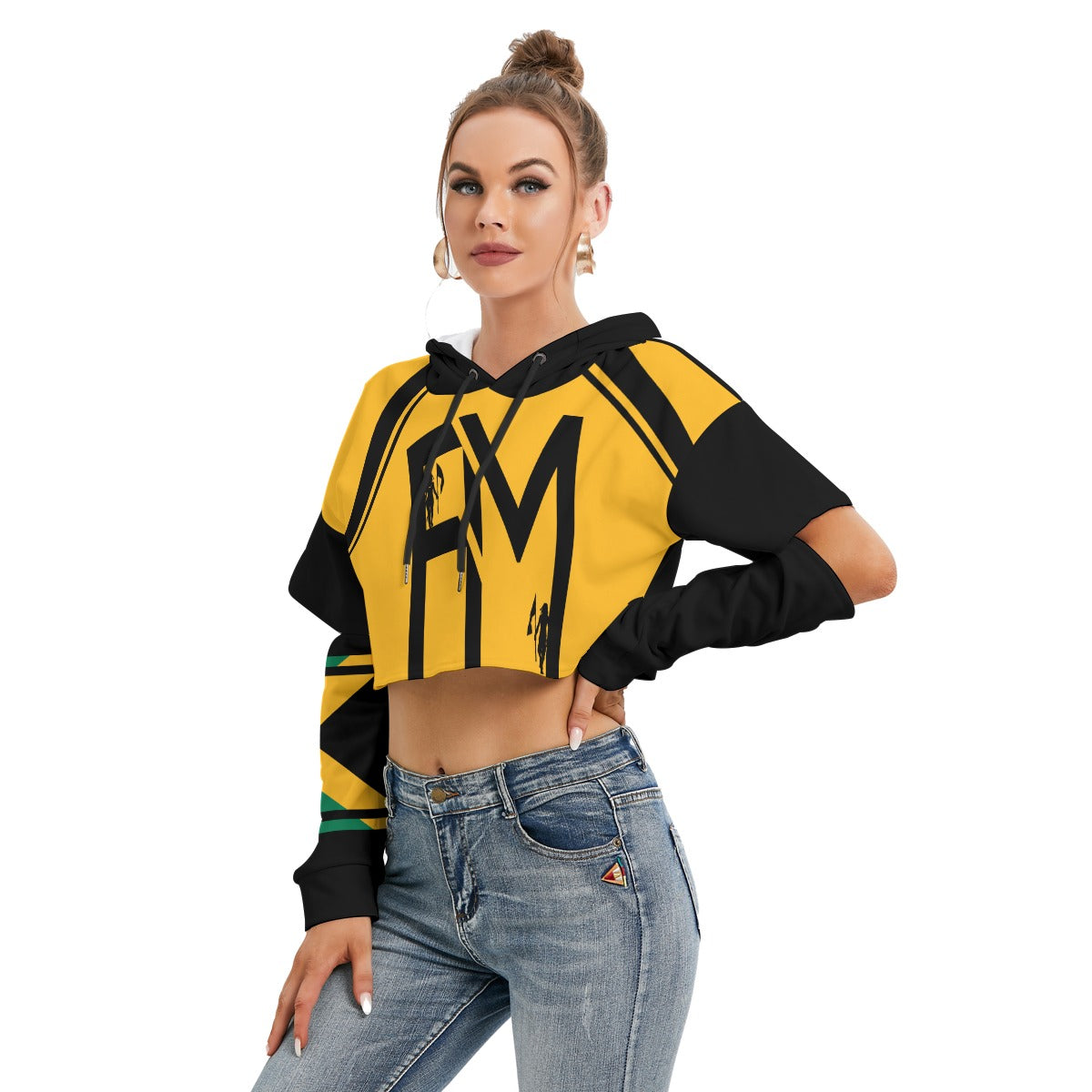
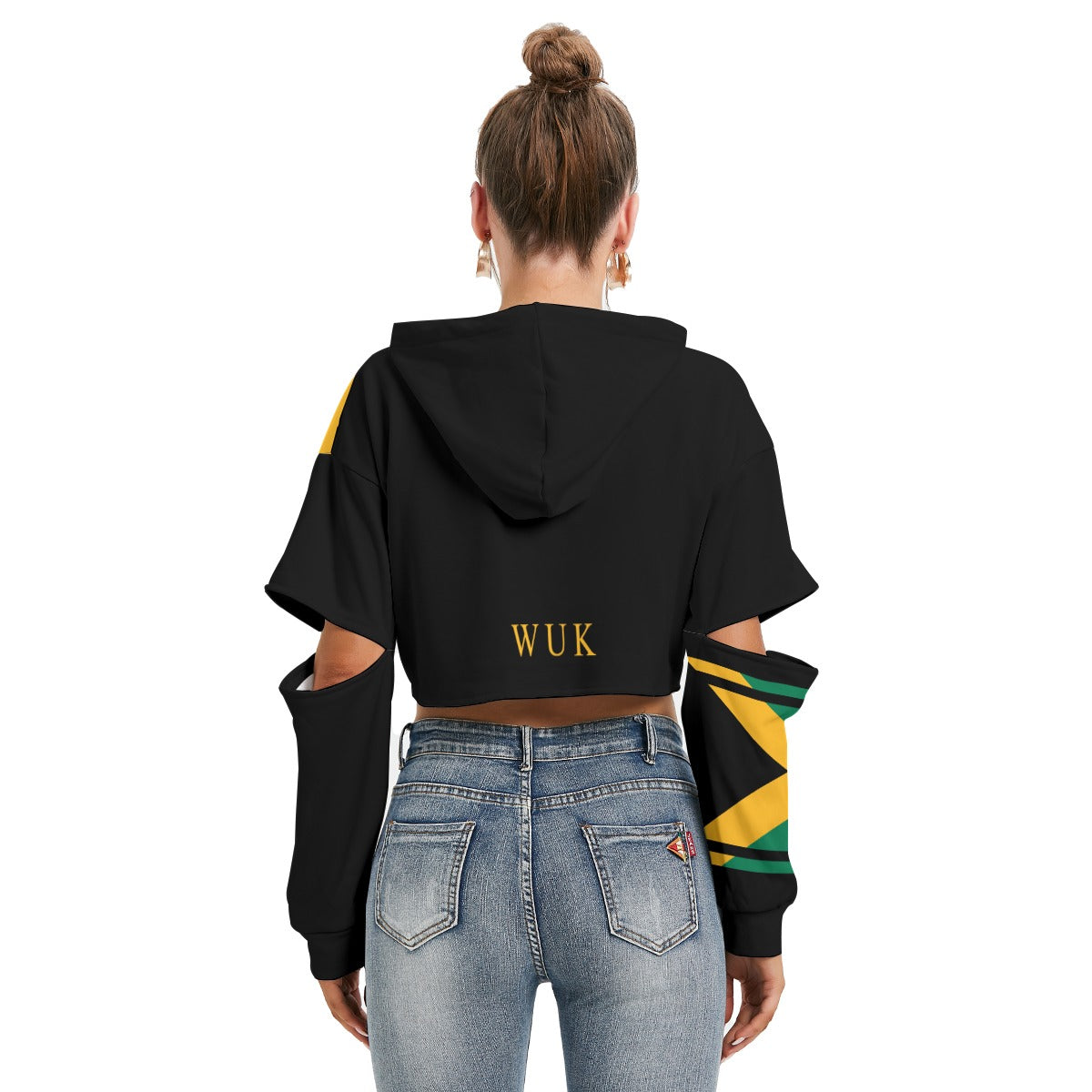
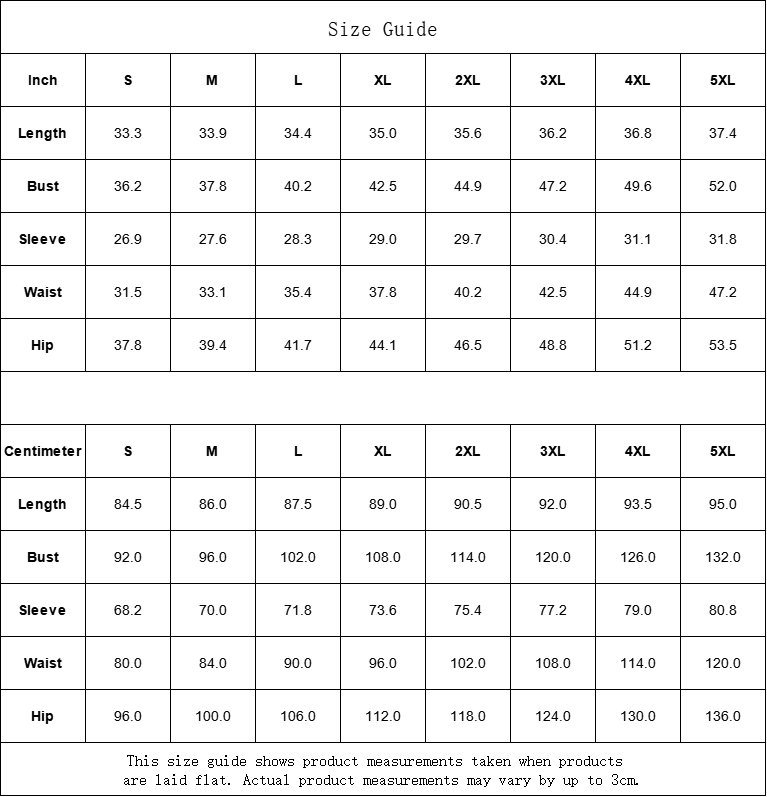
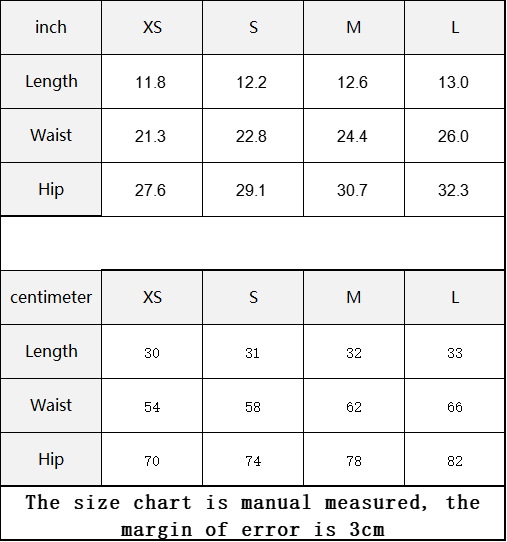
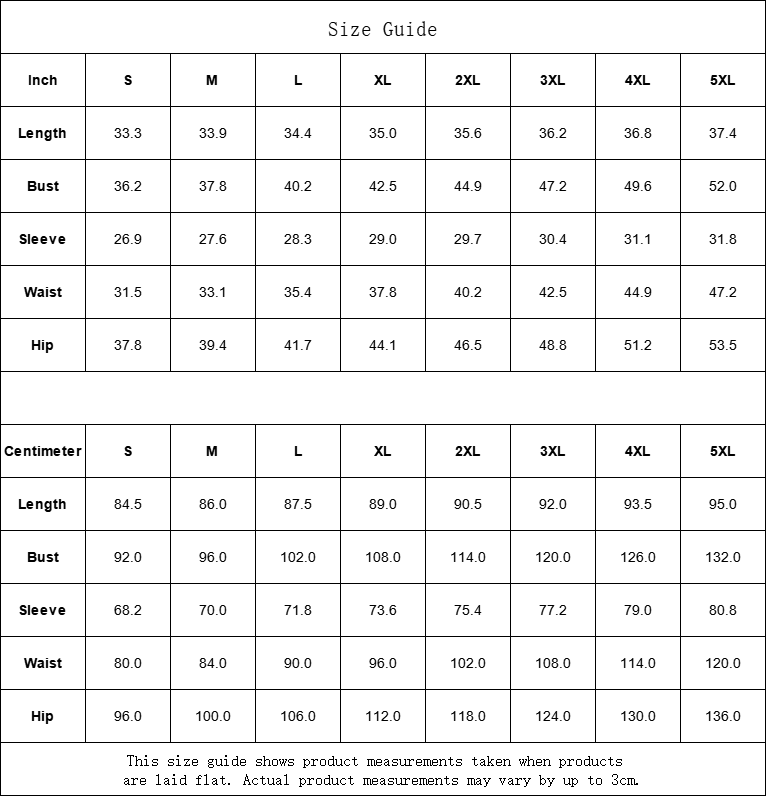
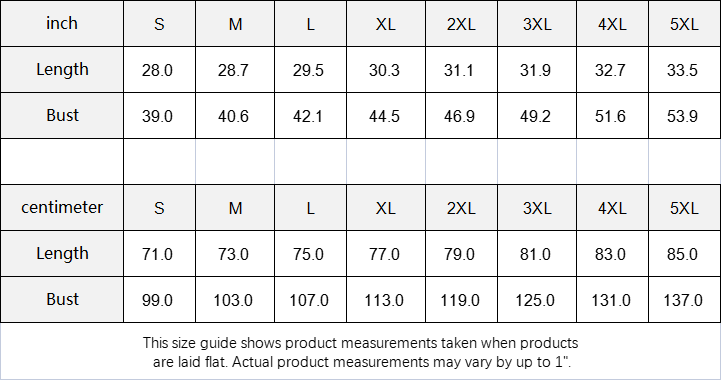
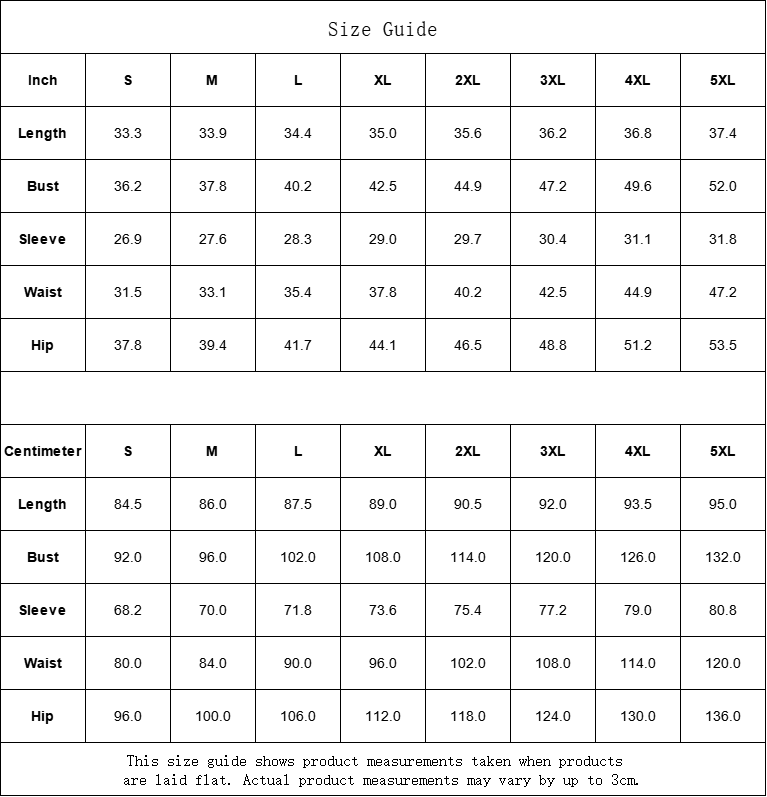
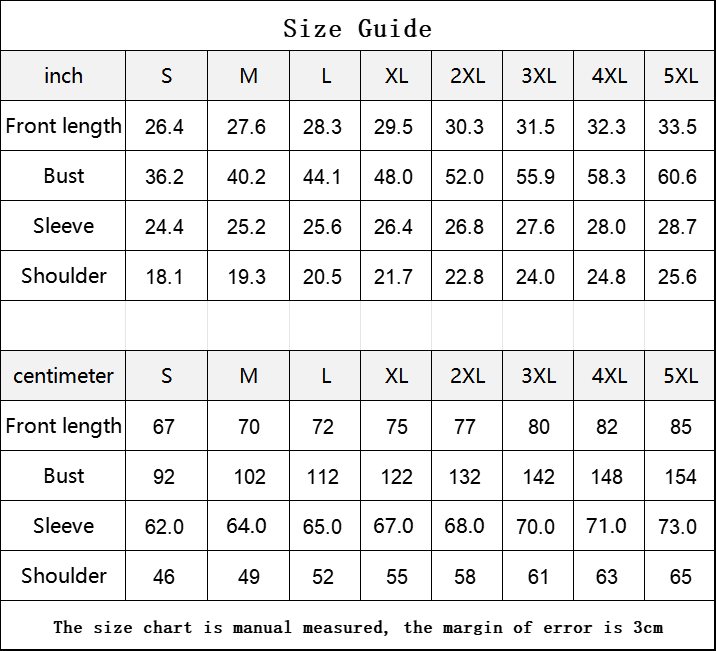
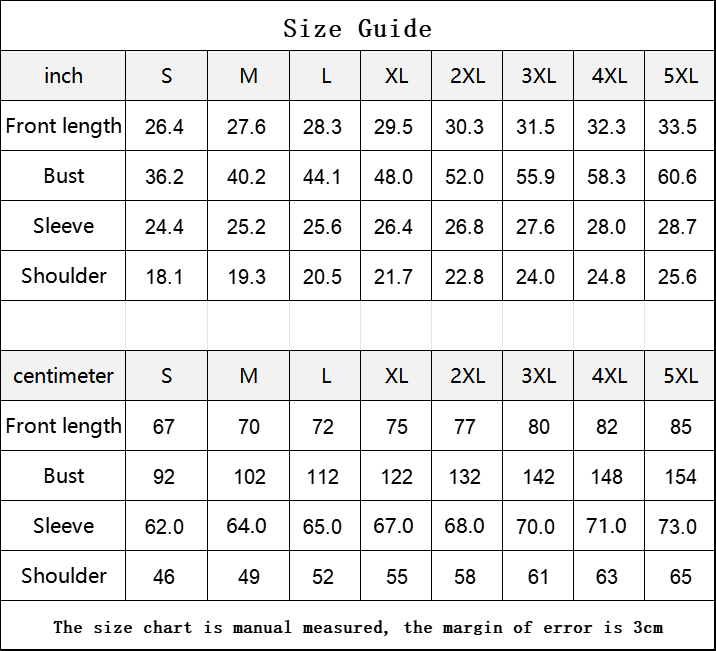
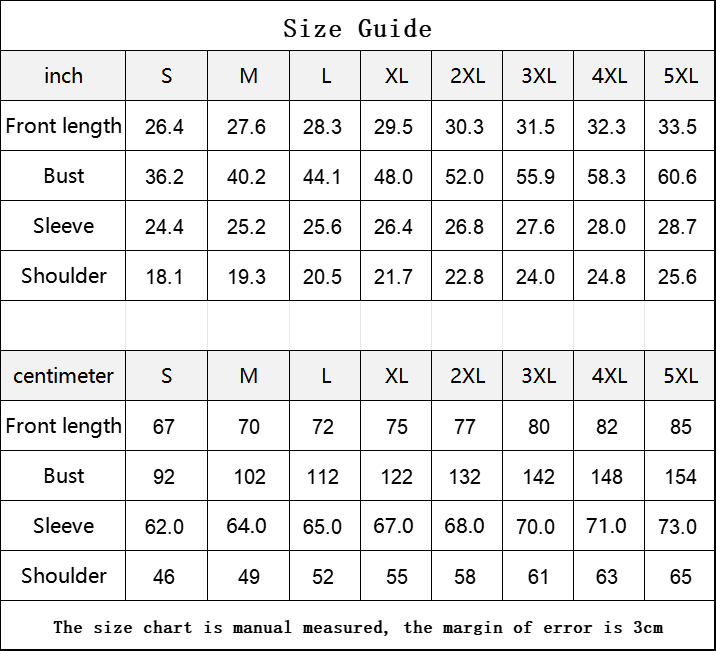
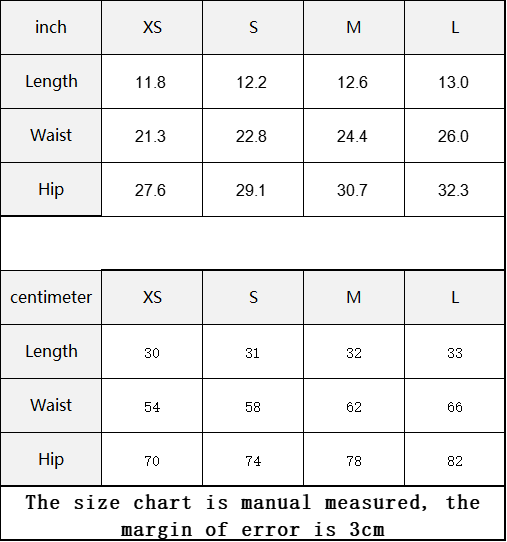
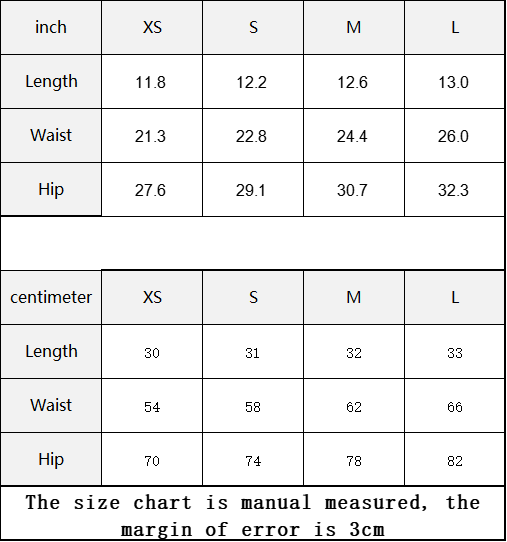
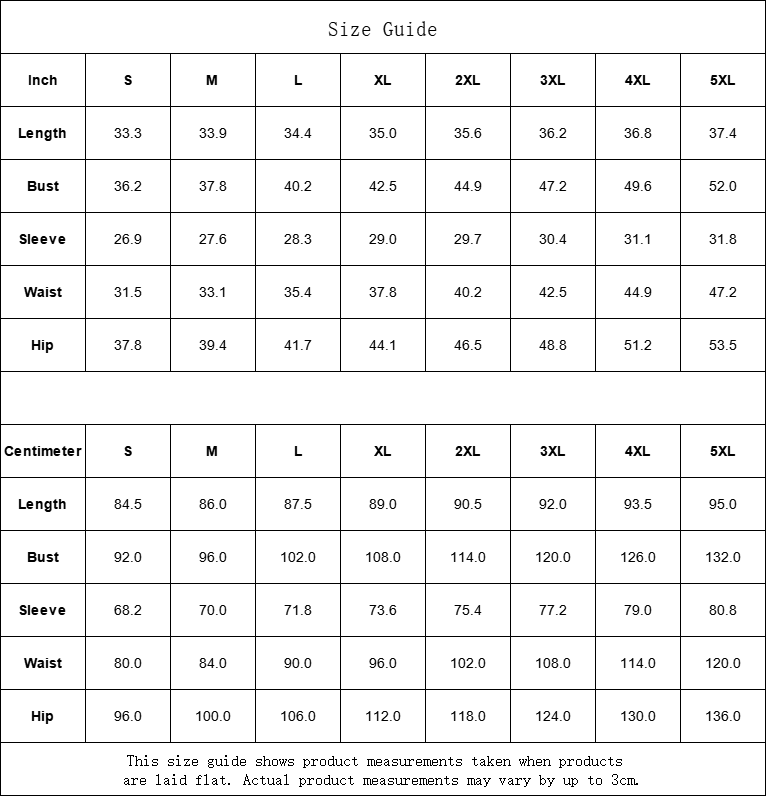
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $50.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$60.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $50.00
Follow Us!
on Instagram.
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$55.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$55.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $40.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
$55.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$55.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $40.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00