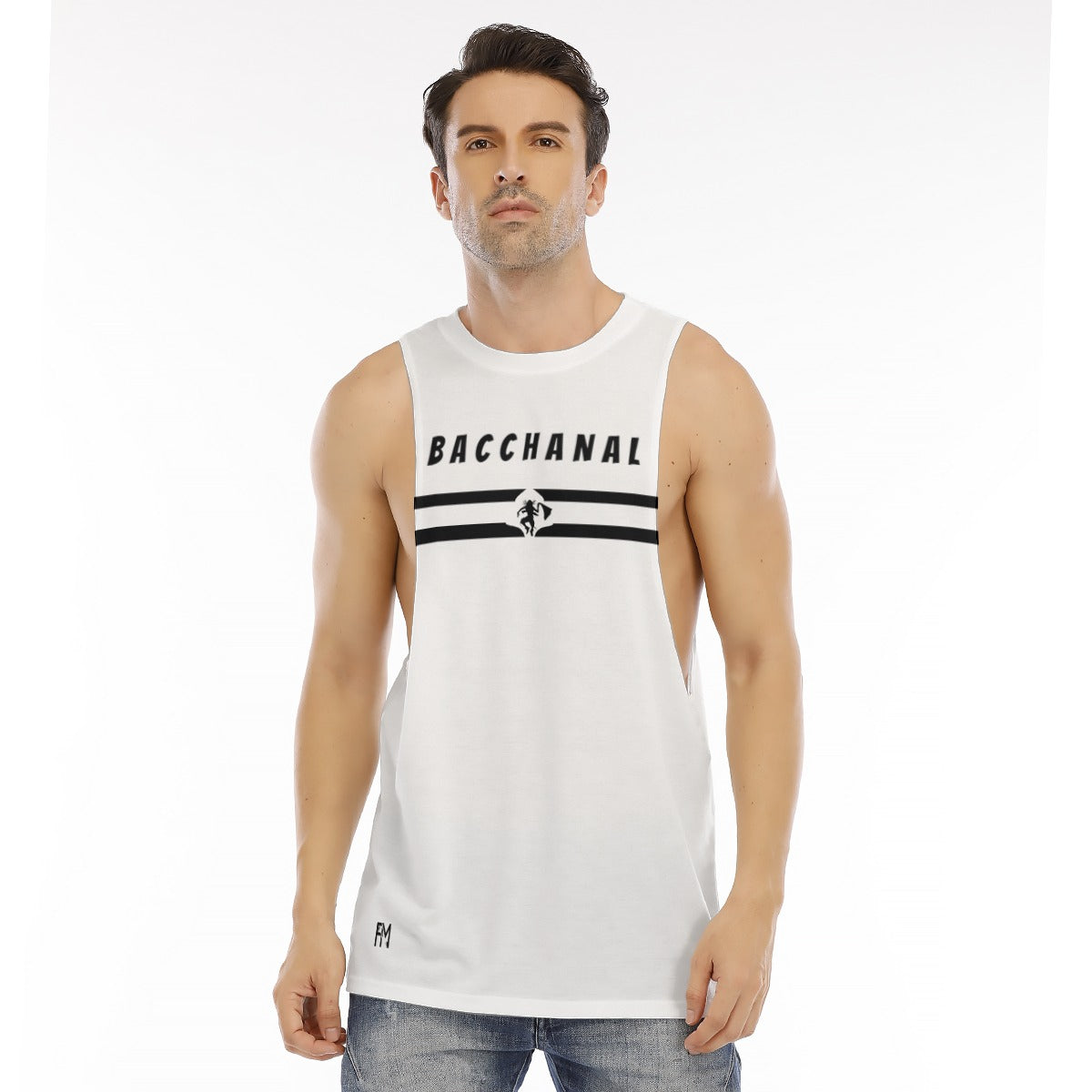
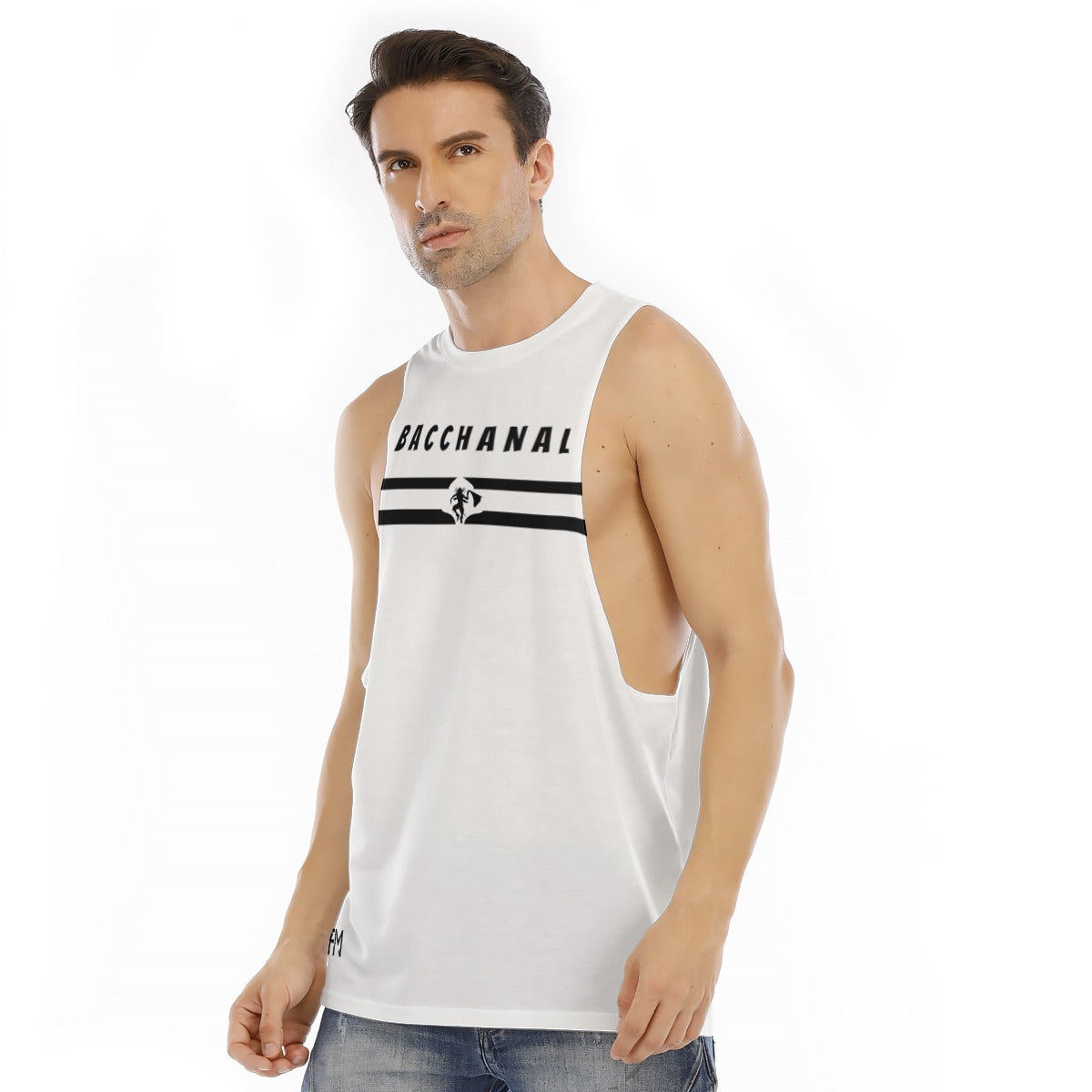
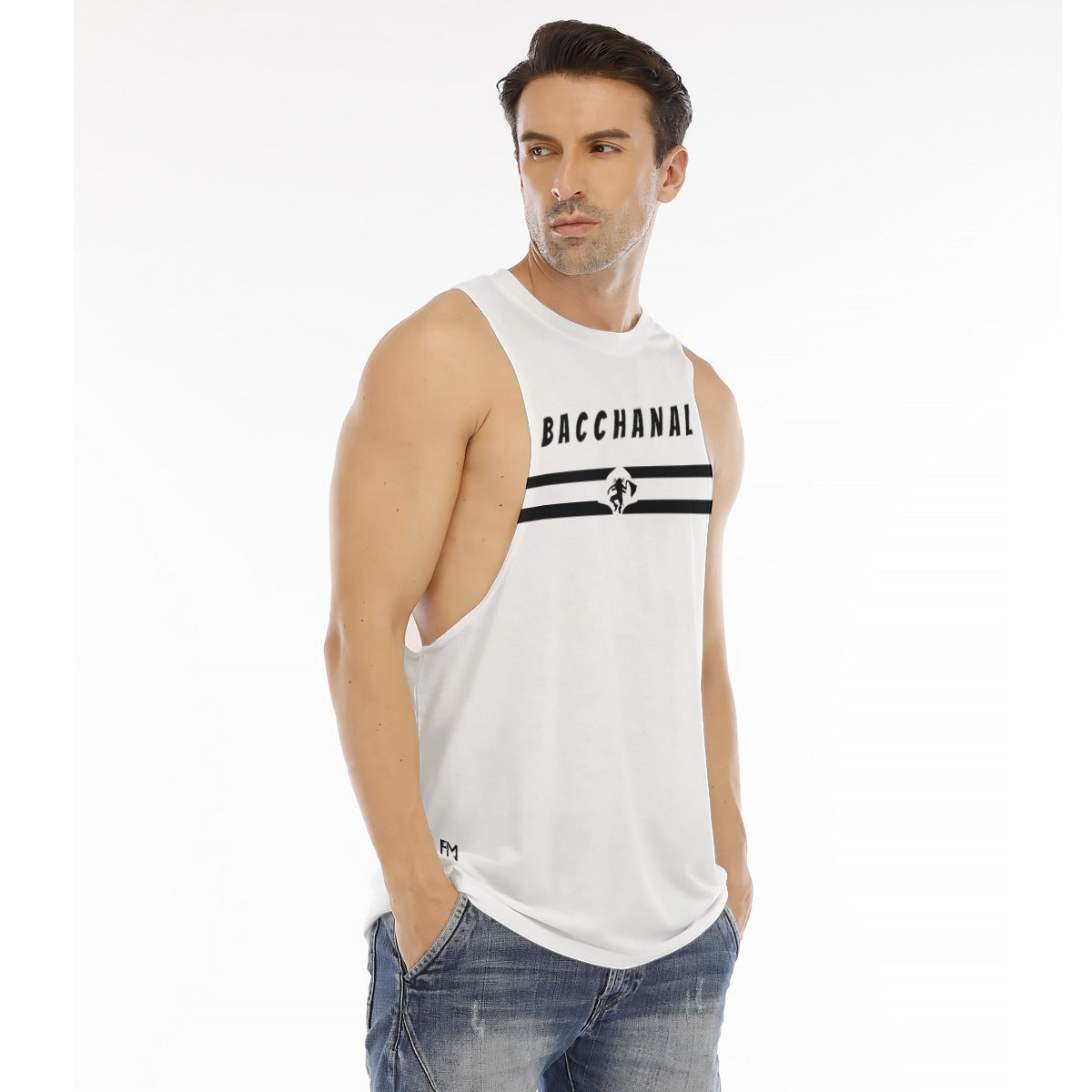
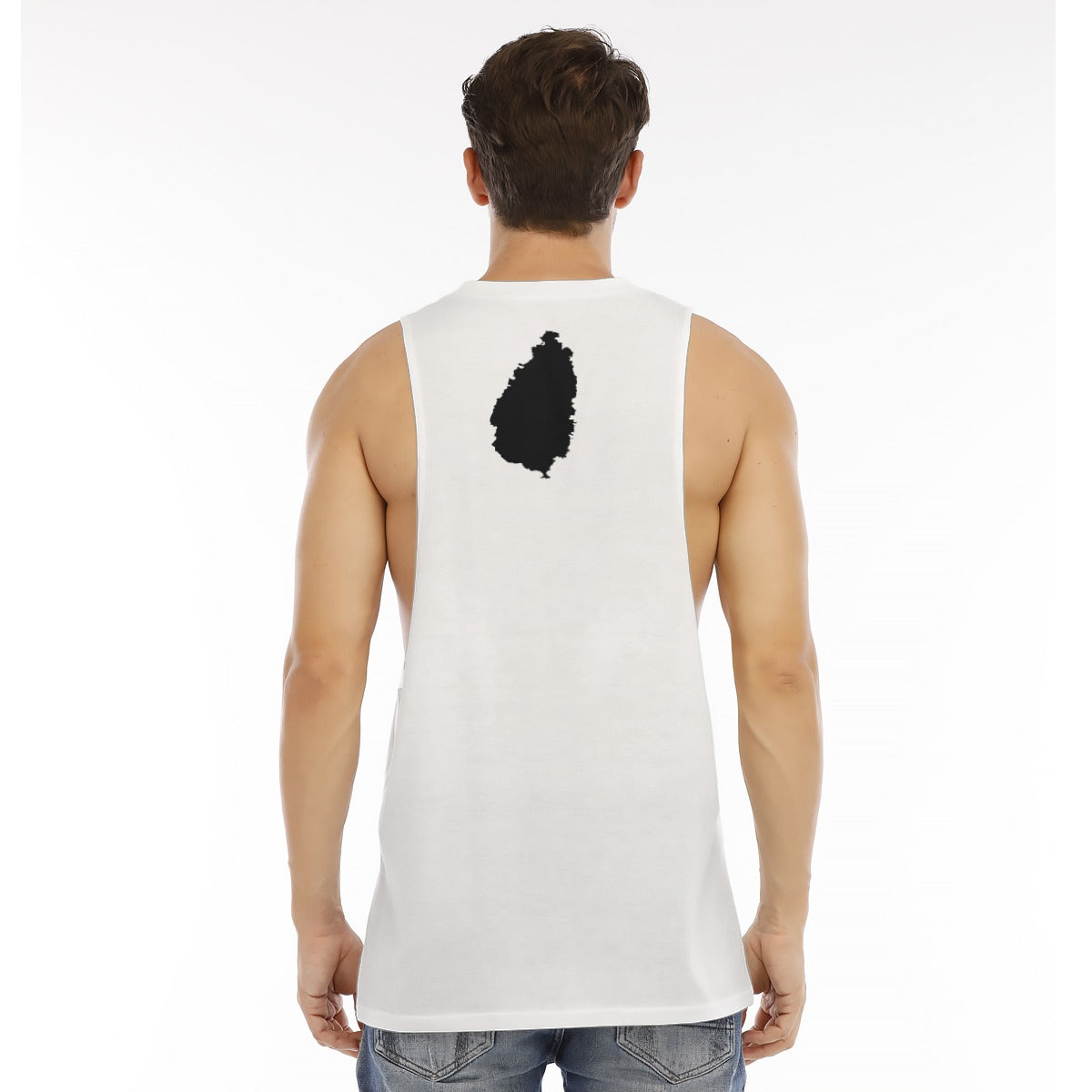
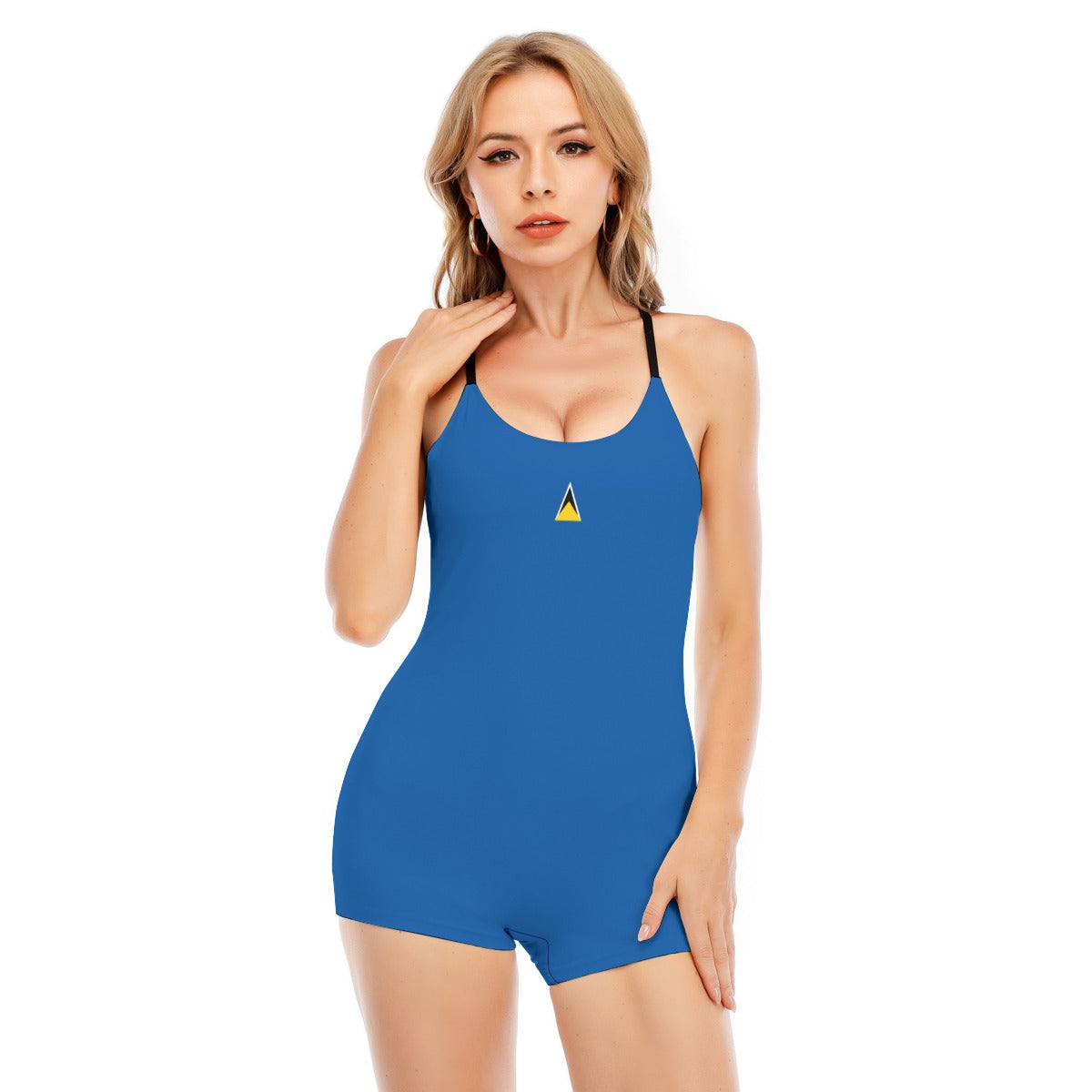
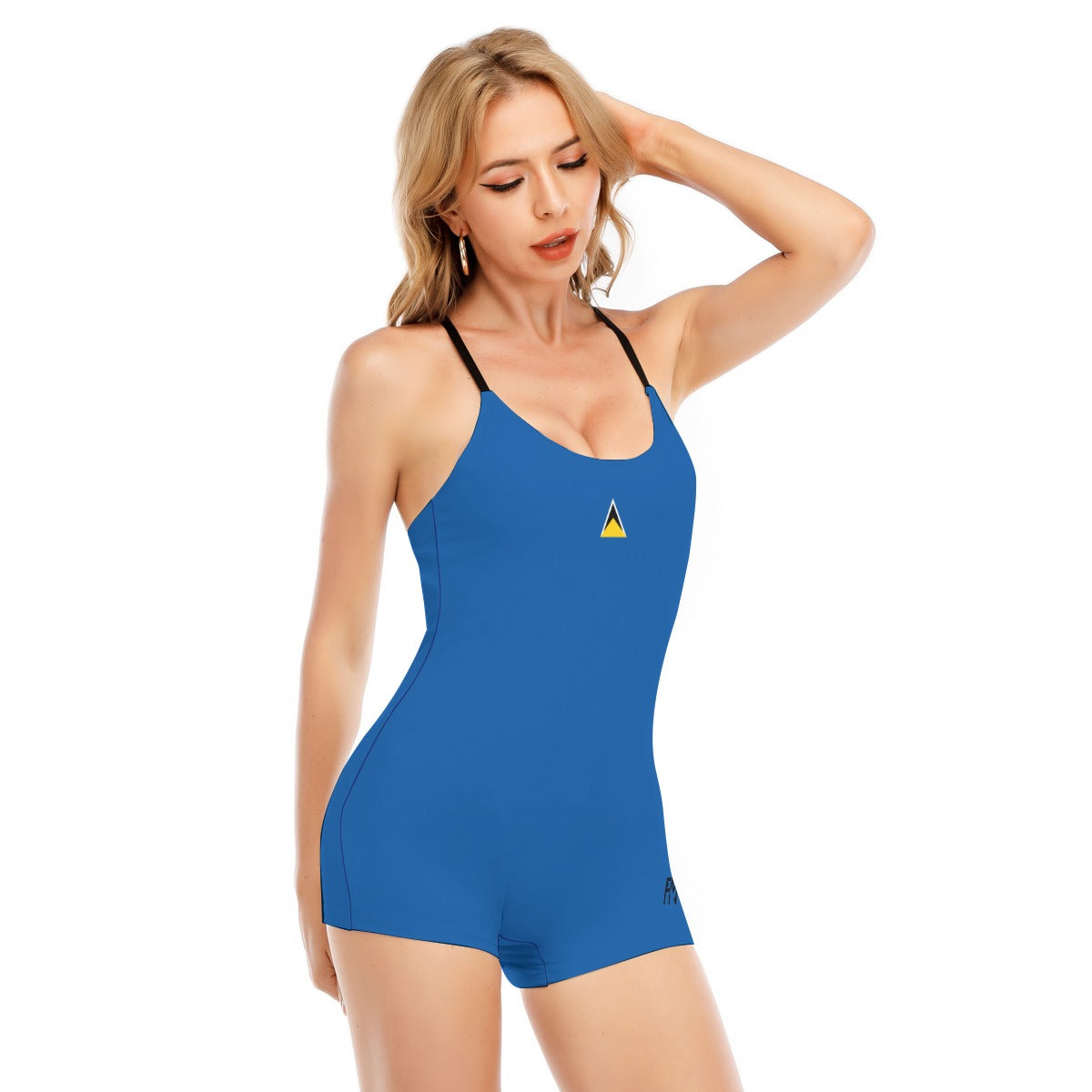
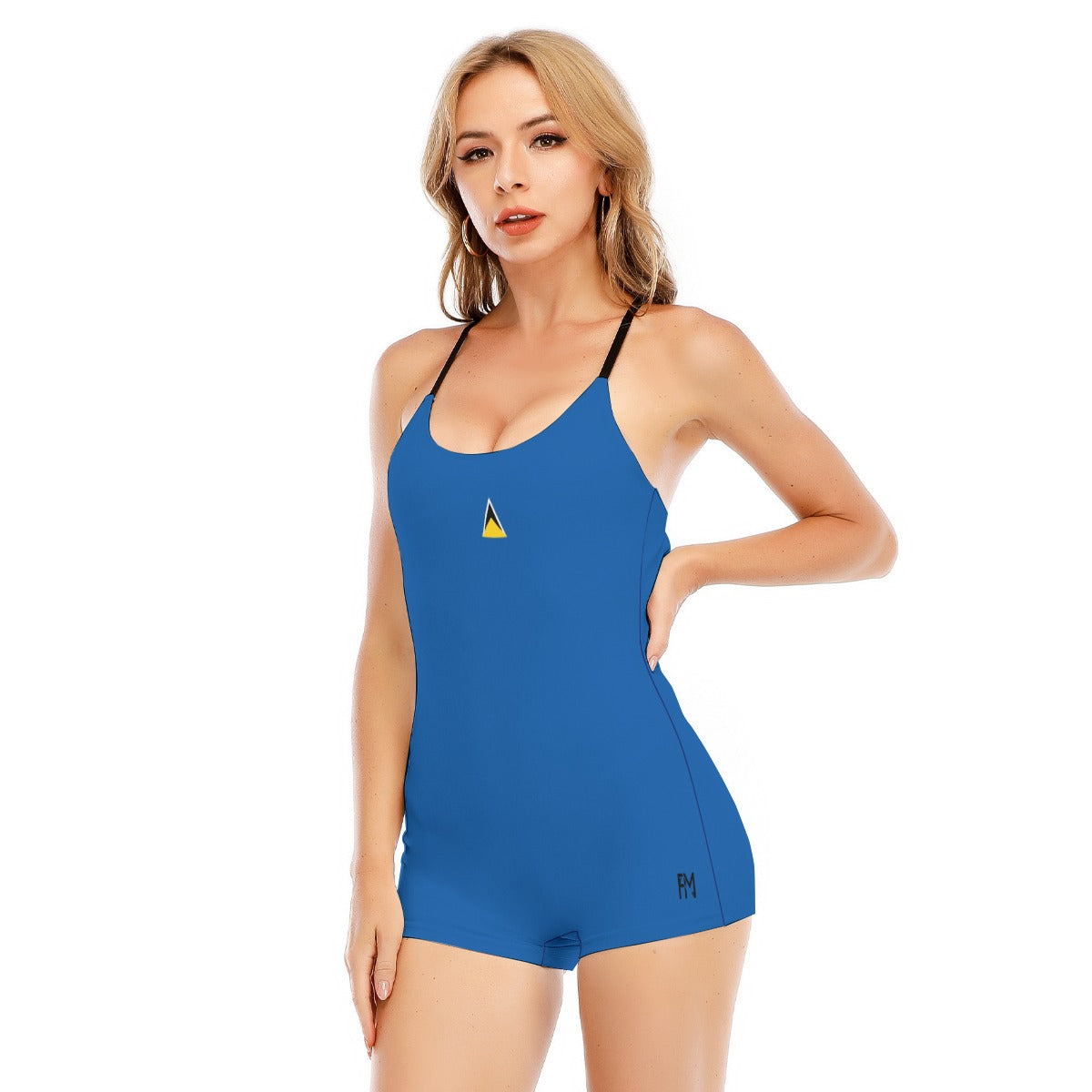
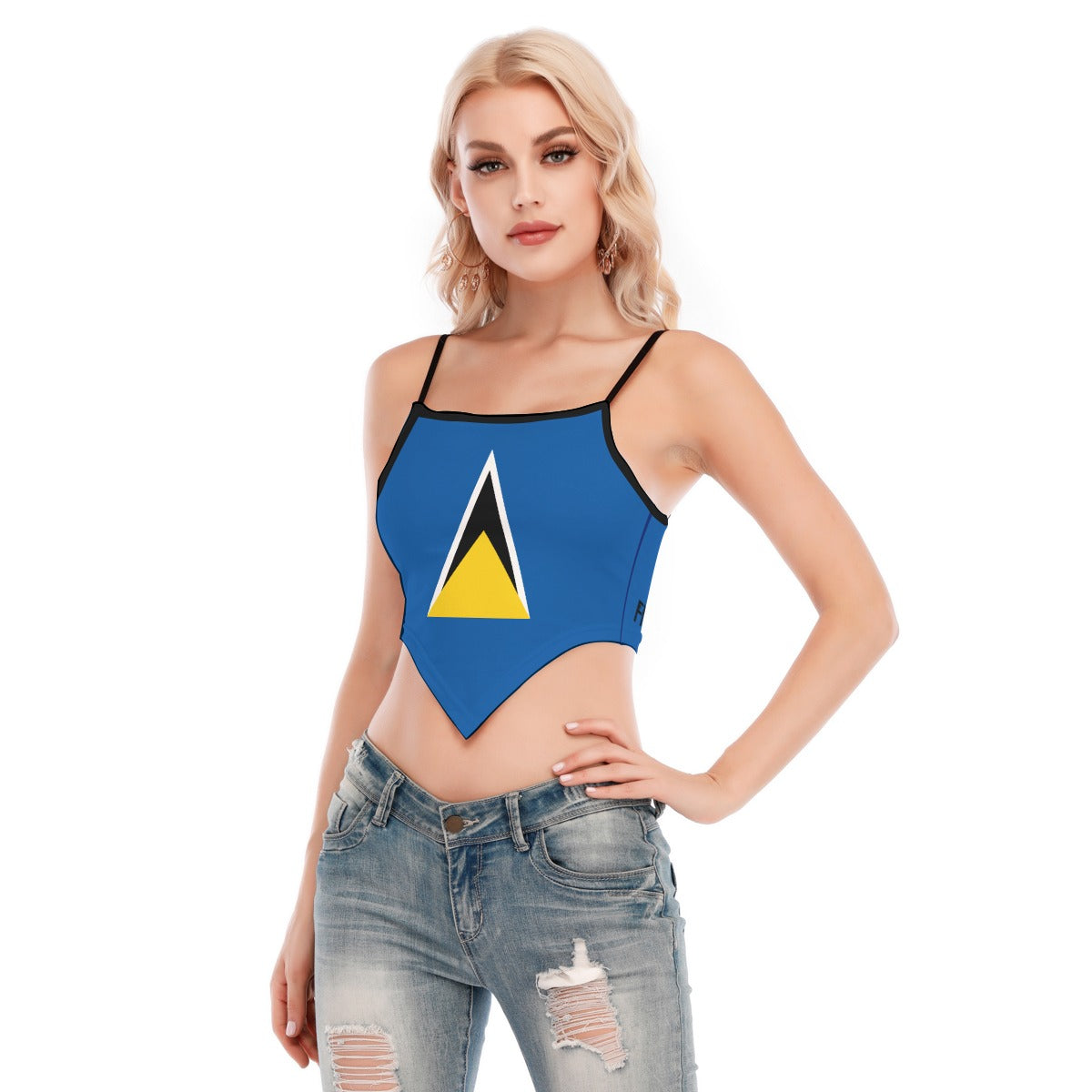
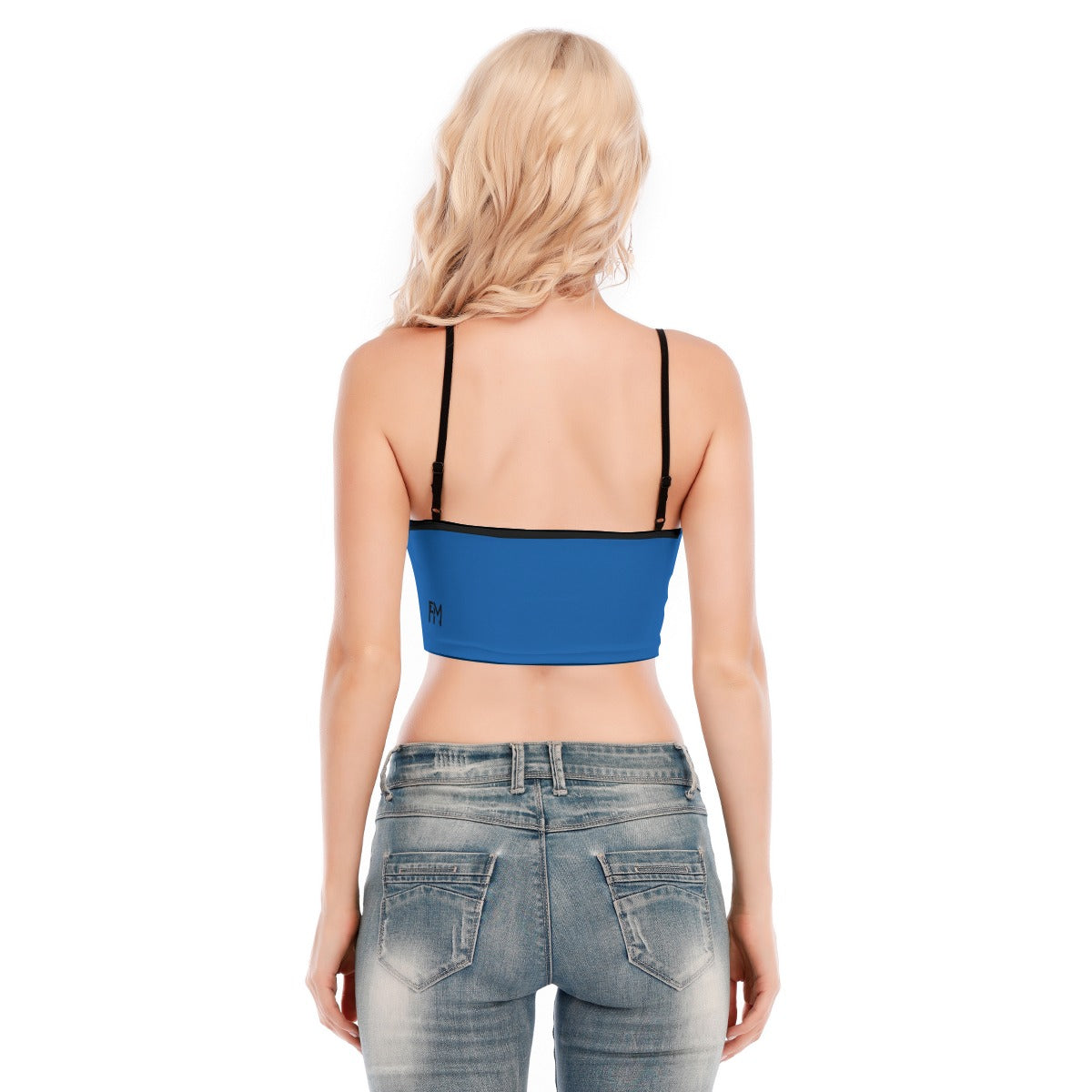
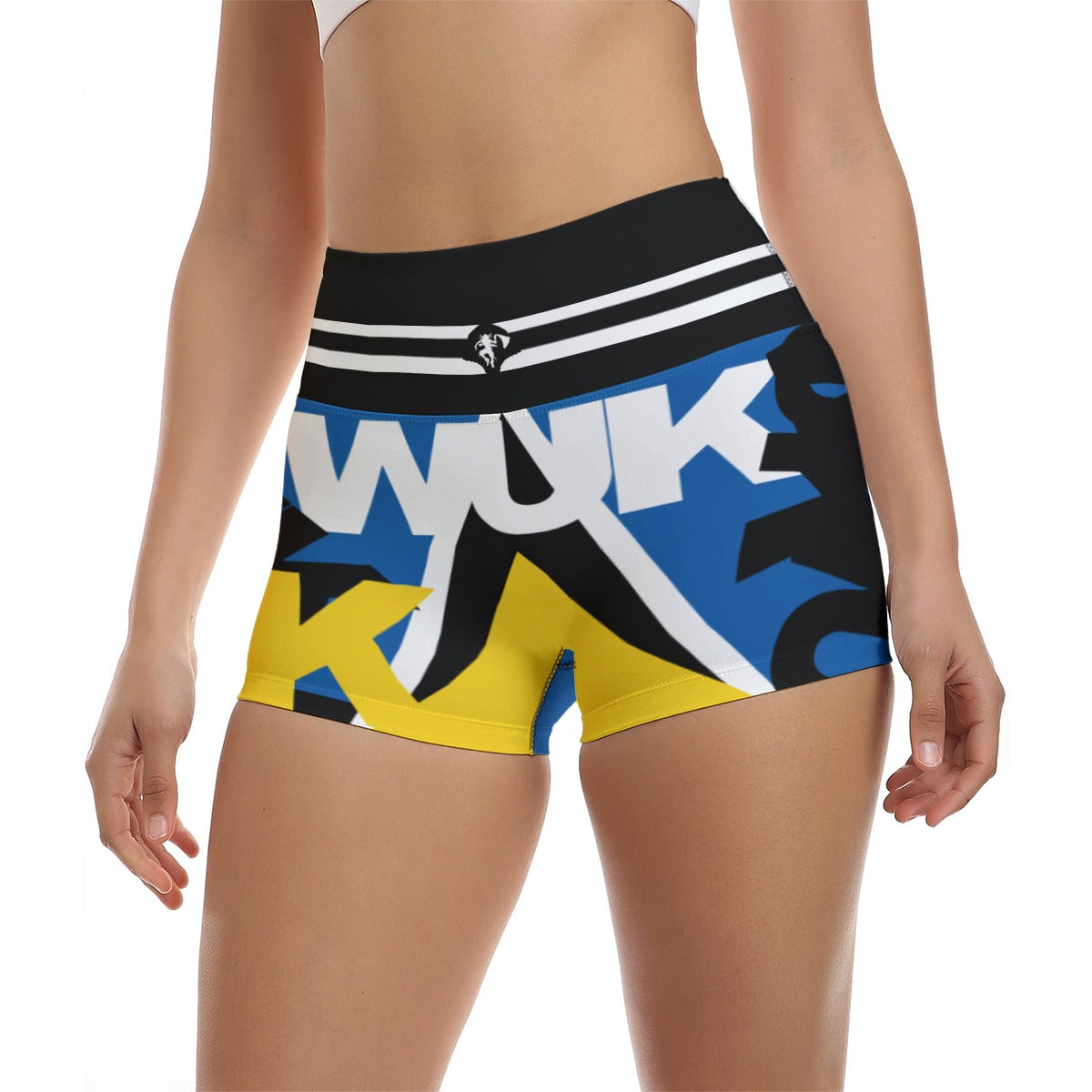
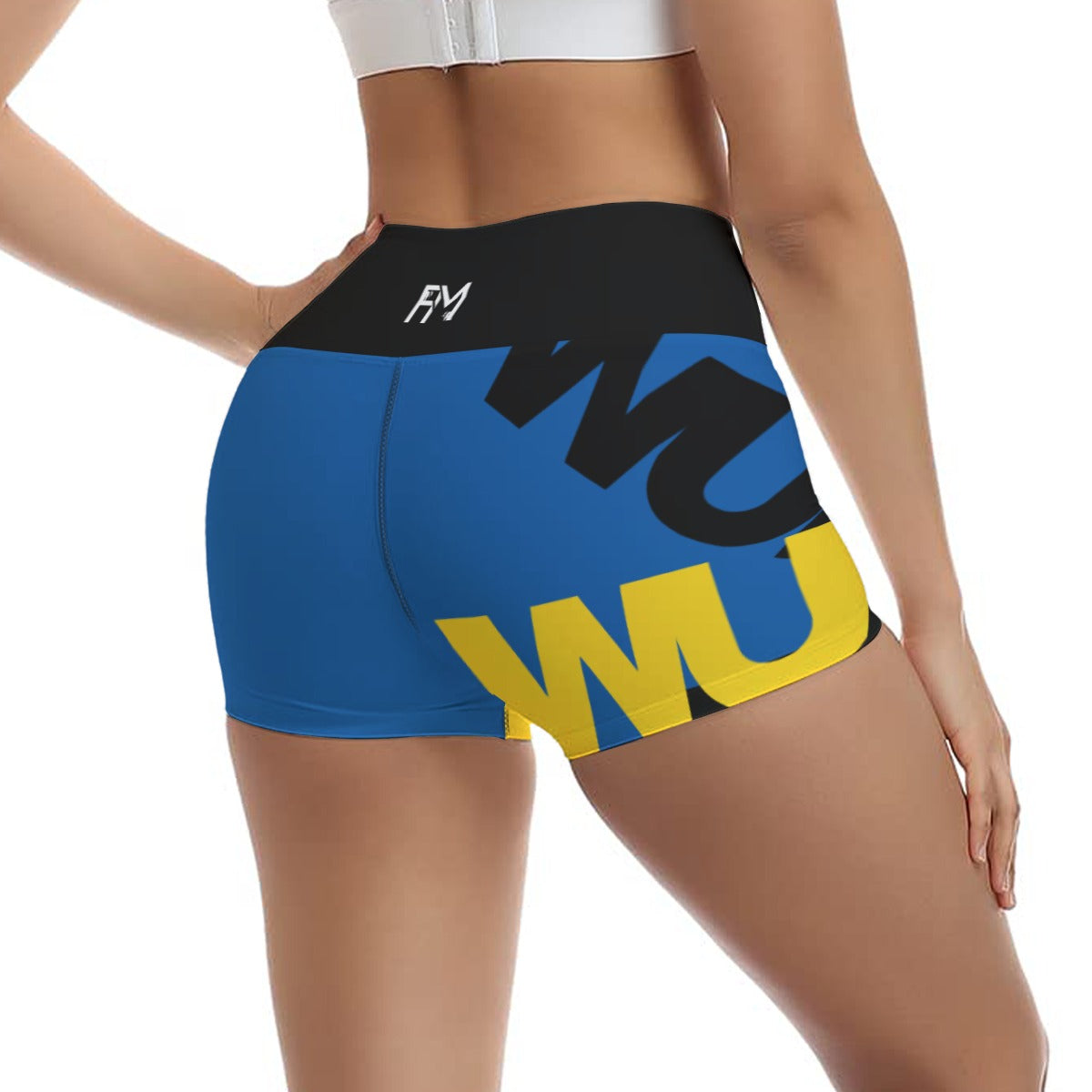
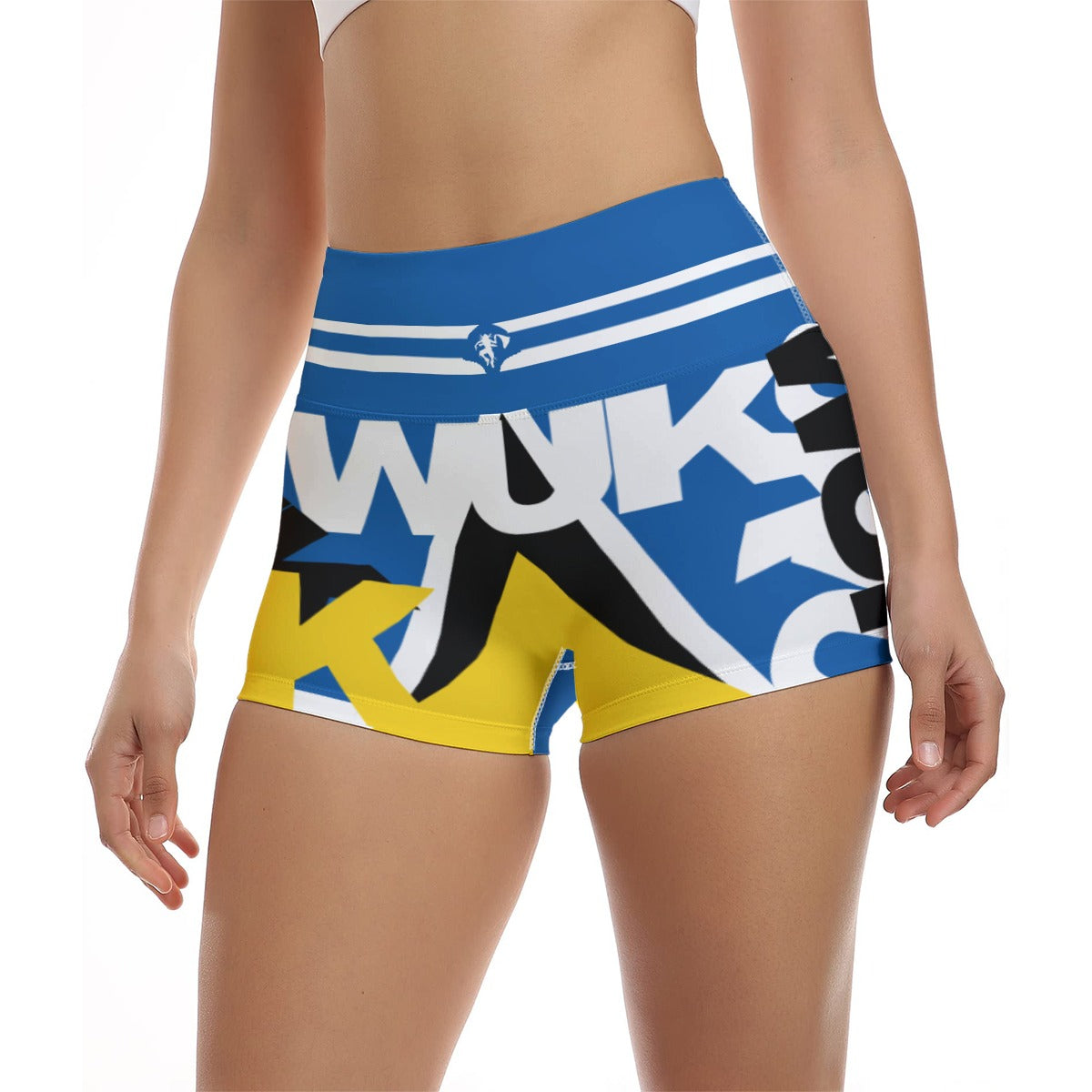
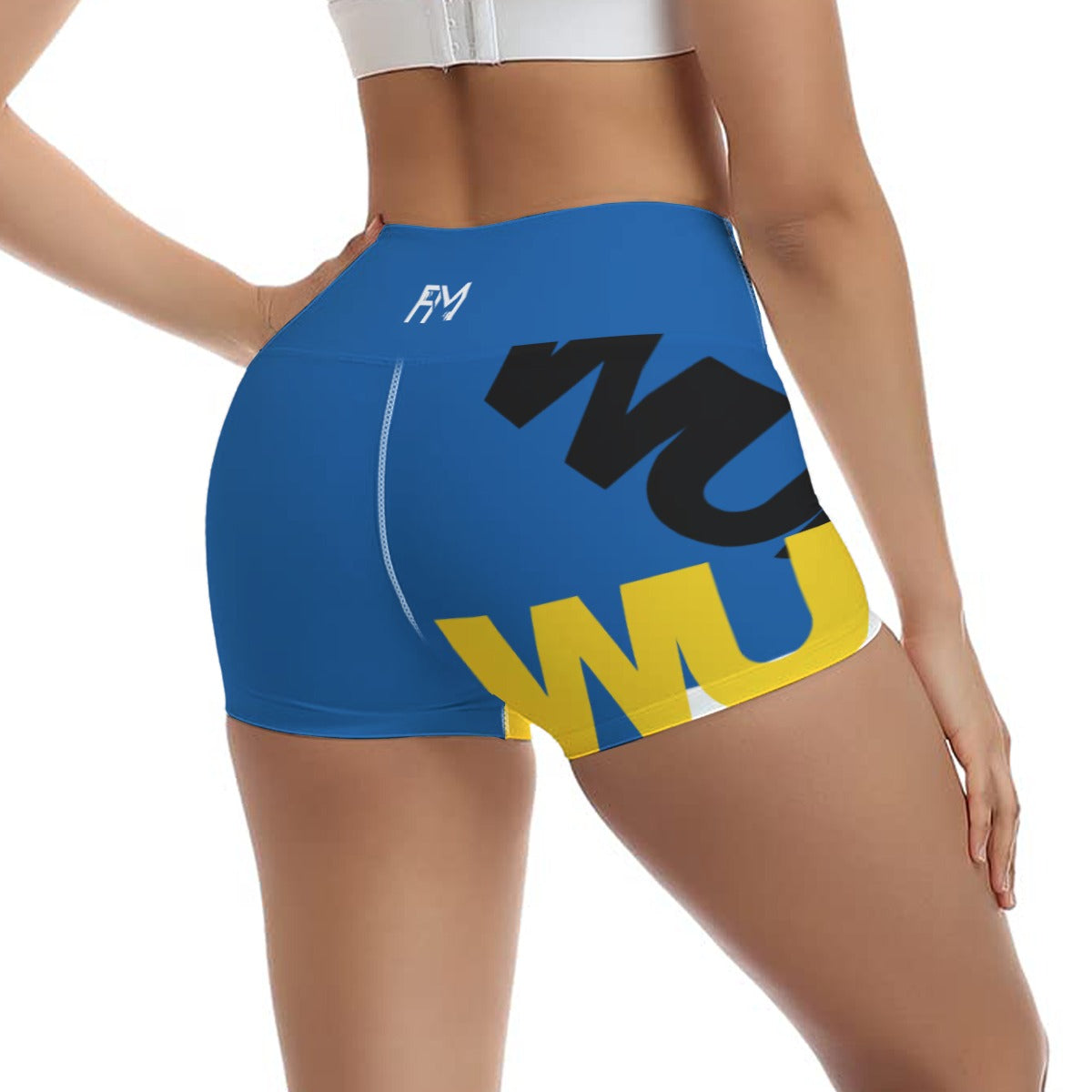
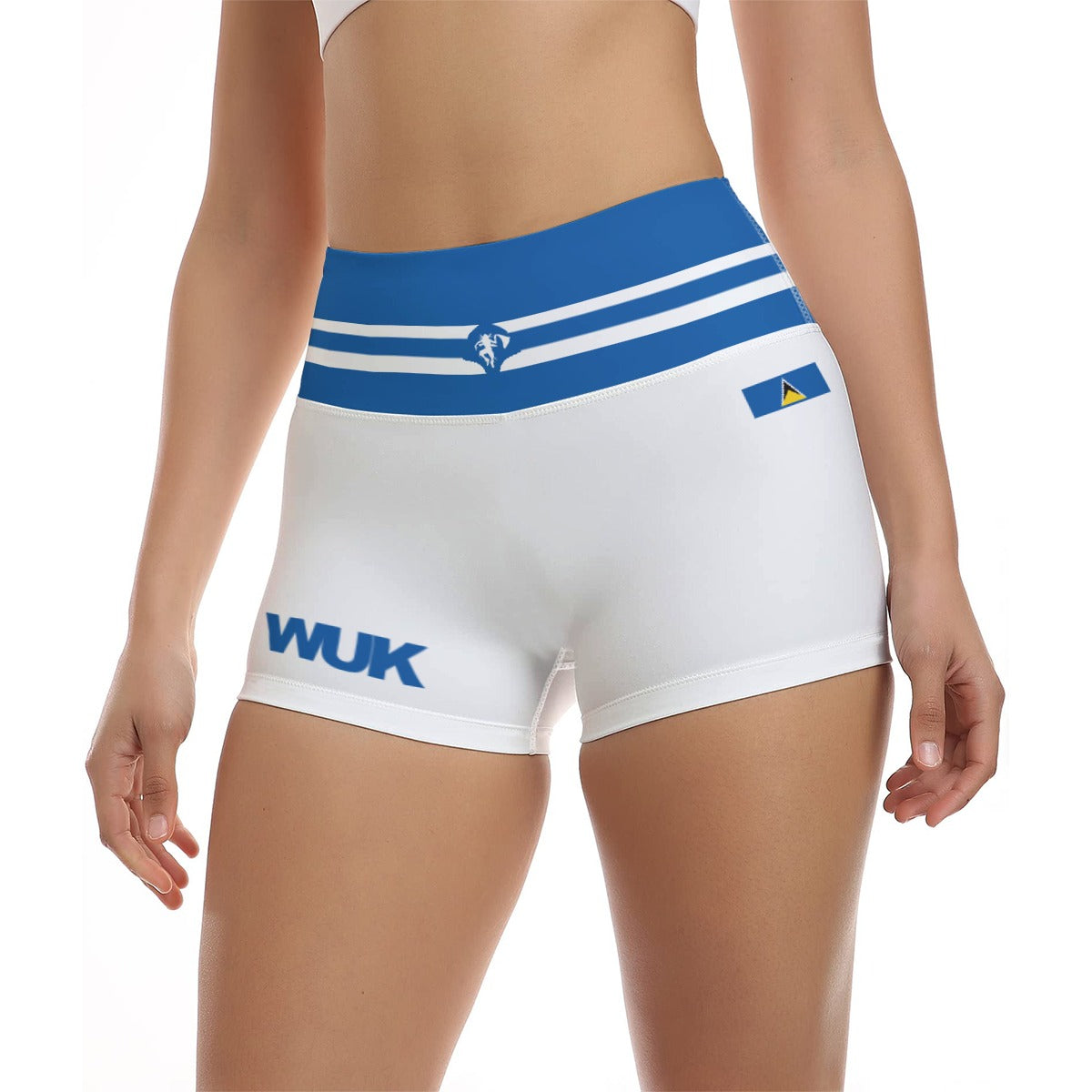
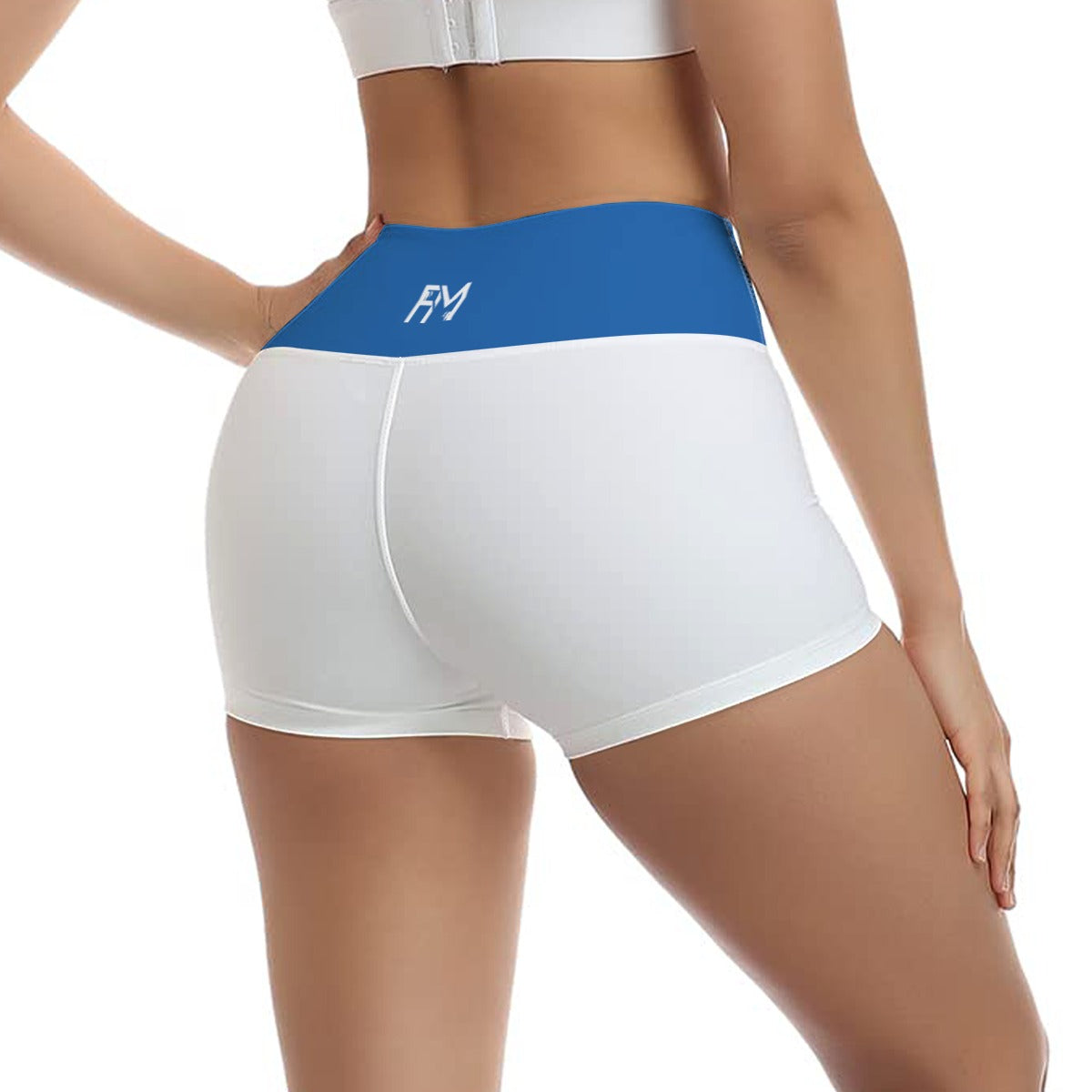
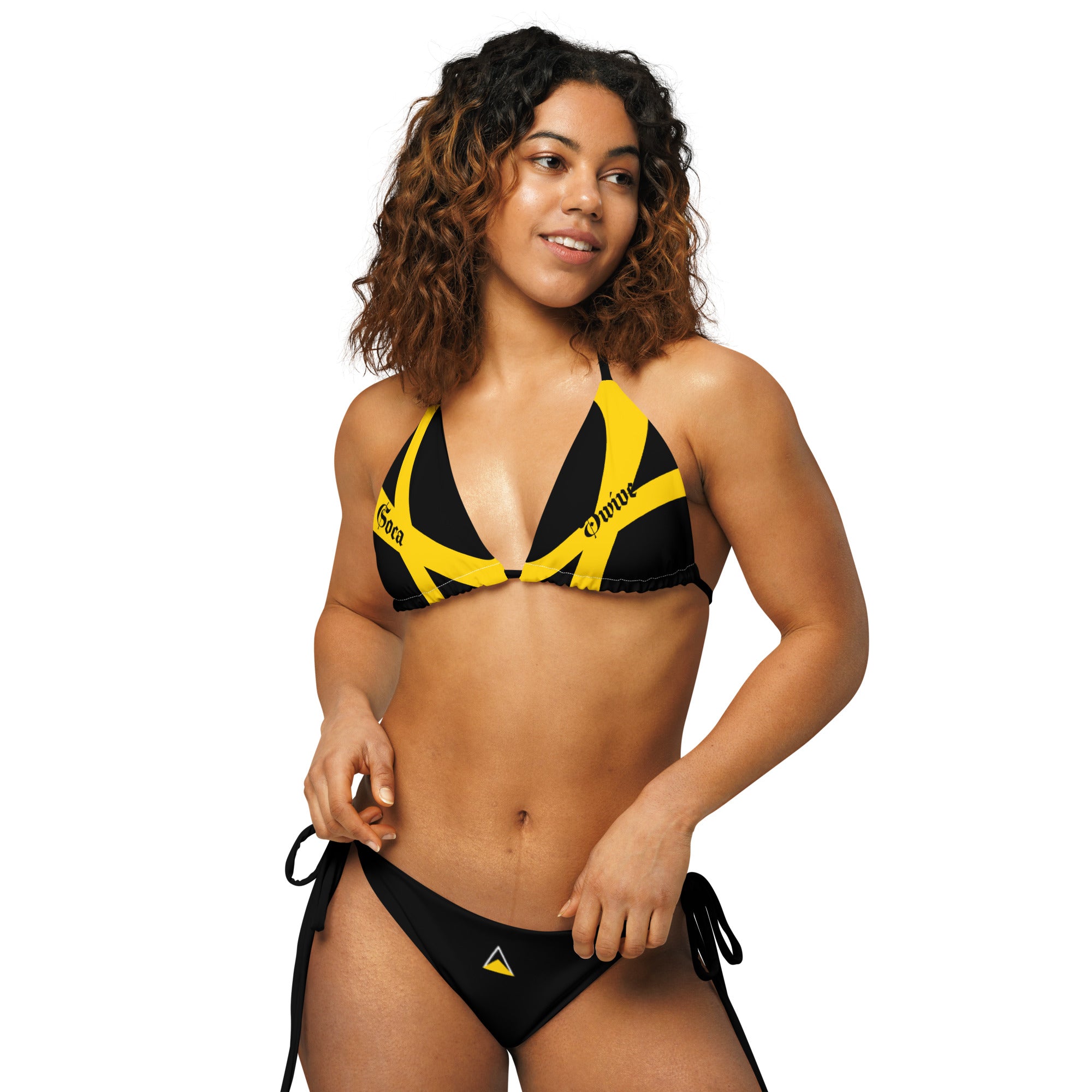
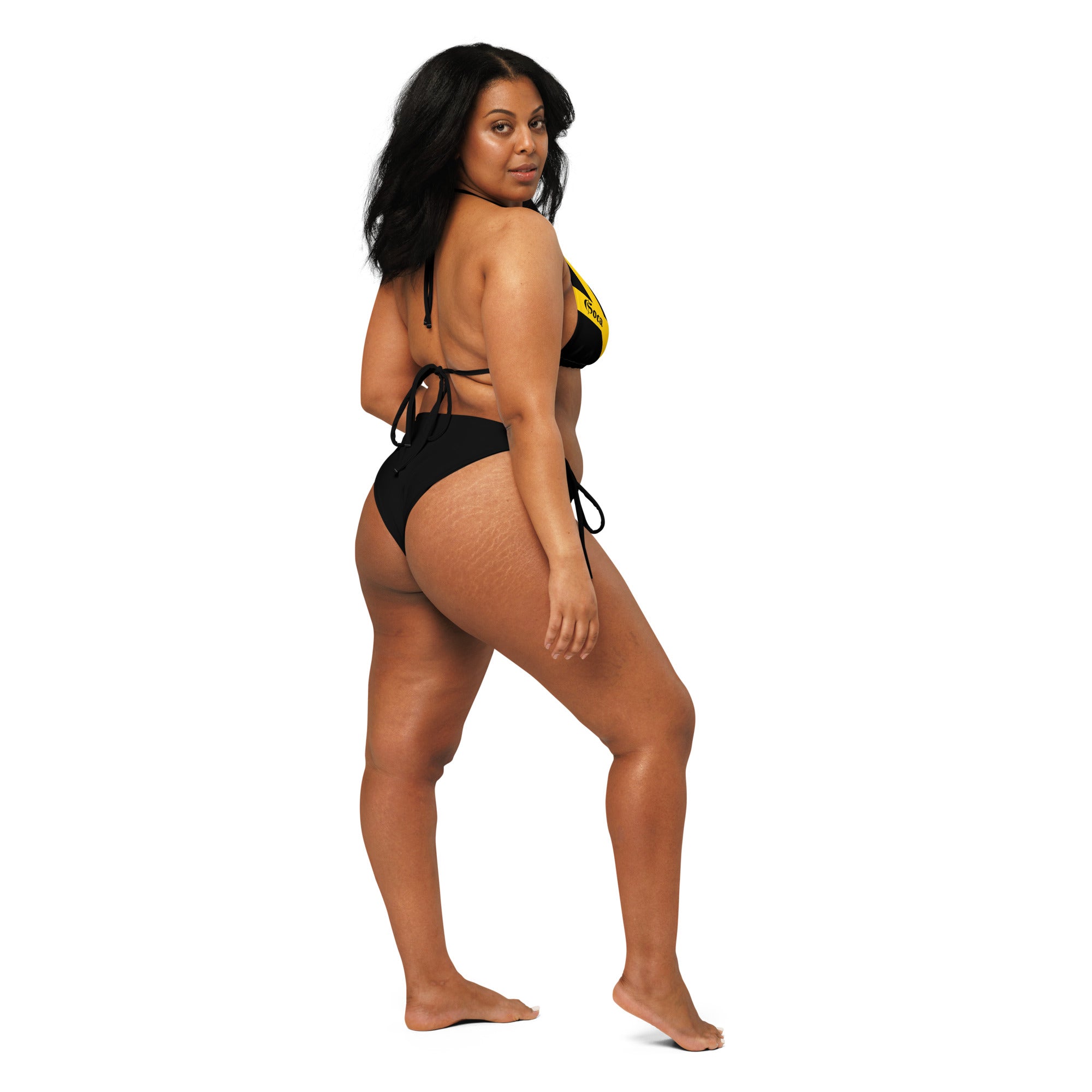
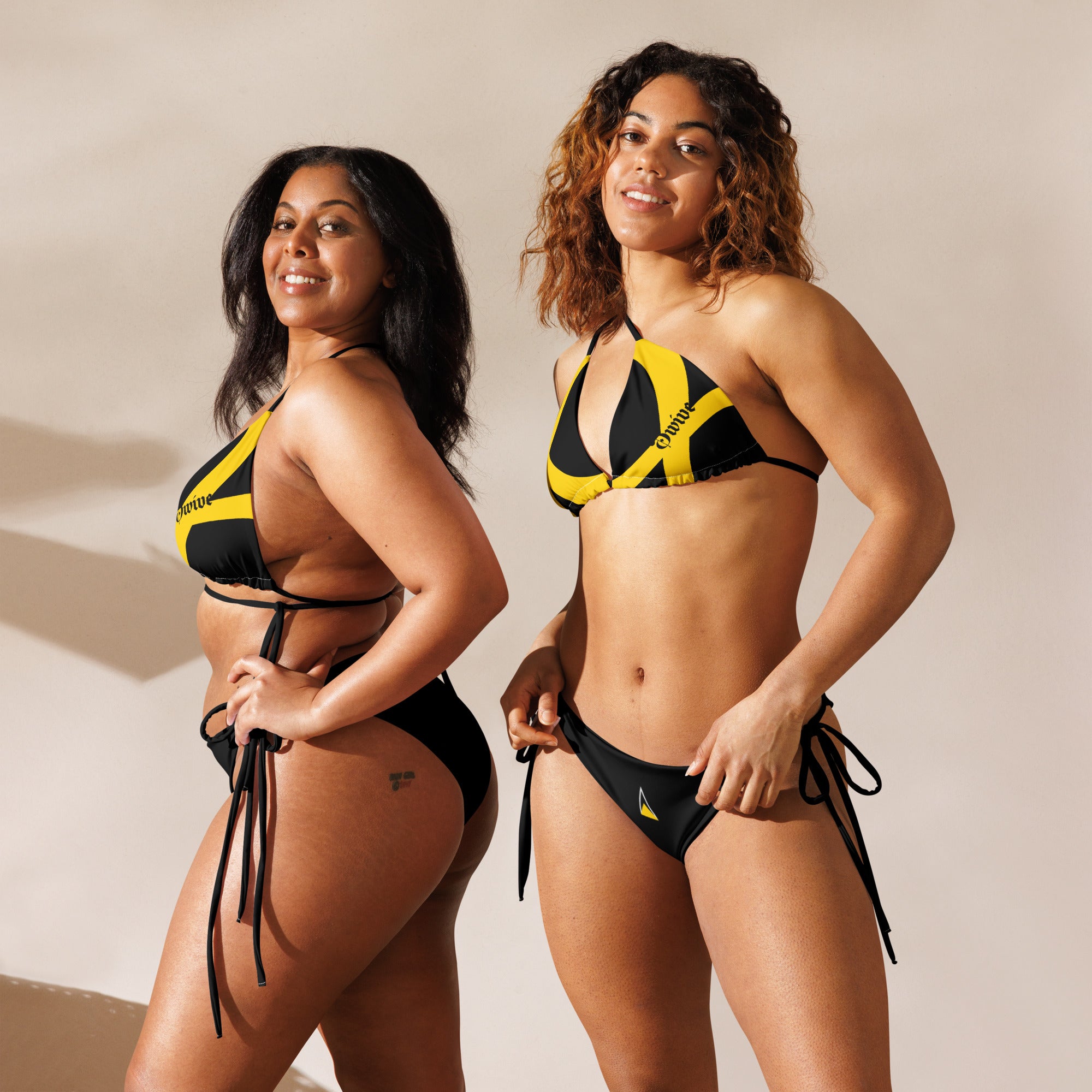
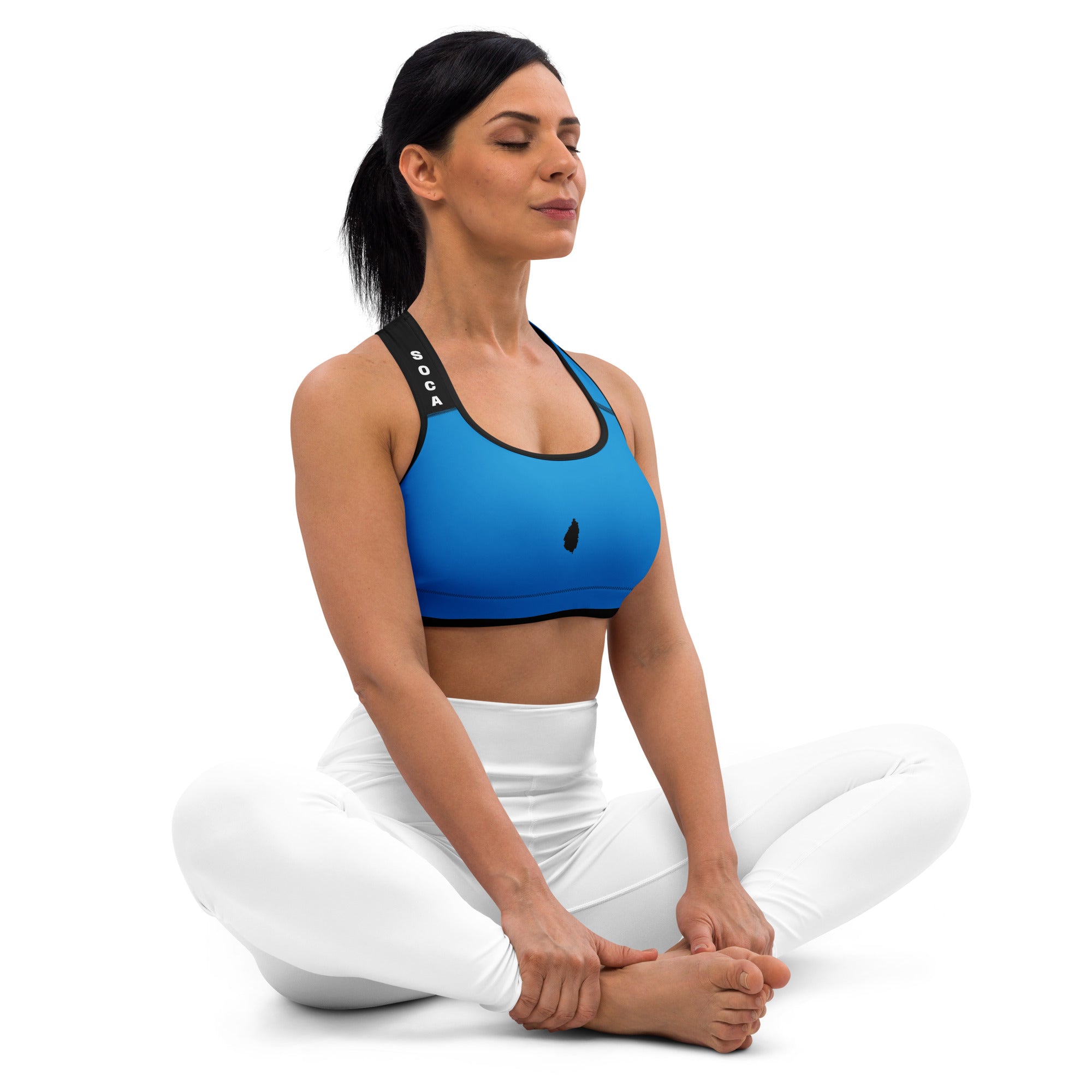
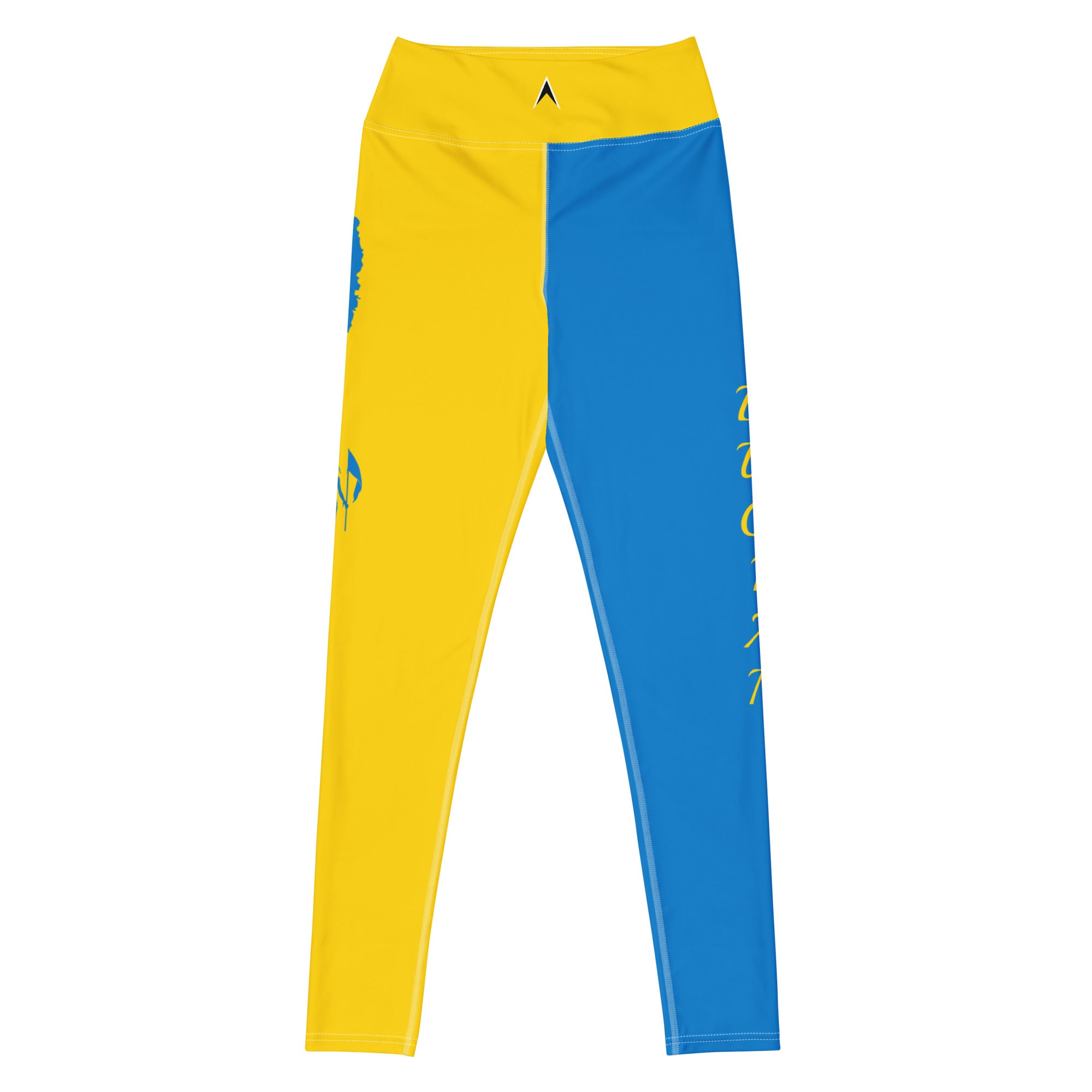
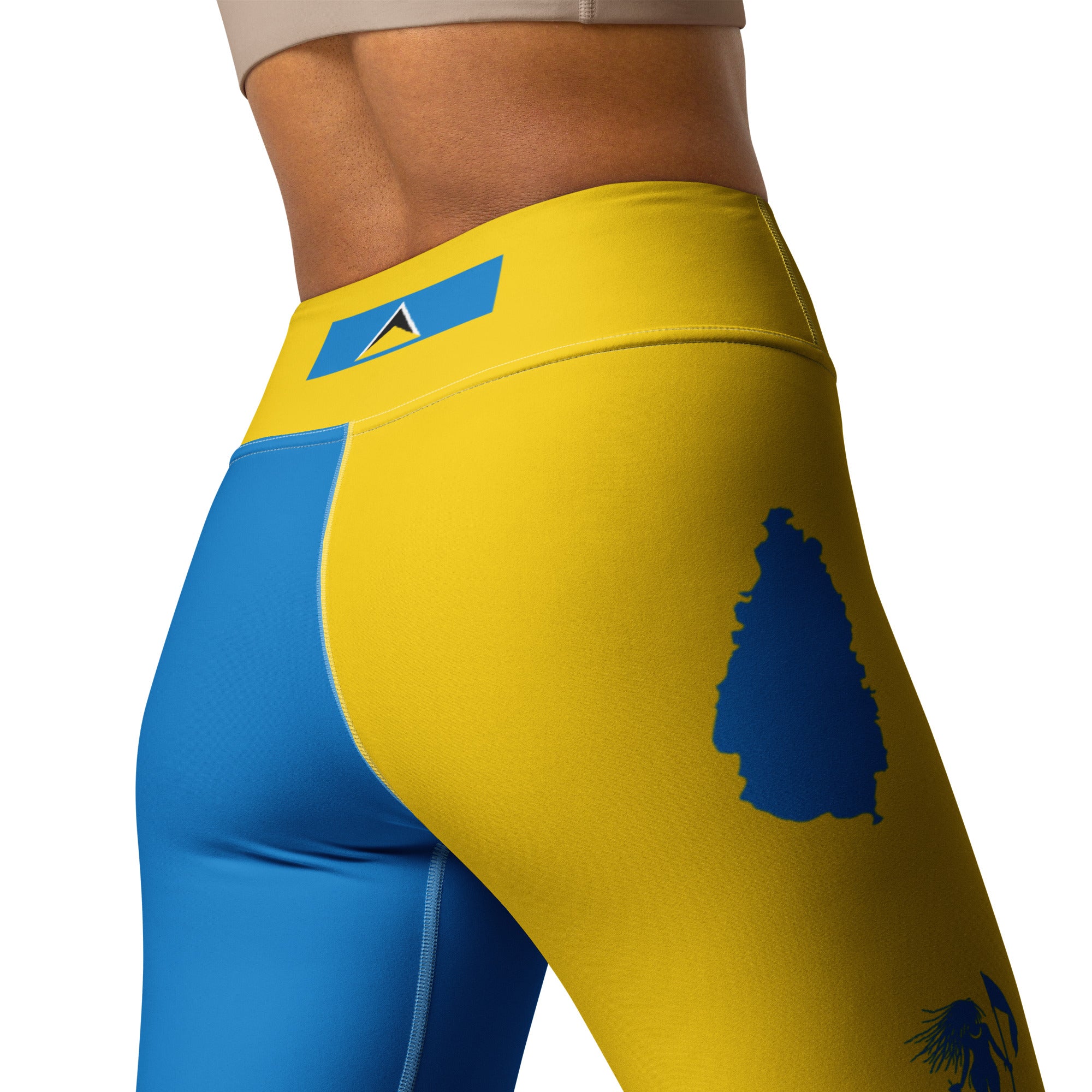
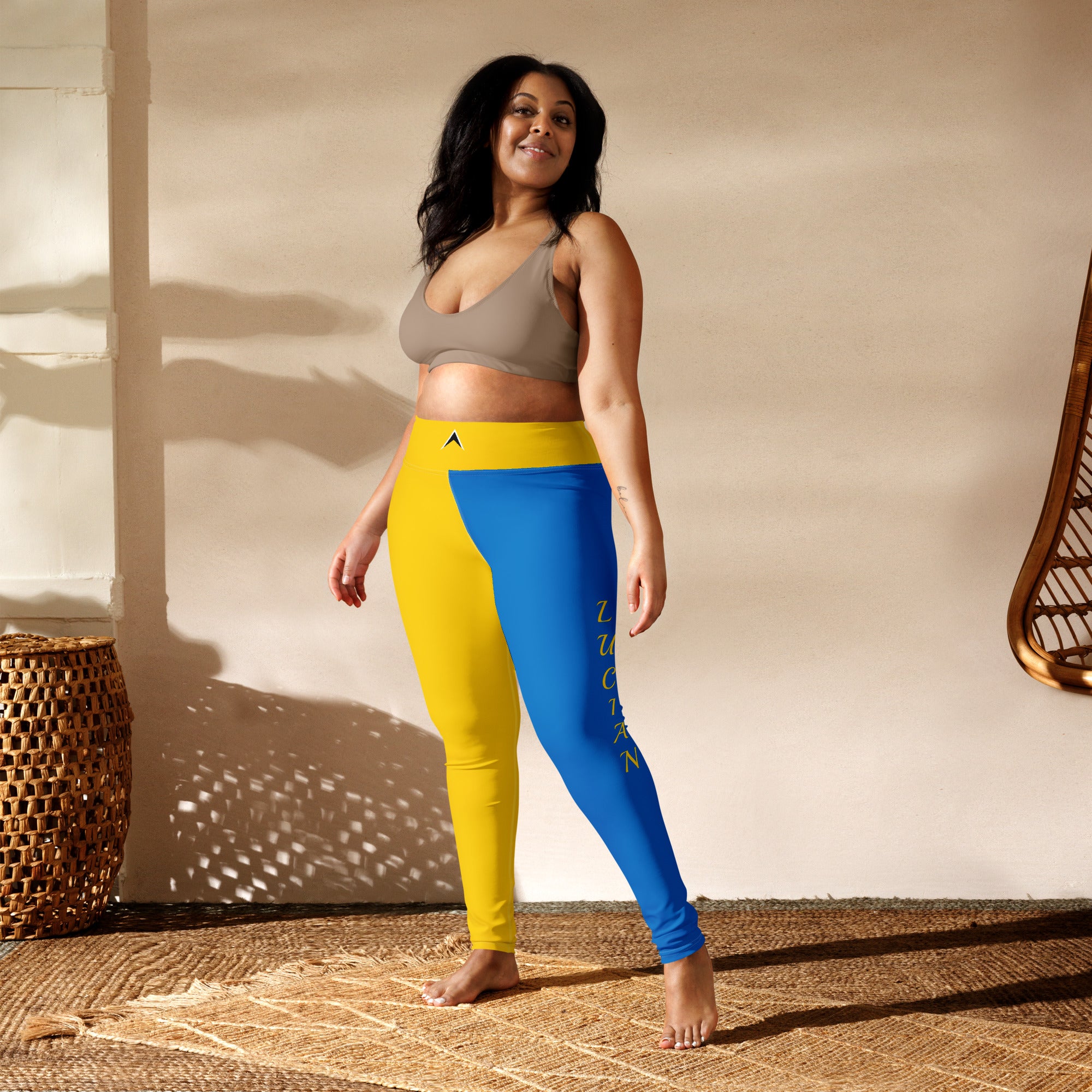
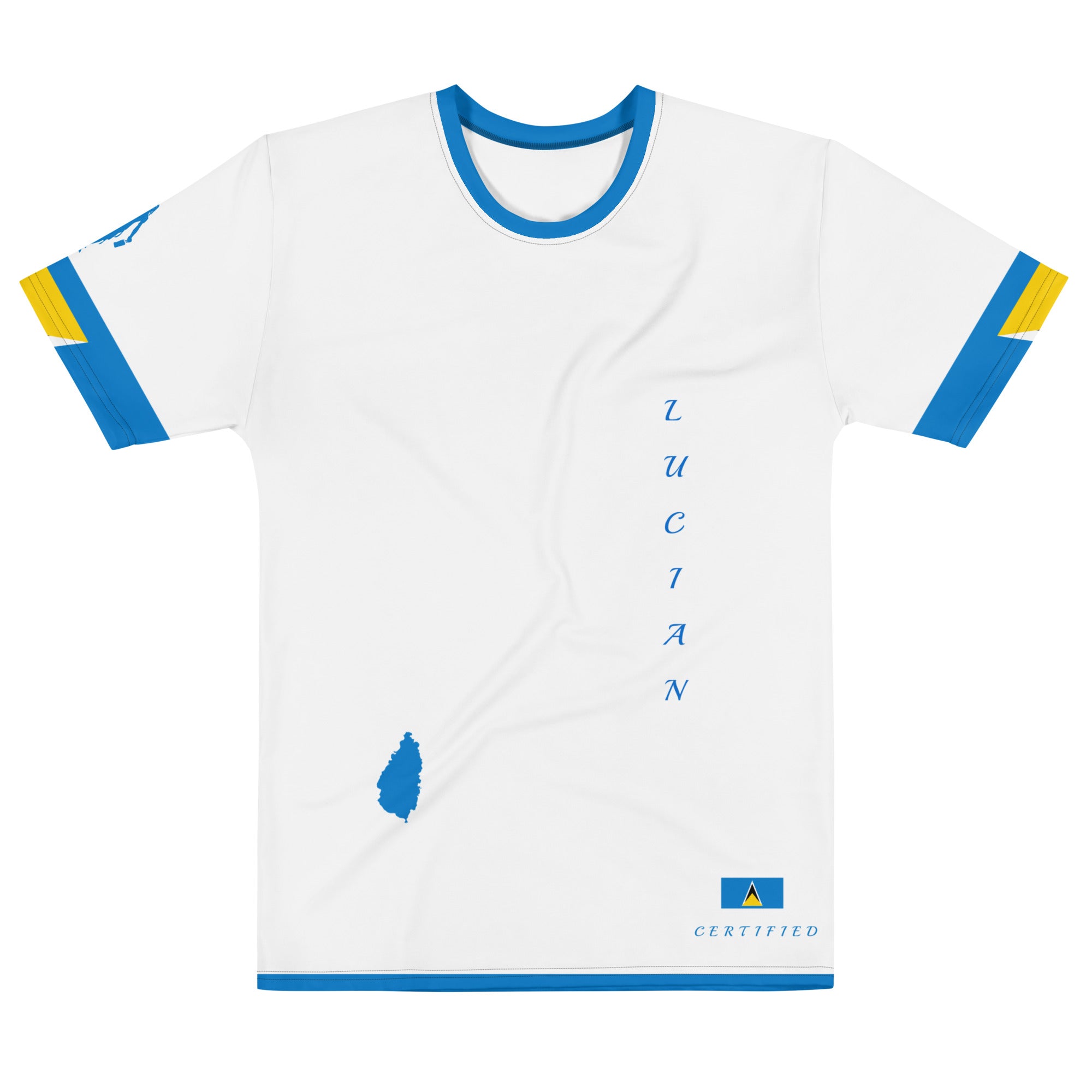
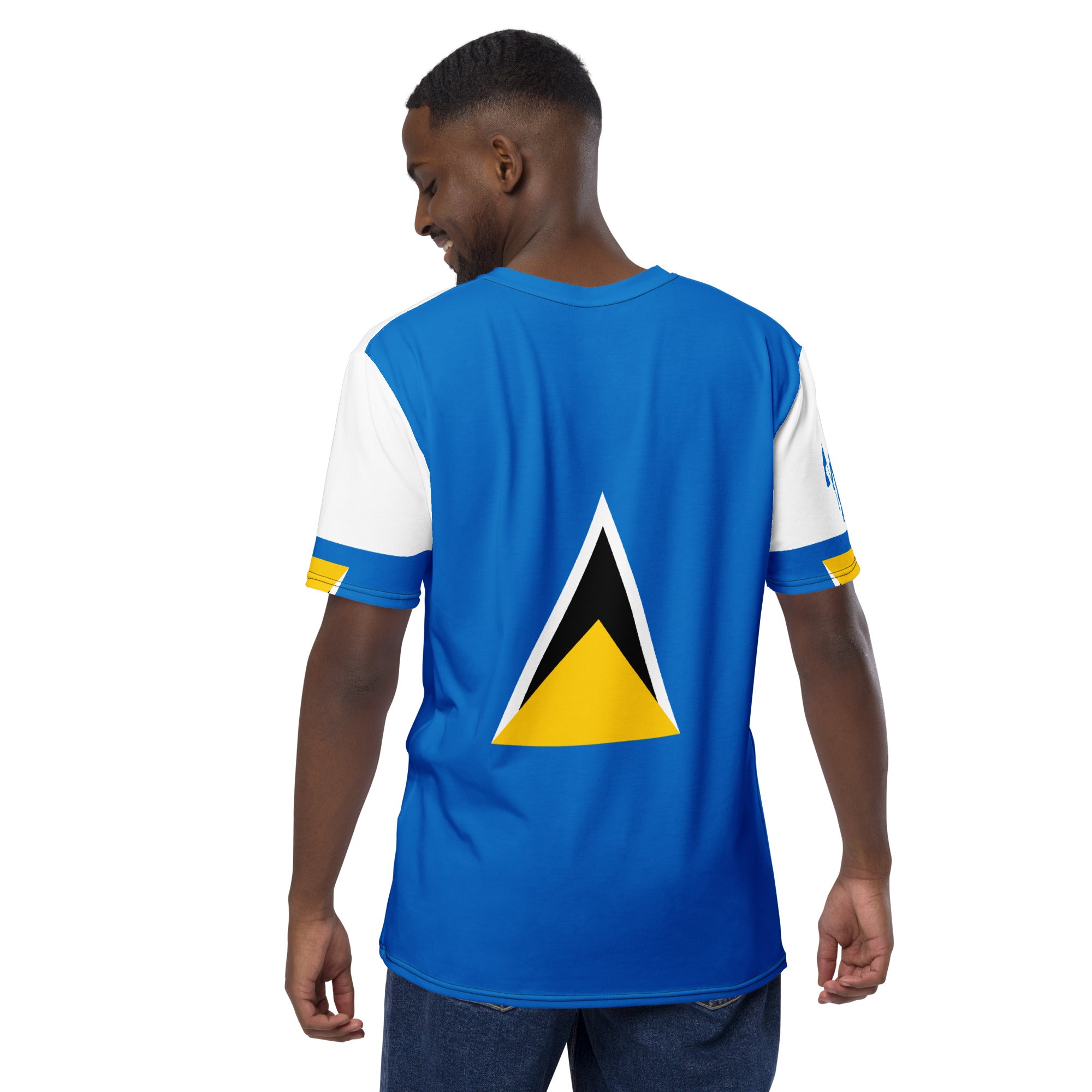
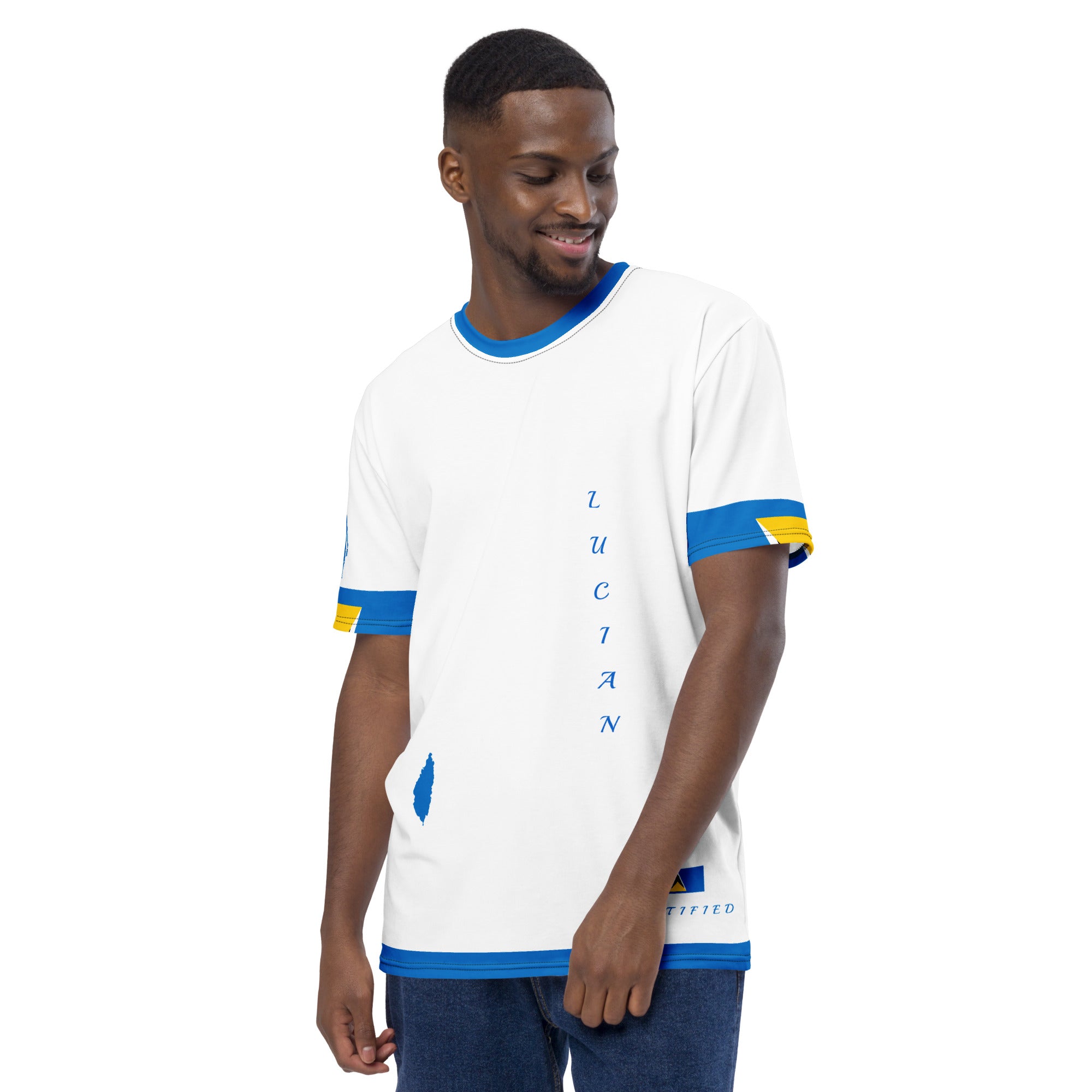
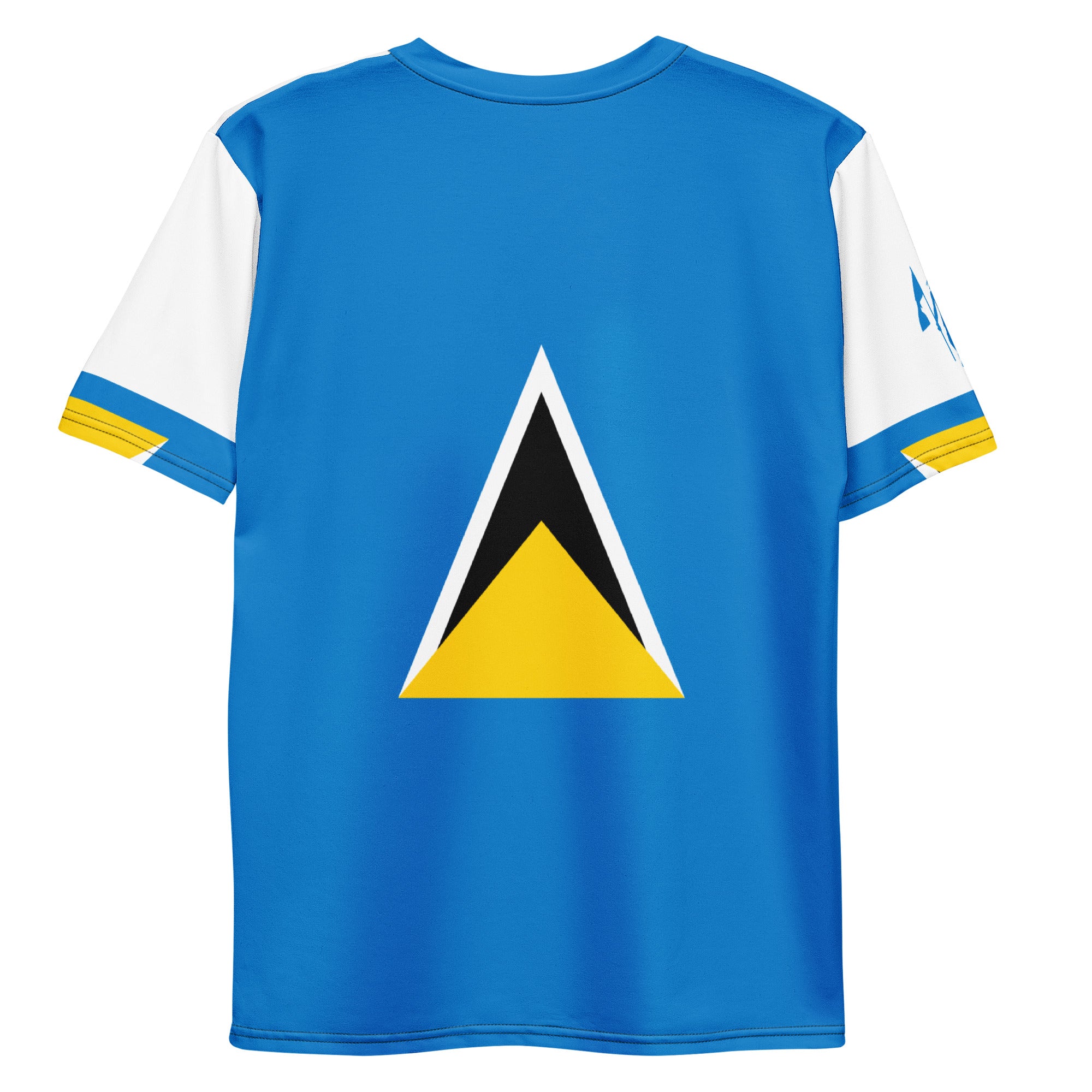
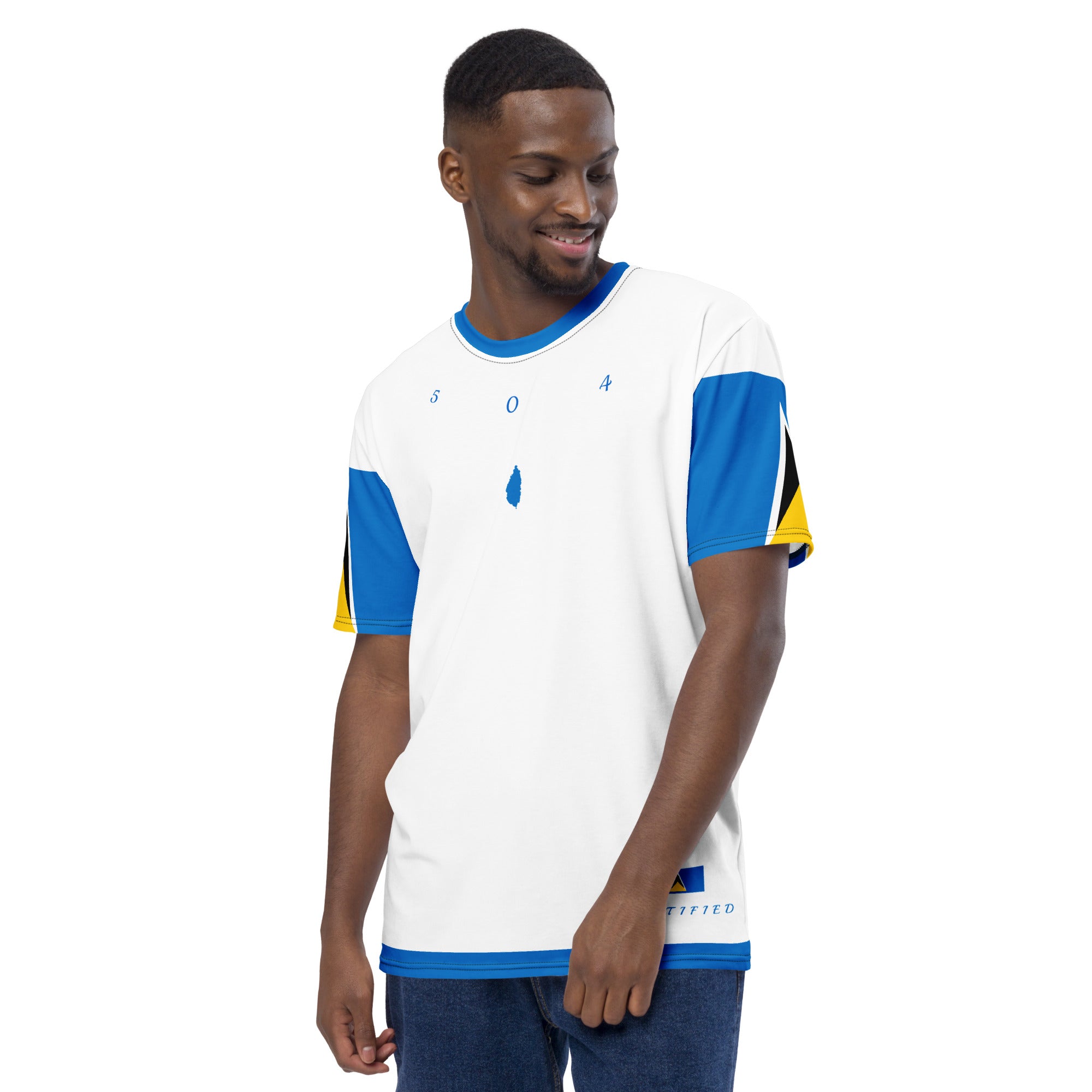
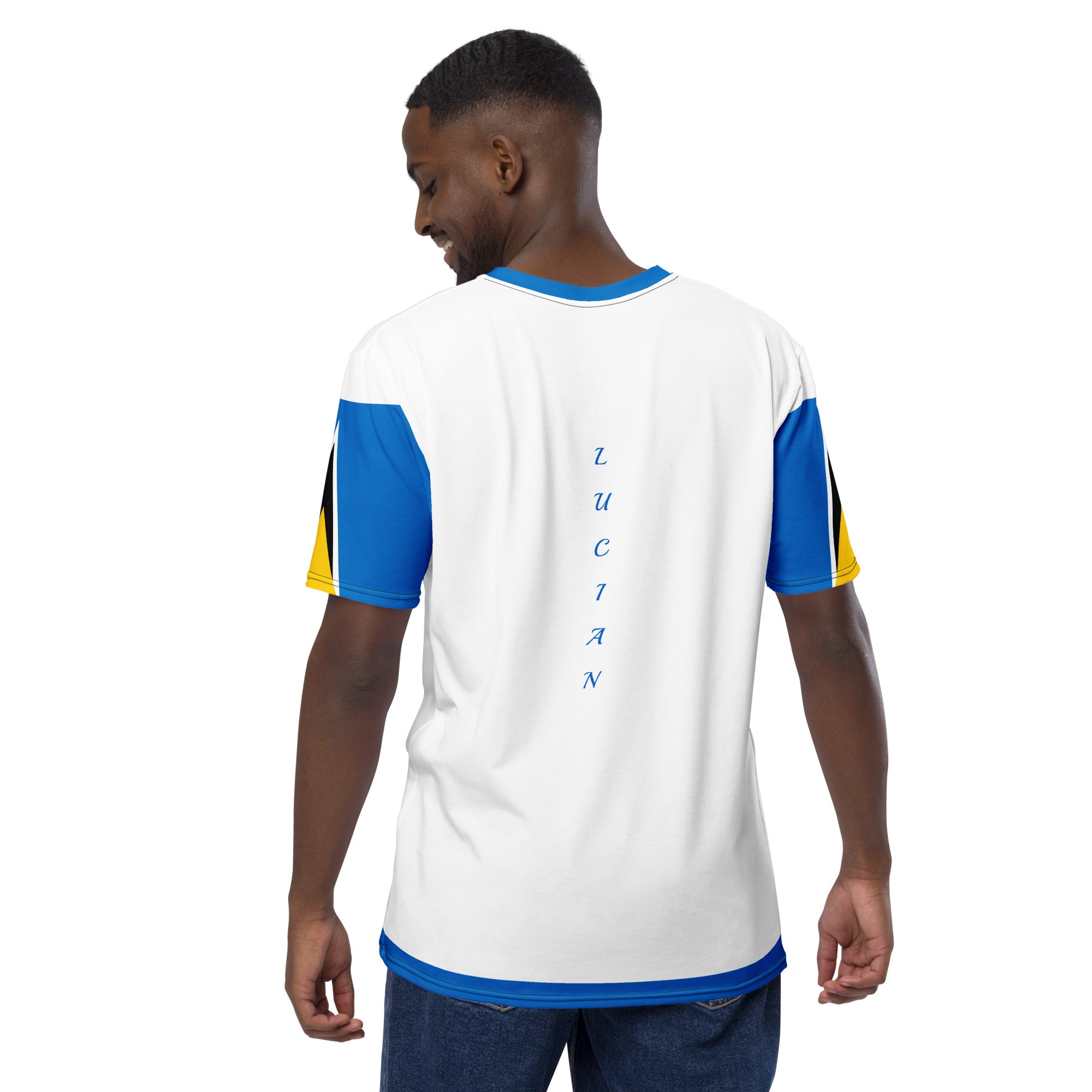
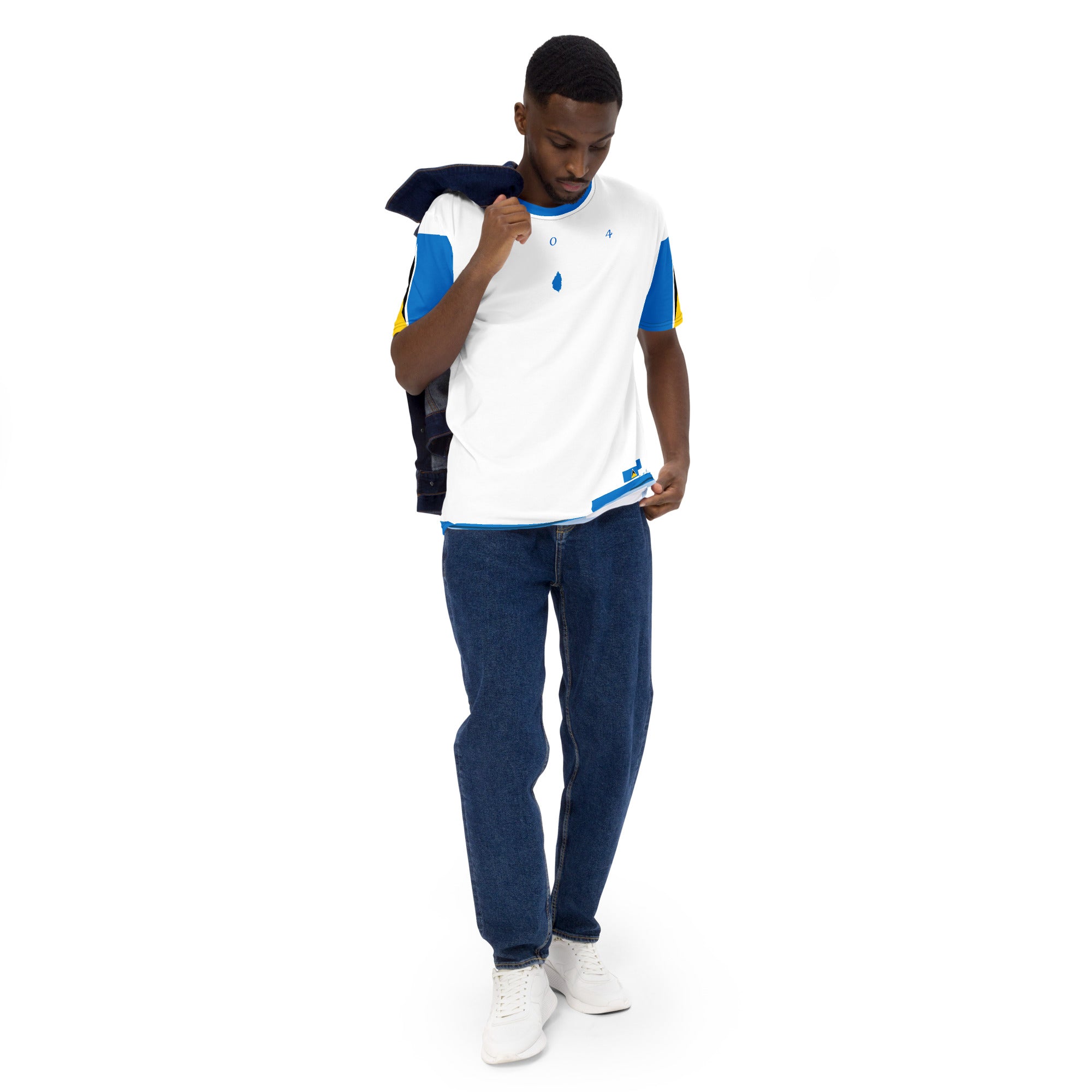
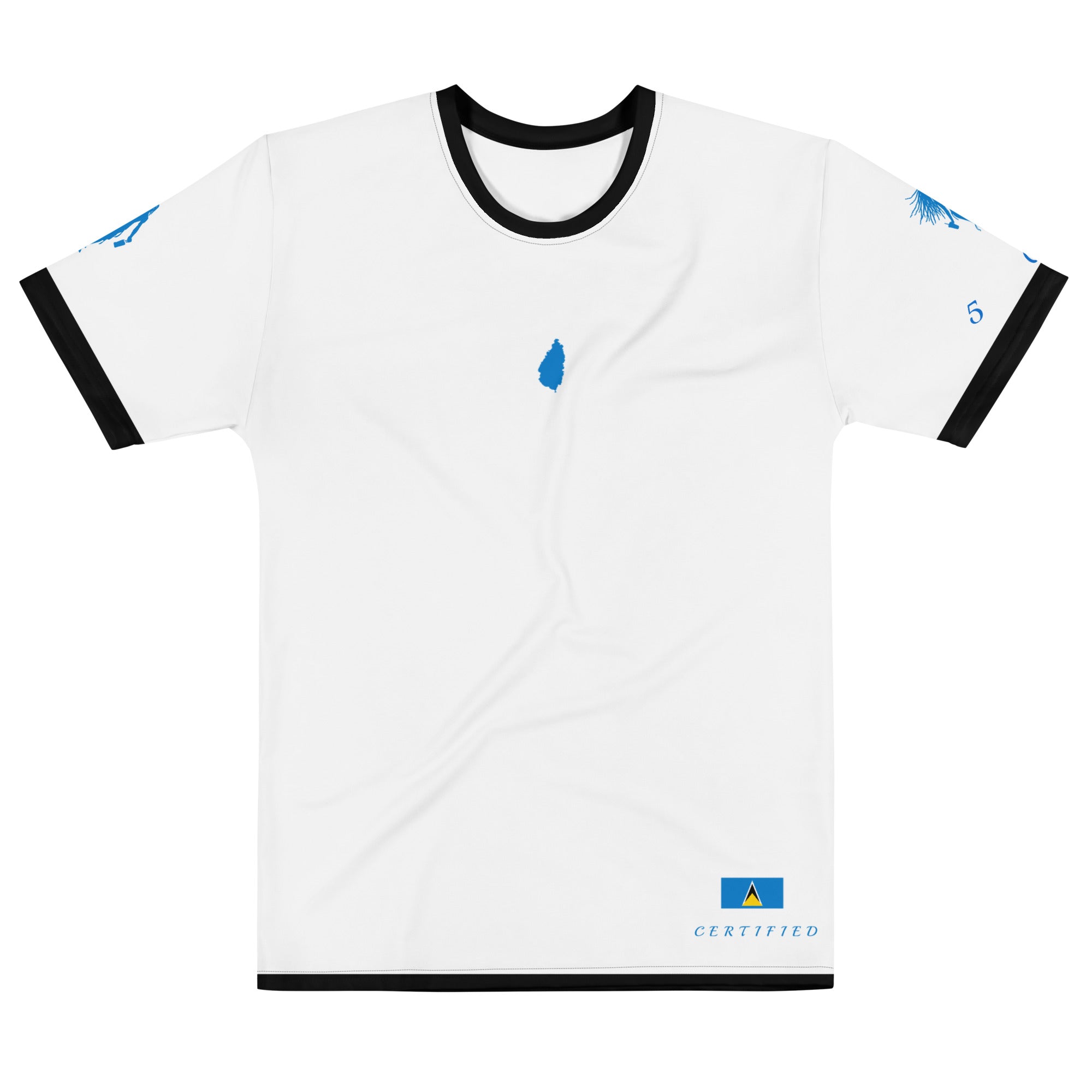
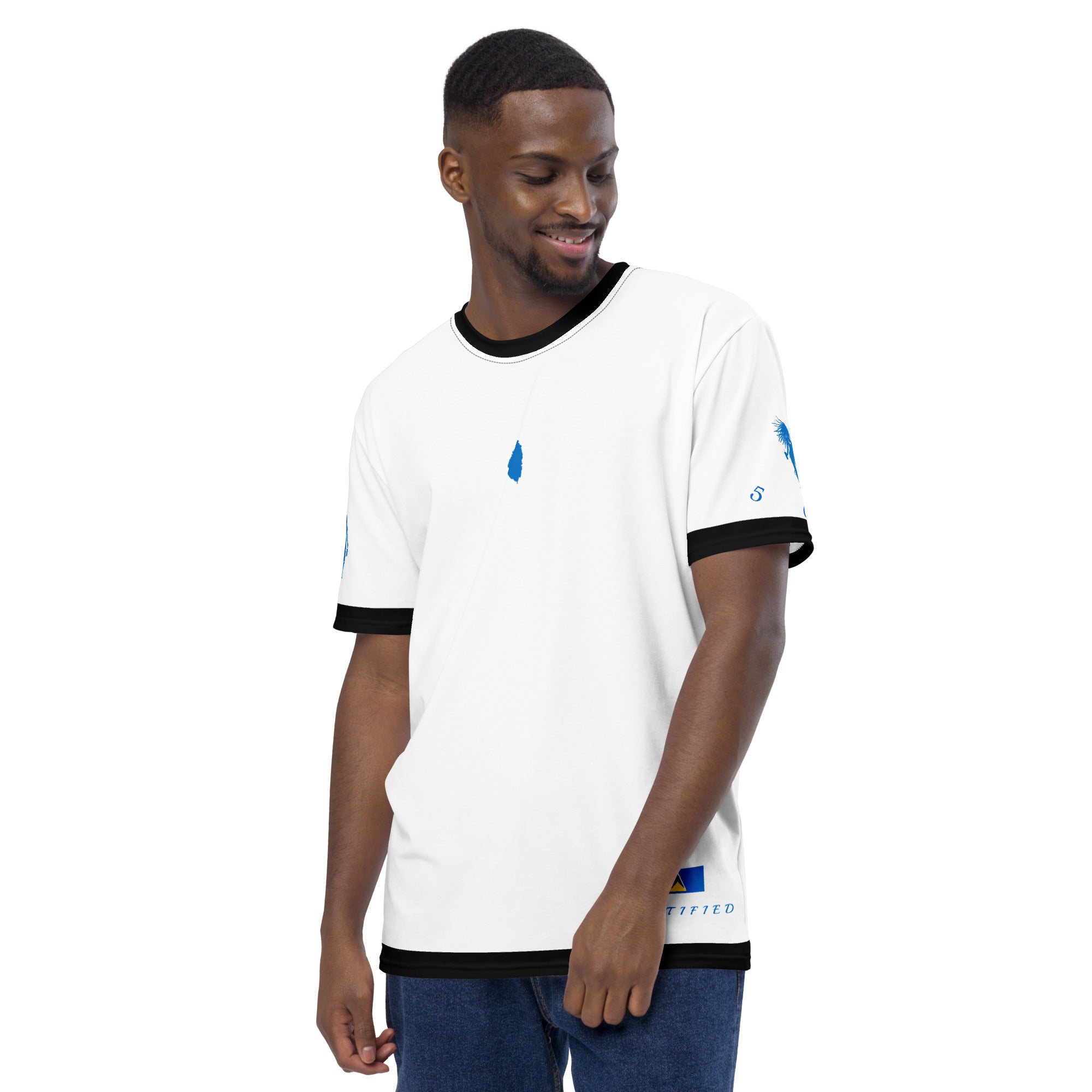
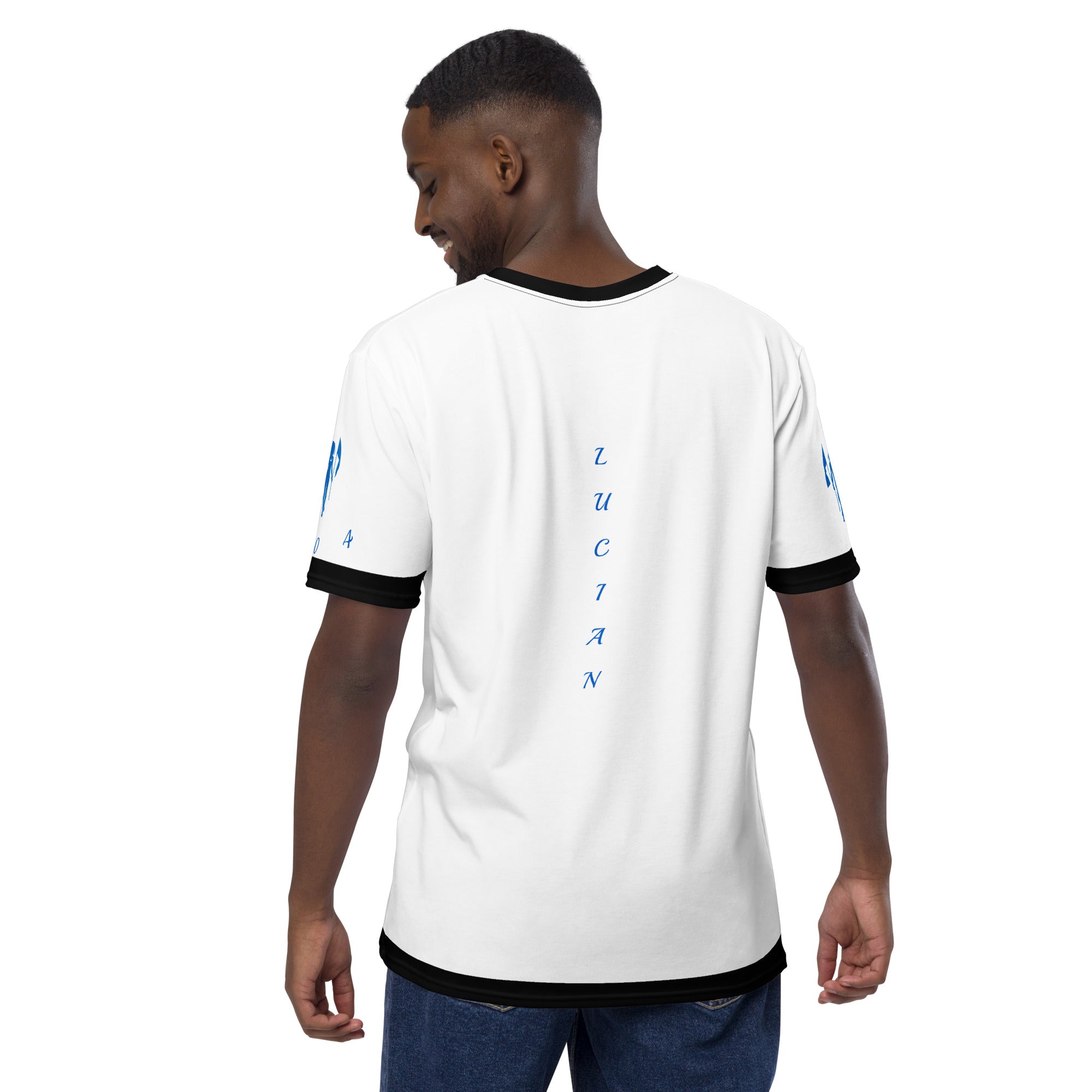
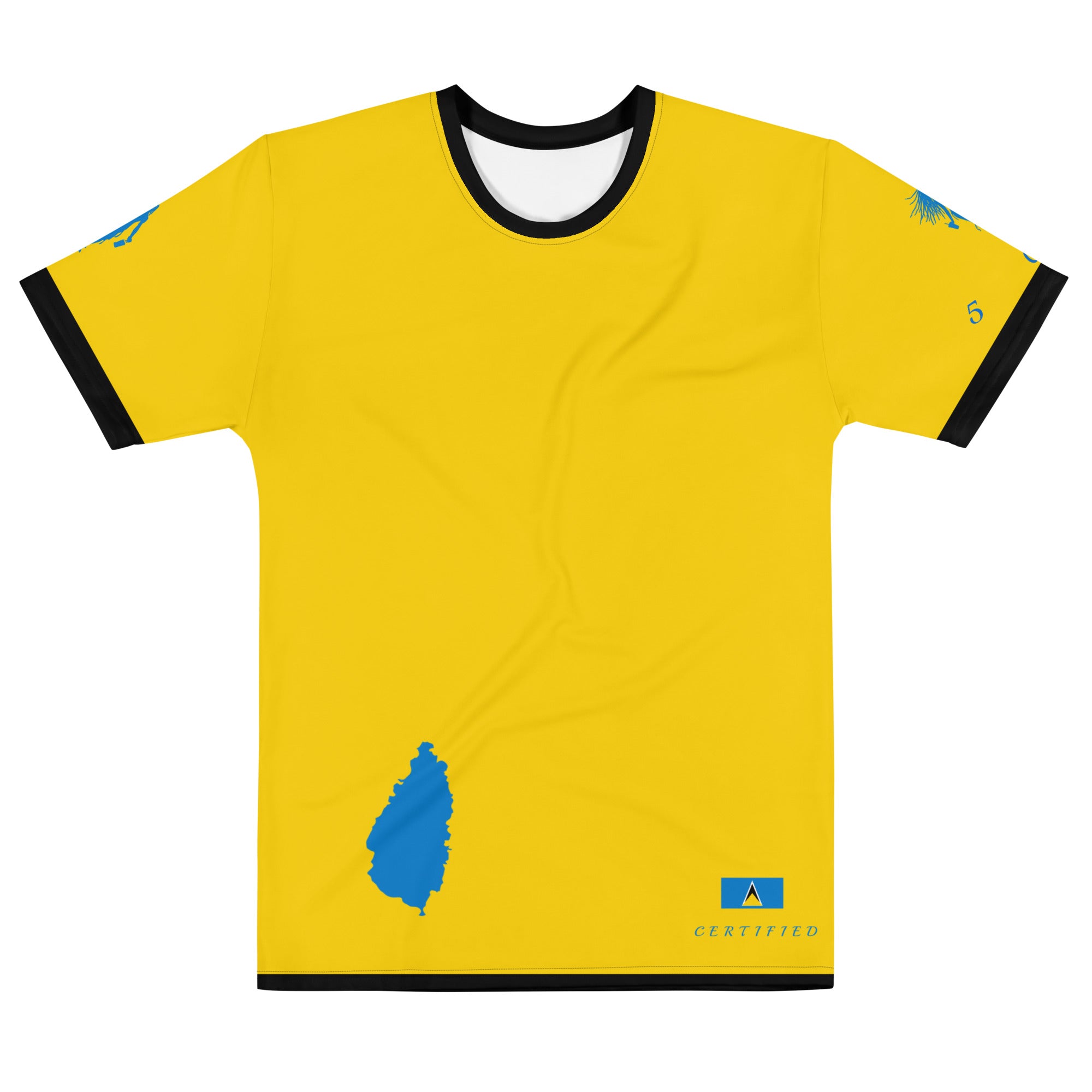
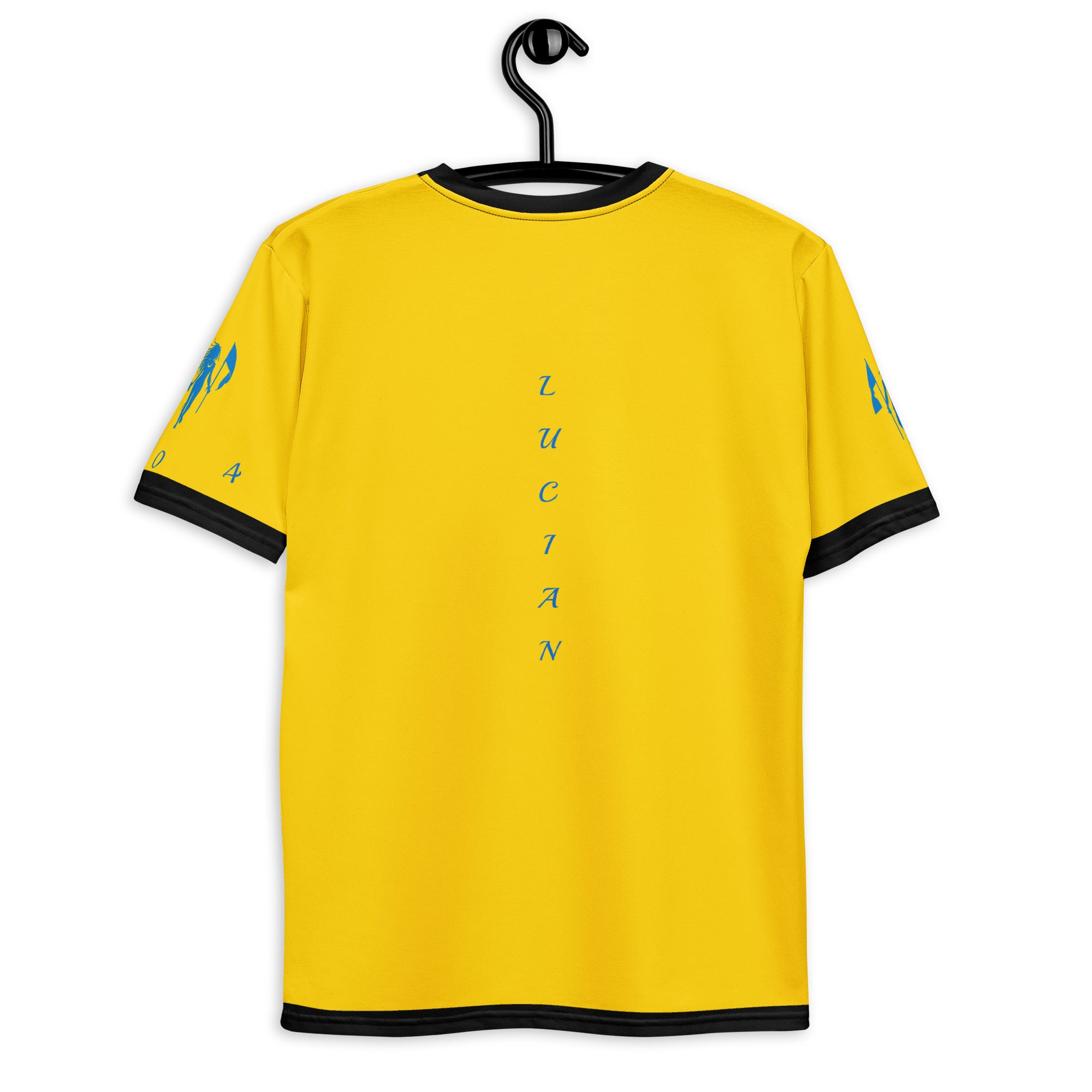
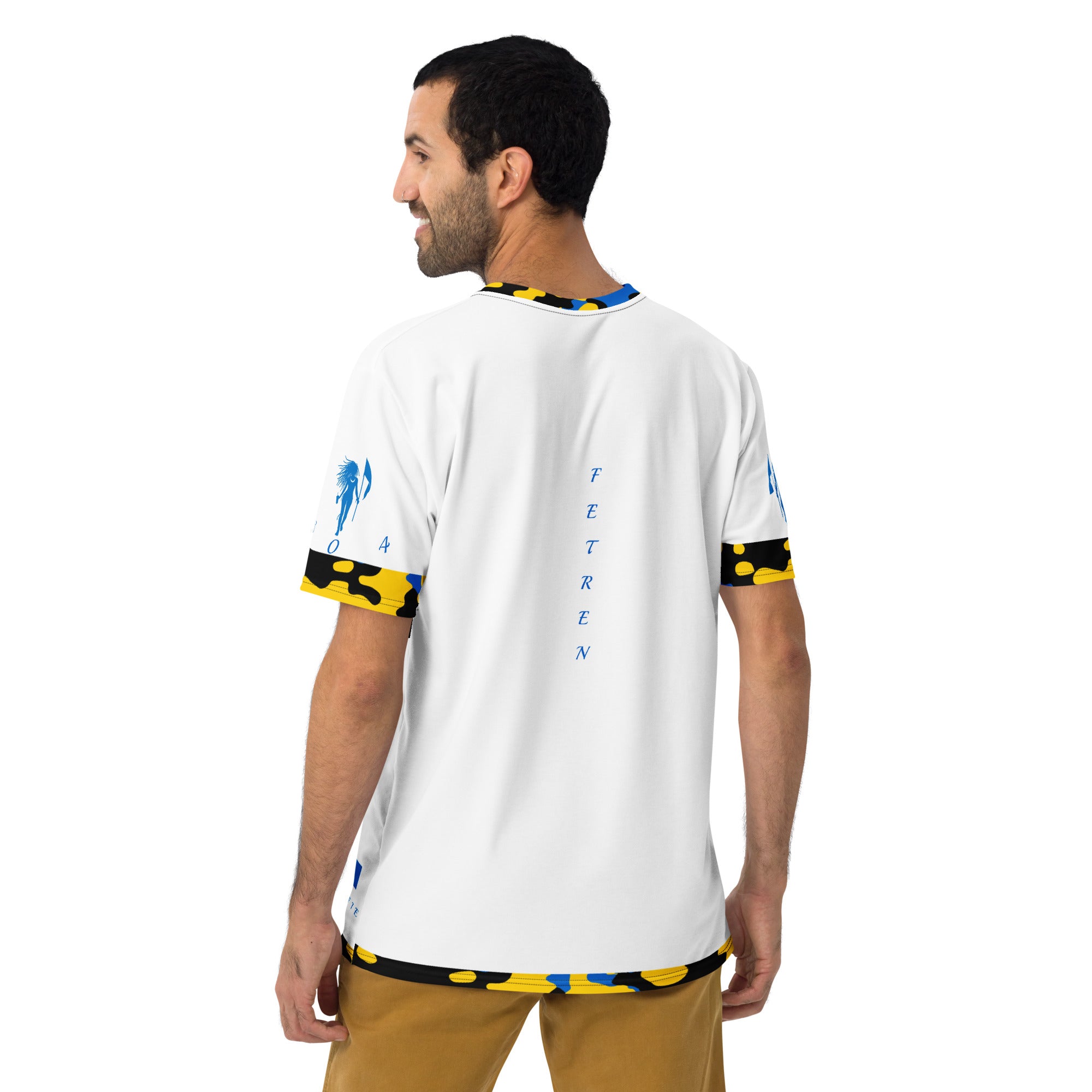
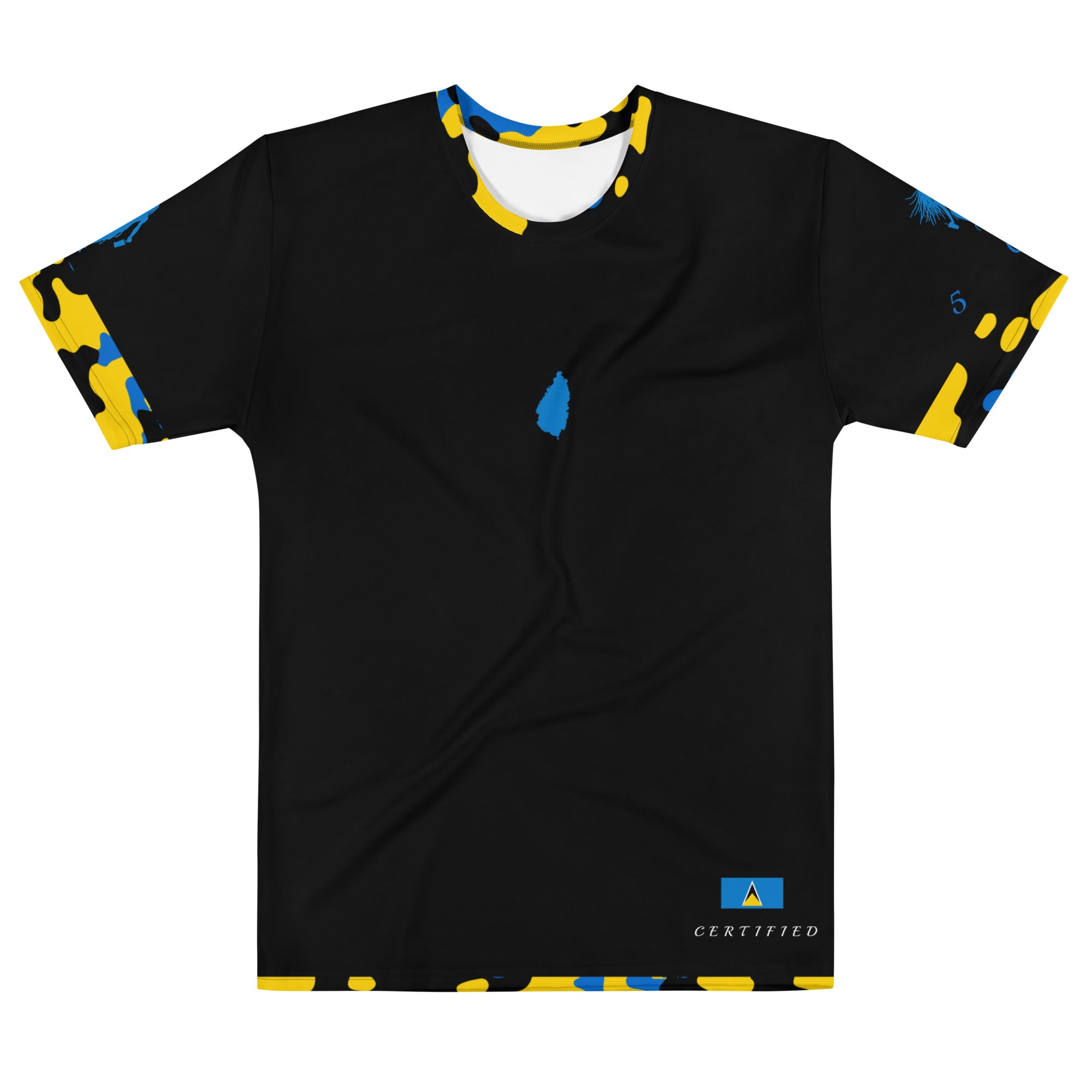
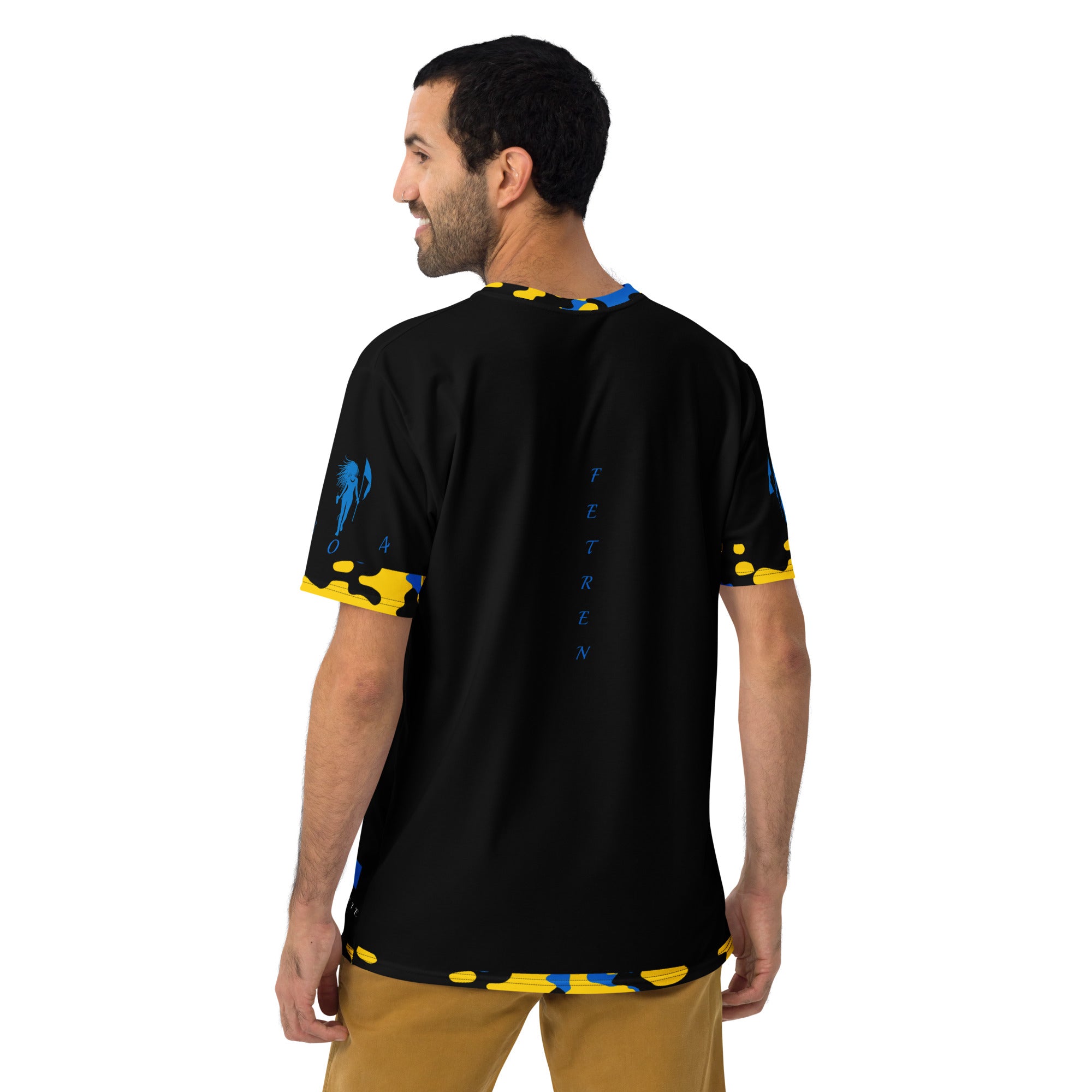
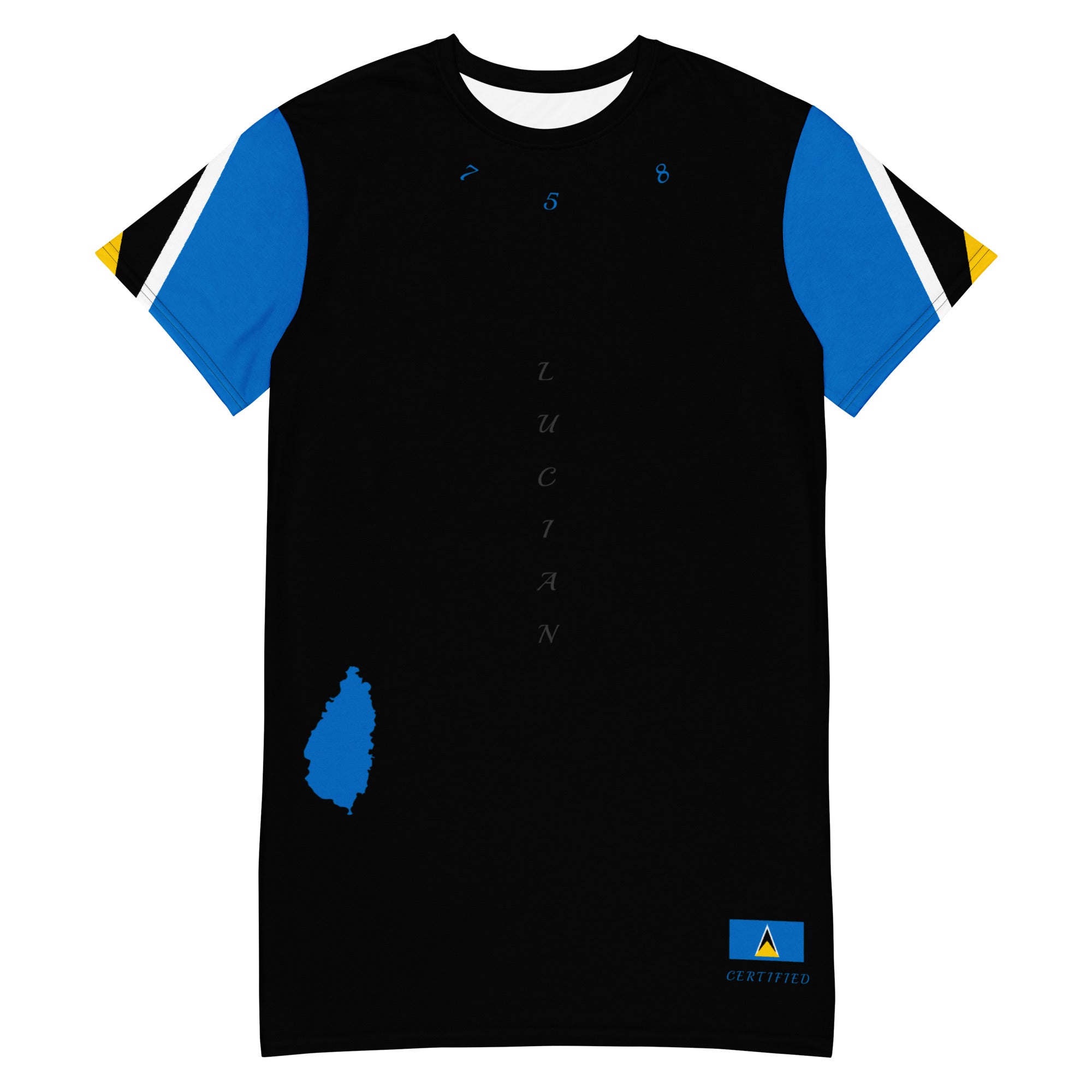
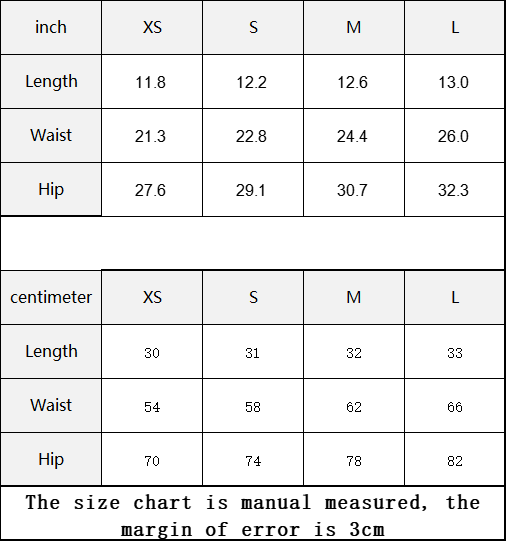
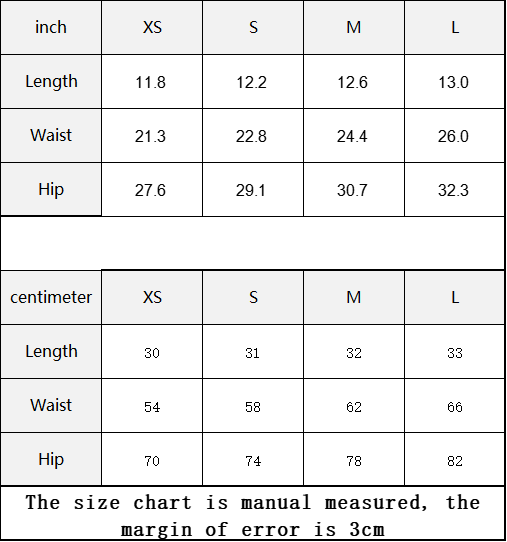
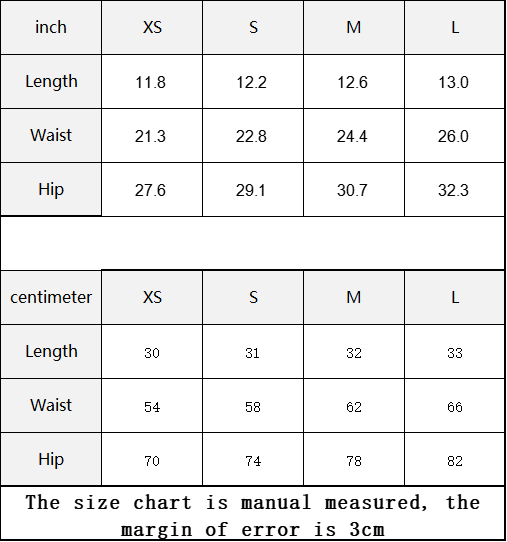
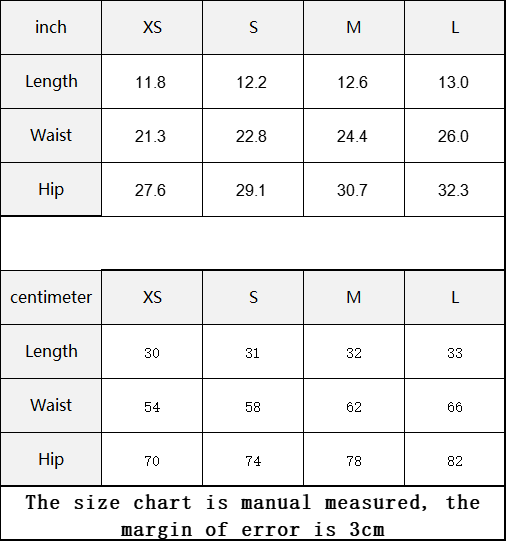
Vendor:Fete Massive
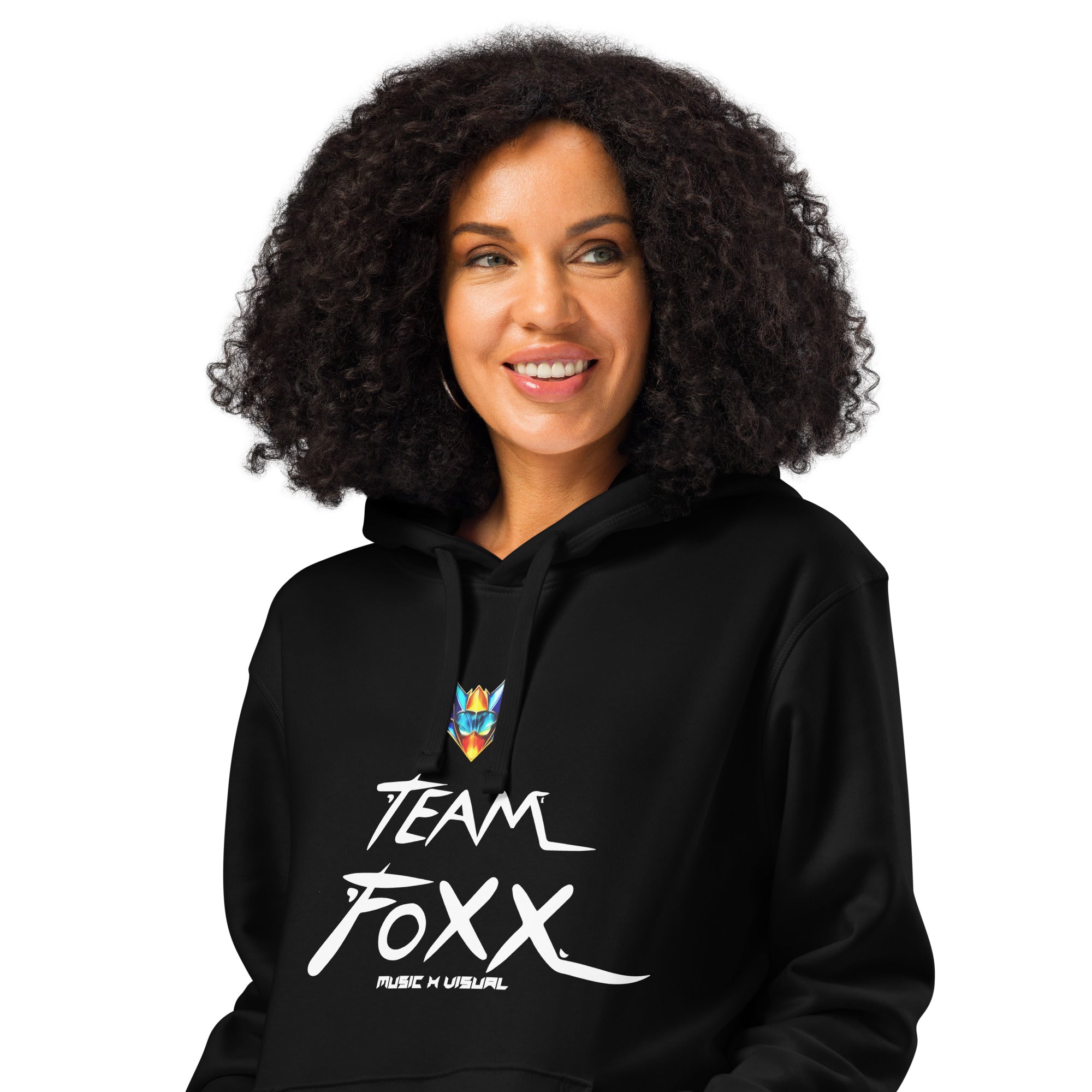
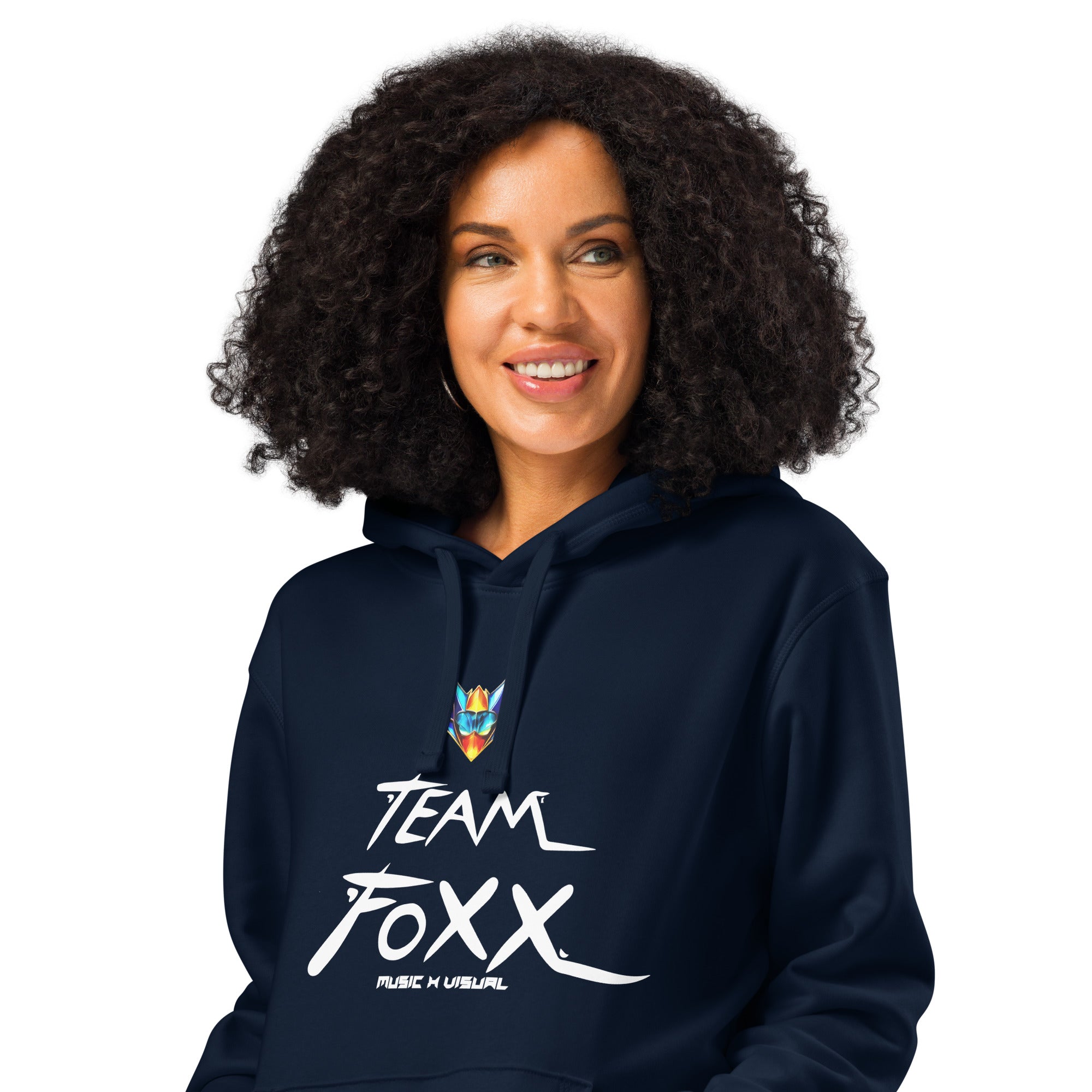
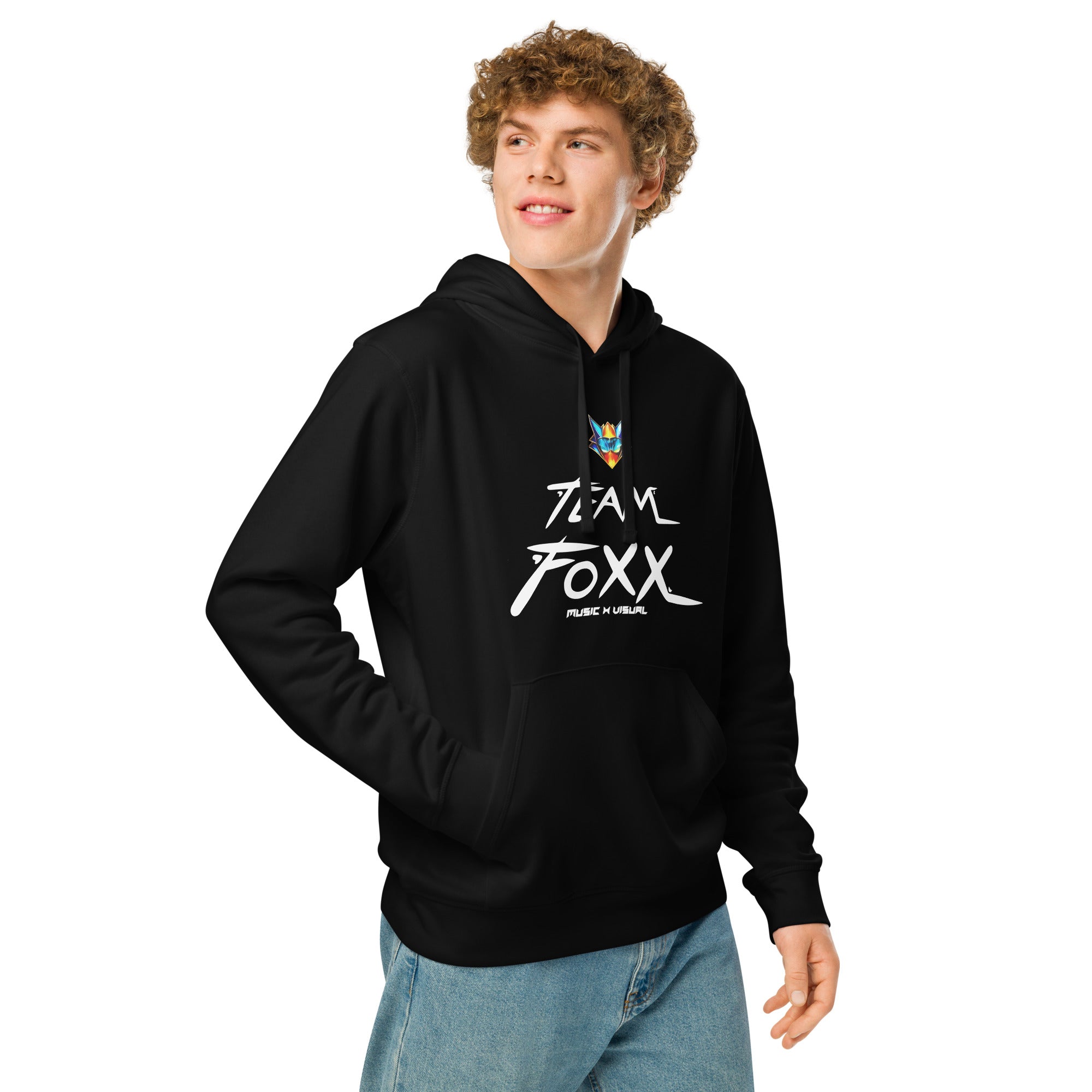
Motto Team FOXX organic mid-weight hoodie
From $40.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$30.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
Follow Us!
on Instagram.
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
$45.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
$35.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
$25.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $23.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
From $23.00
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
Vendor:Fete Massive
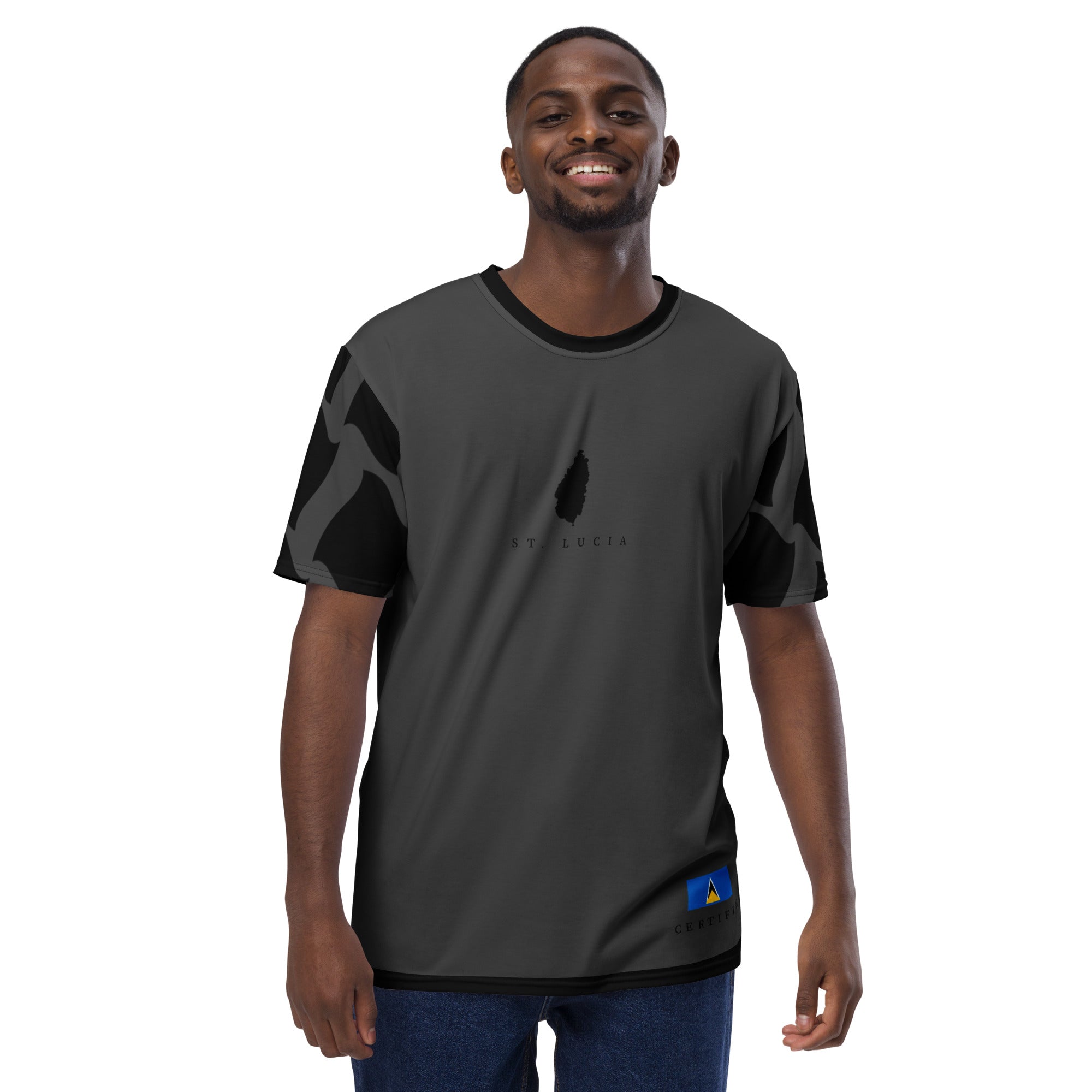
St. Lucia T-shirt dress (Black)
From $35.00